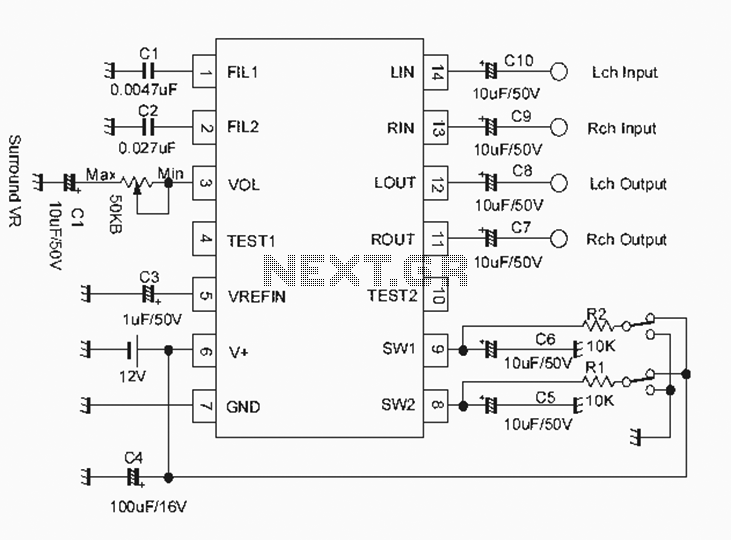
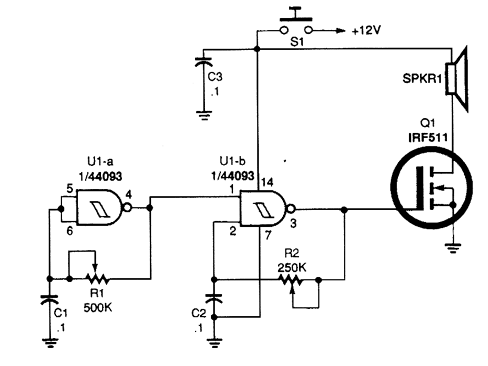
Manual thermostat circuit
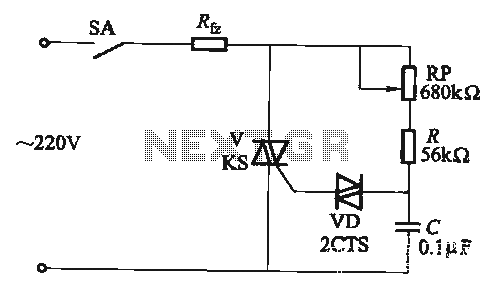
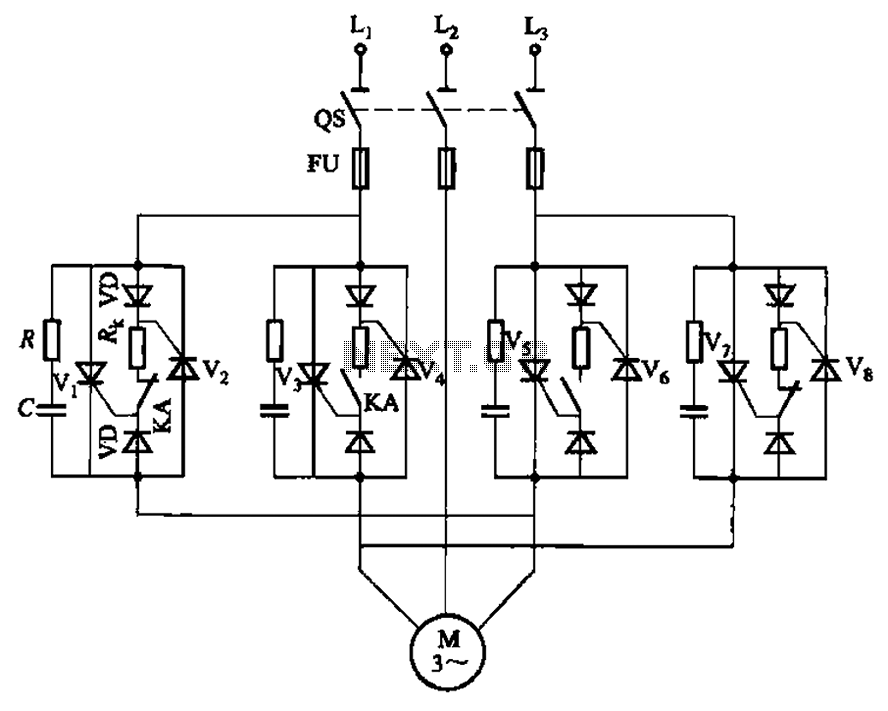
The adjustment potentiometer RP allows for the modification of the TRIAC conduction angle, facilitating temperature control applications.
The adjustment potentiometer (RP) serves a crucial role in controlling the conduction angle of the TRIAC, which in turn regulates the power delivered to a load, such as a heating element. By varying the resistance of the potentiometer, the phase angle at which the TRIAC is triggered can be adjusted. This is essential for applications that require precise temperature control, such as in heating systems or temperature-sensitive processes.
In practical terms, the TRIAC is a semiconductor device that can conduct current in both directions when triggered. The conduction angle, defined as the portion of the AC cycle during which the TRIAC is active, determines the average power delivered to the load. A smaller conduction angle results in lower power output, while a larger angle increases the power delivered.
The potentiometer is typically connected in a phase control circuit, where it alters the timing of the TRIAC triggering. The circuit may include additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes to shape the waveform and ensure stable operation. The adjustment of the potentiometer can be done manually, allowing for fine-tuning of the temperature output according to the requirements of the specific application.
In summary, the adjustment potentiometer RP is an integral component for achieving desired temperature control through the modification of the TRIAC conduction angle, providing versatility and precision in various electronic heating applications.Adjustment potentiometer RP, can change the TRIAC V conduction angle, to achieve tempering purposes.
The adjustment potentiometer (RP) serves a crucial role in controlling the conduction angle of the TRIAC, which in turn regulates the power delivered to a load, such as a heating element. By varying the resistance of the potentiometer, the phase angle at which the TRIAC is triggered can be adjusted. This is essential for applications that require precise temperature control, such as in heating systems or temperature-sensitive processes.
In practical terms, the TRIAC is a semiconductor device that can conduct current in both directions when triggered. The conduction angle, defined as the portion of the AC cycle during which the TRIAC is active, determines the average power delivered to the load. A smaller conduction angle results in lower power output, while a larger angle increases the power delivered.
The potentiometer is typically connected in a phase control circuit, where it alters the timing of the TRIAC triggering. The circuit may include additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes to shape the waveform and ensure stable operation. The adjustment of the potentiometer can be done manually, allowing for fine-tuning of the temperature output according to the requirements of the specific application.
In summary, the adjustment potentiometer RP is an integral component for achieving desired temperature control through the modification of the TRIAC conduction angle, providing versatility and precision in various electronic heating applications.Adjustment potentiometer RP, can change the TRIAC V conduction angle, to achieve tempering purposes.