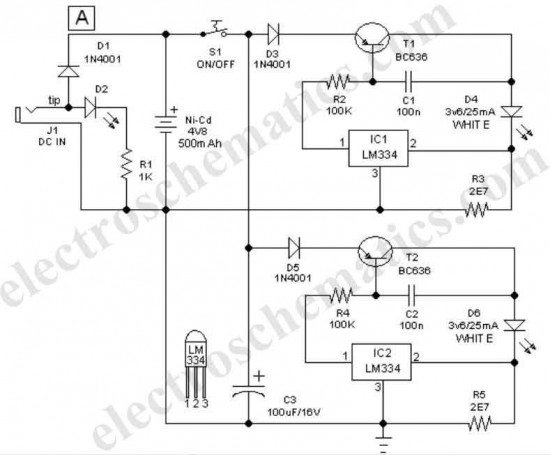
XTR110 voltage - current converter circuit diagram
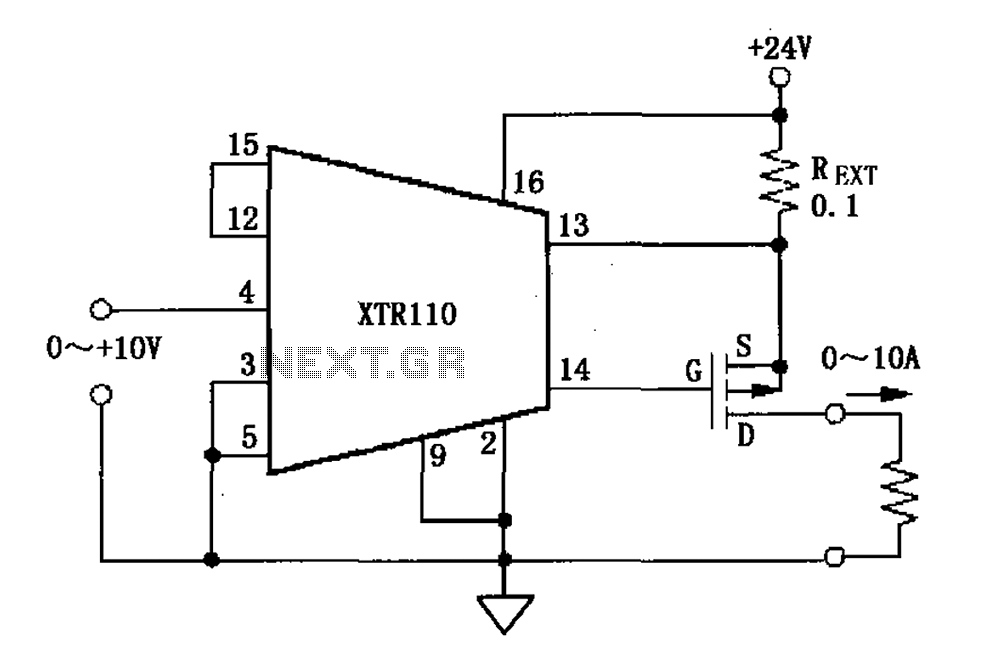
When the output current exceeds 40mA, the XTR110 requires the use of an external resistor (REXT) instead of the internal 50-ohm resistor (R9). REXT should be connected between pin 13 and pin 1. The value of REXT is determined based on the required span. For instance, if the original span of the XTR110 is set to 20mA, and there is a need to change it to a span of 10A, R9 remains at 50 ohms, and REXT can be calculated as R9 multiplied by the ratio of the original span to the new span, which is 50 ohms multiplied by (20/10000), resulting in 0.1 ohms.
The XTR110 is a precision current transmitter designed for converting a voltage input into a proportional output current. In applications where the output current exceeds 40mA, the internal resistor (R9) becomes inadequate, necessitating the addition of an external resistor (REXT) to maintain proper operation and accuracy of the device. The connection points for REXT are critical; it must be connected between pin 13 and pin 1 to ensure correct functionality.
To calculate the value of REXT for different output spans, the relationship between the original span and the desired span must be understood. The formula REXT = R9 * (original span / new span) allows for the adjustment of output current levels. For example, if the original output span is set to 20mA and the application requires a span of 10A, the internal resistor value of 50 ohms is used in the calculation. This results in REXT being set to 0.1 ohms, which allows the XTR110 to output the increased current range effectively while maintaining linearity and precision in the output signal.
This adjustment is crucial in applications where high current outputs are necessary, and it ensures that the XTR110 can adapt to varying requirements without compromising performance. Proper selection and installation of REXT will facilitate the desired output characteristics and enhance the overall efficiency of the circuit. As shown, when the output current exceeds 40mA when, XTR110 internal 50 resistor (R9) on the need to use an external resistor REXT instead, REXT connected between 13 feet and 1 6 feet. REXT R9 (original span/span required). For example, the original figure XTR110 span of 20mA, is now required to span 10A, R9 50, then REXT R9 50 (20/10000) 0.1 .
The XTR110 is a precision current transmitter designed for converting a voltage input into a proportional output current. In applications where the output current exceeds 40mA, the internal resistor (R9) becomes inadequate, necessitating the addition of an external resistor (REXT) to maintain proper operation and accuracy of the device. The connection points for REXT are critical; it must be connected between pin 13 and pin 1 to ensure correct functionality.
To calculate the value of REXT for different output spans, the relationship between the original span and the desired span must be understood. The formula REXT = R9 * (original span / new span) allows for the adjustment of output current levels. For example, if the original output span is set to 20mA and the application requires a span of 10A, the internal resistor value of 50 ohms is used in the calculation. This results in REXT being set to 0.1 ohms, which allows the XTR110 to output the increased current range effectively while maintaining linearity and precision in the output signal.
This adjustment is crucial in applications where high current outputs are necessary, and it ensures that the XTR110 can adapt to varying requirements without compromising performance. Proper selection and installation of REXT will facilitate the desired output characteristics and enhance the overall efficiency of the circuit. As shown, when the output current exceeds 40mA when, XTR110 internal 50 resistor (R9) on the need to use an external resistor REXT instead, REXT connected between 13 feet and 1 6 feet. REXT R9 (original span/span required). For example, the original figure XTR110 span of 20mA, is now required to span 10A, R9 50, then REXT R9 50 (20/10000) 0.1 .