220Mhz Receiving Converter
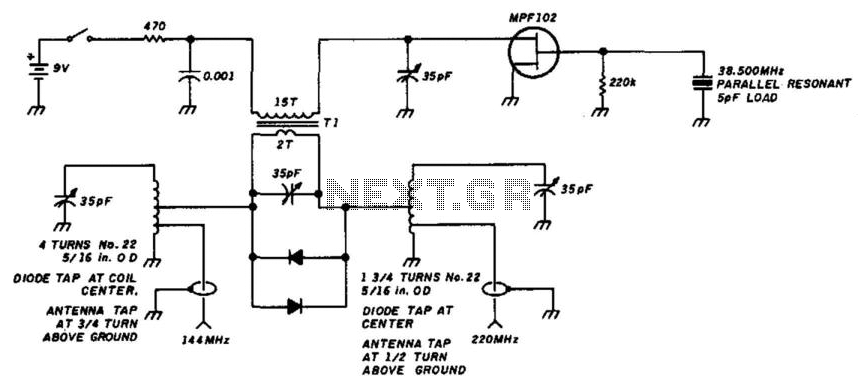
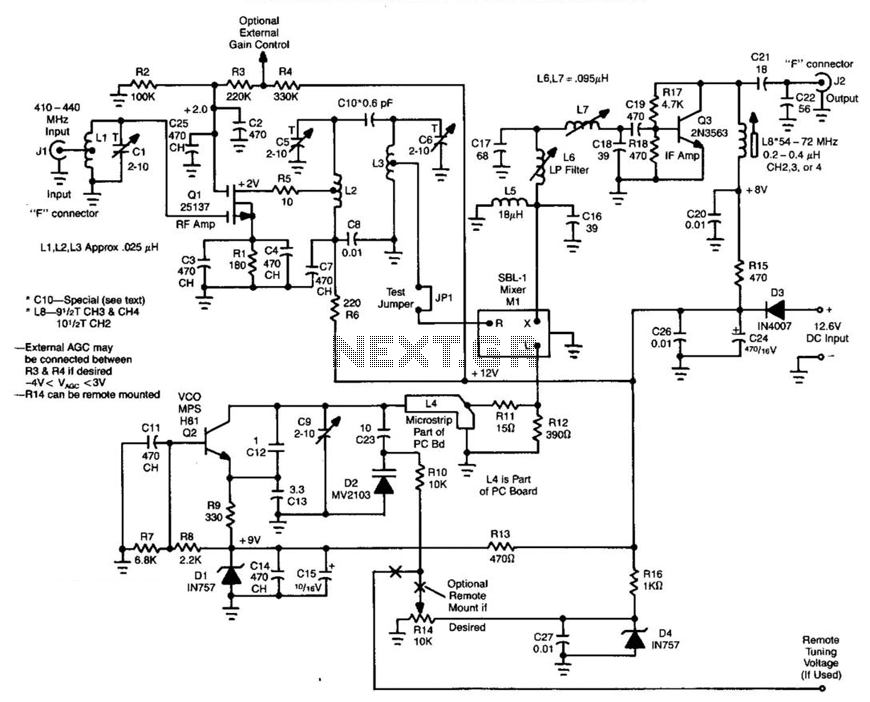
A simple circuit utilizing a single transistor converts 220 MHz to 144 MHz or vice versa, as the mixer is bilateral. The transformer has 15 turns on the primary and 2 turns on the secondary (#24 AWG wire) on a 0.375" ID SF-material toroidal coil.
The described circuit serves as a frequency converter, capable of shifting signals between 220 MHz and 144 MHz, which can be particularly useful in radio frequency applications. The core component of this circuit is a single transistor that functions as a mixer, allowing for bidirectional signal conversion due to its bilateral nature.
The transformer used in this circuit is critical for the conversion process. It consists of a primary winding with 15 turns and a secondary winding with 2 turns, both wound with #24 AWG wire. The choice of wire gauge and the number of turns are essential for achieving the desired impedance transformation and frequency response characteristics. The use of a toroidal core made from SF material (Silicon Ferrite) provides a compact and efficient magnetic structure that minimizes losses and enhances performance at high frequencies.
In terms of operation, the circuit can accept an input signal at one frequency and produce an output signal at the other frequency. This is achieved by mixing the input signal with a local oscillator signal within the transistor, generating the desired frequency output. The design's simplicity allows for ease of implementation, while the careful selection of components ensures reliable operation across the specified frequency range.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective approach to frequency conversion in RF applications, demonstrating the utility of basic electronic components in achieving complex signal processing tasks. A simple circuit using a single transistor converts 220 MHz to 144 MHz or vice versa, because the mixer is bila teral. Tl has 15 turns on the primary, and 2 turns on the secondary (#24 AWG wire) on a 0.375" ID SF-material toroidal coil.
The described circuit serves as a frequency converter, capable of shifting signals between 220 MHz and 144 MHz, which can be particularly useful in radio frequency applications. The core component of this circuit is a single transistor that functions as a mixer, allowing for bidirectional signal conversion due to its bilateral nature.
The transformer used in this circuit is critical for the conversion process. It consists of a primary winding with 15 turns and a secondary winding with 2 turns, both wound with #24 AWG wire. The choice of wire gauge and the number of turns are essential for achieving the desired impedance transformation and frequency response characteristics. The use of a toroidal core made from SF material (Silicon Ferrite) provides a compact and efficient magnetic structure that minimizes losses and enhances performance at high frequencies.
In terms of operation, the circuit can accept an input signal at one frequency and produce an output signal at the other frequency. This is achieved by mixing the input signal with a local oscillator signal within the transistor, generating the desired frequency output. The design's simplicity allows for ease of implementation, while the careful selection of components ensures reliable operation across the specified frequency range.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective approach to frequency conversion in RF applications, demonstrating the utility of basic electronic components in achieving complex signal processing tasks. A simple circuit using a single transistor converts 220 MHz to 144 MHz or vice versa, because the mixer is bila teral. Tl has 15 turns on the primary, and 2 turns on the secondary (#24 AWG wire) on a 0.375" ID SF-material toroidal coil.