make your own portable Guitar Amp

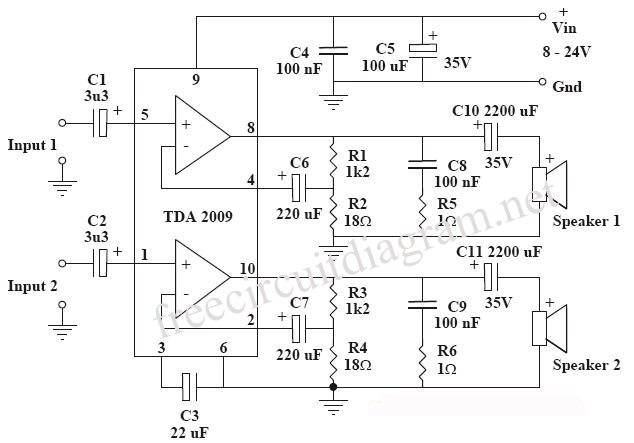
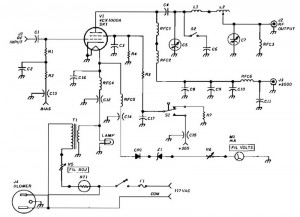
The guitar is a remarkable musical instrument capable of producing both melody and rhythm. However, guitar players often encounter the issue of low volume, making it difficult for the instrument to be heard unless the environment is completely quiet. To address this challenge, a guitar amplifier is typically utilized. For individuals familiar with reading circuit diagrams, this tutorial will provide guidance on constructing a portable guitar amplifier. The estimated cost of this project varies based on the components one needs to purchase, what is already available, and any materials that can be salvaged. It is essential to build the necessary circuit, and while the tutorial will not delve deeply into the specifics of the circuit, a diagram will be presented for reference. The positive terminal of the charger should be connected to one terminal of an ammeter, while the other terminal connects to the positive end of the battery. The negative terminal of the battery should be linked to the negative terminal of the charger. The recommended speaker for this project has an 8-ohm resistance and can handle approximately 3 watts of power. Its shallow depth allows for the installation of heat sinks, which are critical for managing heat produced in the circuit. Adhering to the specified speaker is advisable unless a suitable alternative with similar specifications is available, as different speakers may yield varying performance results. Experimentation with different components is encouraged, but caution is advised. Heat sinks are utilized to dissipate heat generated within the circuit, as excessive heat can damage components. In this project, the heat sinks are simply cut pieces from a standard heat sink that have been modified to fit. Thermal glue is recommended for securing the heat sinks in place. Care should be taken when using hot glue and quick-setting glue, as they bond quickly and can cause skin injuries if not handled properly.
The construction of a portable guitar amplifier involves several key components, including a power supply, amplifier circuitry, and a speaker. The power supply typically consists of a rechargeable battery, which provides the necessary voltage and current for the amplifier circuit. The ammeter is used to monitor the current flowing from the charger to the battery, ensuring that the battery is charged correctly without exceeding its rated capacity.
The amplifier circuit can be built using operational amplifiers or dedicated audio amplifier ICs, which are designed to boost the audio signal from the guitar. The circuit should include capacitors for filtering and stabilizing the power supply, as well as resistors to set gain levels and prevent distortion. It is crucial to design the circuit layout to minimize noise and interference, which can significantly affect audio quality.
The speaker selection is vital for the performance of the amplifier. An 8-ohm speaker rated for 3 watts is suitable for a portable application, as it can deliver adequate sound levels without requiring excessive power. The physical dimensions of the speaker should also be considered to ensure it fits within the enclosure of the portable amplifier.
Heat management is another critical aspect of the design. The heat sinks should be strategically placed near components that generate significant heat, such as the amplifier IC. Proper thermal management will enhance the reliability and longevity of the amplifier. Additionally, using thermal adhesive ensures a secure attachment of the heat sinks, allowing for efficient heat transfer away from sensitive components.
