low power receiver serves multiple wireless standards
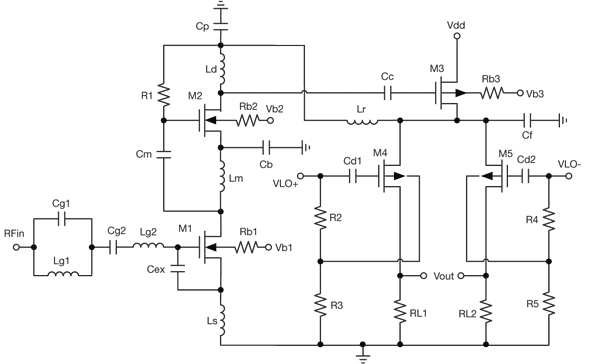
By combining a current-reuse amplifier and a switch-based mixer, a dual-band receiver front end offers excellent performance with extremely low power consumption.
The dual-band receiver front end integrates a current-reuse amplifier and a switch-based mixer to achieve high performance while maintaining low power usage. The current-reuse amplifier is designed to maximize efficiency by reusing bias current, which minimizes power dissipation while providing sufficient gain for signal processing. This design is particularly beneficial in battery-powered applications where power efficiency is critical.
The switch-based mixer operates by utilizing electronic switches to selectively route signals from different frequency bands. This allows the receiver to process multiple frequency channels without the need for multiple separate mixers, thereby reducing component count and overall system complexity. The combination of these two technologies enables the receiver to achieve a wide dynamic range and improved linearity, resulting in better signal fidelity and reduced distortion.
In practical applications, this dual-band receiver front end can be employed in various communication systems, including wireless networks, satellite communications, and radio frequency identification (RFID) systems. The low power consumption characteristic is especially advantageous for portable devices, where battery life is a concern. Additionally, the compact design resulting from the integration of the amplifier and mixer contributes to a smaller overall footprint, making it suitable for space-constrained environments.
Overall, the synergy between the current-reuse amplifier and switch-based mixer in this dual-band receiver front end represents a significant advancement in receiver technology, optimizing performance while minimizing energy consumption.By combining a current-reuse amplifier and switch based mixer, a dual-band receiver front end offers excellent performance with extremely low power consumption.. 🔗 External reference
The dual-band receiver front end integrates a current-reuse amplifier and a switch-based mixer to achieve high performance while maintaining low power usage. The current-reuse amplifier is designed to maximize efficiency by reusing bias current, which minimizes power dissipation while providing sufficient gain for signal processing. This design is particularly beneficial in battery-powered applications where power efficiency is critical.
The switch-based mixer operates by utilizing electronic switches to selectively route signals from different frequency bands. This allows the receiver to process multiple frequency channels without the need for multiple separate mixers, thereby reducing component count and overall system complexity. The combination of these two technologies enables the receiver to achieve a wide dynamic range and improved linearity, resulting in better signal fidelity and reduced distortion.
In practical applications, this dual-band receiver front end can be employed in various communication systems, including wireless networks, satellite communications, and radio frequency identification (RFID) systems. The low power consumption characteristic is especially advantageous for portable devices, where battery life is a concern. Additionally, the compact design resulting from the integration of the amplifier and mixer contributes to a smaller overall footprint, making it suitable for space-constrained environments.
Overall, the synergy between the current-reuse amplifier and switch-based mixer in this dual-band receiver front end represents a significant advancement in receiver technology, optimizing performance while minimizing energy consumption.By combining a current-reuse amplifier and switch based mixer, a dual-band receiver front end offers excellent performance with extremely low power consumption.. 🔗 External reference