Finally, the enclosure of the amplifier should be designed to protect the internal components while allowing for adequate ventilation. Materials such as wood or plastic can be used to construct a lightweight yet sturdy enclosure. The design should also consider accessibility for controls and connections, such as input jacks for the guitar and output connections for headphones or external speakers. Overall, careful attention to detail in the circuit design, component selection, and enclosure will result in a functional and effective portable guitar amplifier.The guitar is a wonderful musical instrument which is capable of providing both melody and rhythm. However, every guitar player would have experienced the problem of low volume. The guitar is rarely heard unless the surroundings are absolutely quiet! To solve this problem, the guitar amp is often employed. If you have some knowledge in reading cir cuit diagrams, this tutorial will guide you to make your very own portable guitar amp. Estimated cost: The cost here depends entirely on what you will have to purchase, what you already have and what you manage to scavenge. Hence, it is totally variable. 8. Now built the circuit that is necessary. Instead of going into the details of explaining the circuit, we present the circuit diagram below. Follow it to the hilt. 9. Hook the positive end of the charger to one terminal of an ammeter. The other terminal is connected to the positive end of the battery. Connect the negative end of the battery with the negative end of the charger. Ans: The speaker that has been suggested here has a resistance of 8 ohms and can thus handle about 3 Watts of power.
It is also shallow in its depth and makes it possible to insert heat sinks. These specifications are important for the project and it would be better to stick to the above mentioned speaker unless you can obtain another one with the same specifications. Different speakers will also give different performances. Experiment at your own risk. Ans: Heat sinks help to dissipate the heat that is formed in the circuit. Too much heating can harm the circuit. The heat sinks used in this project are nothing but cut pieces of a regular heat sink that have been filed to fit in.
You can glue them using thermal glue that is available. 2. Be careful while using the hot glue and quick glue. These glues bond very strong and fast. Skin could easily get bonded by mistake and result in injuries. 🔗 External reference
The construction of a portable guitar amplifier involves several key components, including a power supply, amplifier circuitry, and a speaker. The power supply typically consists of a rechargeable battery, which provides the necessary voltage and current for the amplifier circuit. The ammeter is used to monitor the current flowing from the charger to the battery, ensuring that the battery is charged correctly without exceeding its rated capacity.
The amplifier circuit can be built using operational amplifiers or dedicated audio amplifier ICs, which are designed to boost the audio signal from the guitar. The circuit should include capacitors for filtering and stabilizing the power supply, as well as resistors to set gain levels and prevent distortion. It is crucial to design the circuit layout to minimize noise and interference, which can significantly affect audio quality.
The speaker selection is vital for the performance of the amplifier. An 8-ohm speaker rated for 3 watts is suitable for a portable application, as it can deliver adequate sound levels without requiring excessive power. The physical dimensions of the speaker should also be considered to ensure it fits within the enclosure of the portable amplifier.
Heat management is another critical aspect of the design. The heat sinks should be strategically placed near components that generate significant heat, such as the amplifier IC. Proper thermal management will enhance the reliability and longevity of the amplifier. Additionally, using thermal adhesive ensures a secure attachment of the heat sinks, allowing for efficient heat transfer away from sensitive components.
Finally, the enclosure of the amplifier should be designed to protect the internal components while allowing for adequate ventilation. Materials such as wood or plastic can be used to construct a lightweight yet sturdy enclosure. The design should also consider accessibility for controls and connections, such as input jacks for the guitar and output connections for headphones or external speakers. Overall, careful attention to detail in the circuit design, component selection, and enclosure will result in a functional and effective portable guitar amplifier.The guitar is a wonderful musical instrument which is capable of providing both melody and rhythm. However, every guitar player would have experienced the problem of low volume. The guitar is rarely heard unless the surroundings are absolutely quiet! To solve this problem, the guitar amp is often employed. If you have some knowledge in reading cir cuit diagrams, this tutorial will guide you to make your very own portable guitar amp. Estimated cost: The cost here depends entirely on what you will have to purchase, what you already have and what you manage to scavenge. Hence, it is totally variable. 8. Now built the circuit that is necessary. Instead of going into the details of explaining the circuit, we present the circuit diagram below. Follow it to the hilt. 9. Hook the positive end of the charger to one terminal of an ammeter. The other terminal is connected to the positive end of the battery. Connect the negative end of the battery with the negative end of the charger. Ans: The speaker that has been suggested here has a resistance of 8 ohms and can thus handle about 3 Watts of power.
It is also shallow in its depth and makes it possible to insert heat sinks. These specifications are important for the project and it would be better to stick to the above mentioned speaker unless you can obtain another one with the same specifications. Different speakers will also give different performances. Experiment at your own risk. Ans: Heat sinks help to dissipate the heat that is formed in the circuit. Too much heating can harm the circuit. The heat sinks used in this project are nothing but cut pieces of a regular heat sink that have been filed to fit in.
You can glue them using thermal glue that is available. 2. Be careful while using the hot glue and quick glue. These glues bond very strong and fast. Skin could easily get bonded by mistake and result in injuries. 🔗 External reference