microcontroller complete code midi emulated ps 2 keyboard
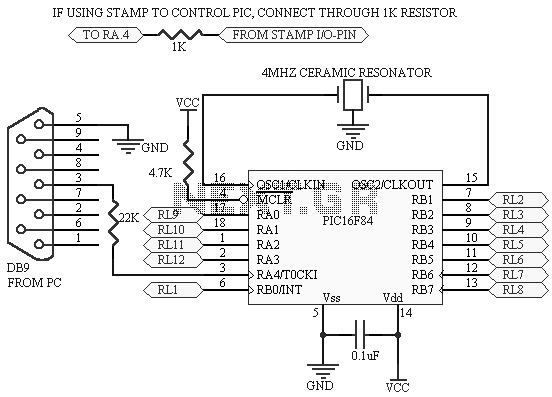
A code has been developed to process MIDI data received on the RX pin of the USART. It stores three bytes of data in a buffer, checks the first byte to determine if it is a MIDI "on" message (indicated by the binary pattern xxxx1001) by masking the upper nibble and performing a subtraction from a constant to check if the result equals zero. If this condition is met, the subsequent byte is converted using a lookup table. The processed data is then transmitted via RA0 and RA1 in a loop, simulating a PS/2 keyboard after calculating the odd parity bit. Additionally, a diagnostic LED section was implemented, but it is malfunctioning: LED1 remains constantly on, LED2 flashes on and off before staying on, and LED3 does not illuminate at all. The configuration settings include: _CONFIG _CONFIG1, _CP_OFF & _CCP1_RB0 & _DEBUG_OFF & _WRT_PROTECT_OFF & _CPD_OFF & _LVP_OFF & _BODEN_OFF & _MCLR_ON & _PWRTE_ON & _WDT_OFF & _HS_OSC.
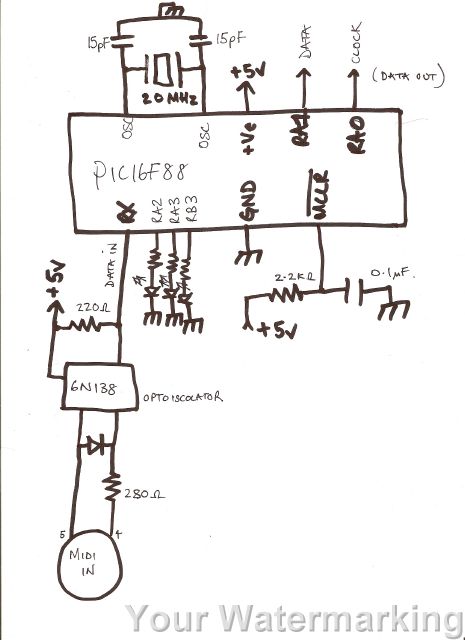
The described circuit is designed to interface with MIDI devices using a USART (Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) for data reception and processing. The primary function of the circuit is to receive MIDI messages, specifically "note on" messages, which are identified by examining the first byte of the incoming data. This byte is masked to isolate the relevant bits, allowing for the determination of whether it corresponds to a MIDI "on" message.
Upon receiving a valid MIDI "on" message, the next byte of data is processed through a lookup table, converting it into a format suitable for transmission. The output is then sent through RA0 and RA1 pins, which emulate the behavior of a PS/2 keyboard, enabling the circuit to communicate with devices that expect keyboard input.
The implementation of diagnostic LEDs serves as a feedback mechanism for troubleshooting the circuit. LED1, which remains constantly on, may indicate an issue with the power supply or configuration settings. LED2's flashing behavior followed by a constant state could suggest intermittent operation or a fault in the code execution. The failure of LED3 to illuminate at all may point to a complete malfunction in that segment of the circuit or an error in the configuration settings.
The configuration settings provided are critical for the operation of the microcontroller within the circuit. These settings include disabling various features such as code protection (_CP_OFF), watchdog timer (_WDT_OFF), and enabling the high-speed oscillator (_HS_OSC), which are essential for ensuring reliable operation and performance of the system. Proper attention to these configurations is necessary to rectify the issues observed with the diagnostic LEDs and to ensure the successful transmission of MIDI data.hi i have been working on this code for a while now and i have come to a complete dead end. the following code takes midi data on the rx pin of the usart, saves the 3 bytes of data in the cblock, tests the first byte to see if it is a midi on message (xxxx1001) by masking the upper nibble and subtracting from a constant to see if it equals zero, i f so take the next byte, convert it using the lookup table. THEN send this data via ra0 and ra1 in a loop which emulates a ps/2 keyboard after calculating the odd parity bit. first things first, i wrote the diagnostic LED part which doesn`t work, led 1 is constantly ON and led2 flashes on, then off, then is constantly on, AND THEN led 3 won`t even come on.
_CONFIG _CONFIG1, _CP_OFF & _CCP1_RB0 & _DEBUG_OFF & _WRT_PROTECT_OFF & _CPD_OFF & _LVP_OFF & _BODEN_OFF & _MCLR_ON & _PWRTE_ON & _WDT_OFF & _HS_OSC 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is designed to interface with MIDI devices using a USART (Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) for data reception and processing. The primary function of the circuit is to receive MIDI messages, specifically "note on" messages, which are identified by examining the first byte of the incoming data. This byte is masked to isolate the relevant bits, allowing for the determination of whether it corresponds to a MIDI "on" message.
Upon receiving a valid MIDI "on" message, the next byte of data is processed through a lookup table, converting it into a format suitable for transmission. The output is then sent through RA0 and RA1 pins, which emulate the behavior of a PS/2 keyboard, enabling the circuit to communicate with devices that expect keyboard input.
The implementation of diagnostic LEDs serves as a feedback mechanism for troubleshooting the circuit. LED1, which remains constantly on, may indicate an issue with the power supply or configuration settings. LED2's flashing behavior followed by a constant state could suggest intermittent operation or a fault in the code execution. The failure of LED3 to illuminate at all may point to a complete malfunction in that segment of the circuit or an error in the configuration settings.
The configuration settings provided are critical for the operation of the microcontroller within the circuit. These settings include disabling various features such as code protection (_CP_OFF), watchdog timer (_WDT_OFF), and enabling the high-speed oscillator (_HS_OSC), which are essential for ensuring reliable operation and performance of the system. Proper attention to these configurations is necessary to rectify the issues observed with the diagnostic LEDs and to ensure the successful transmission of MIDI data.hi i have been working on this code for a while now and i have come to a complete dead end. the following code takes midi data on the rx pin of the usart, saves the 3 bytes of data in the cblock, tests the first byte to see if it is a midi on message (xxxx1001) by masking the upper nibble and subtracting from a constant to see if it equals zero, i f so take the next byte, convert it using the lookup table. THEN send this data via ra0 and ra1 in a loop which emulates a ps/2 keyboard after calculating the odd parity bit. first things first, i wrote the diagnostic LED part which doesn`t work, led 1 is constantly ON and led2 flashes on, then off, then is constantly on, AND THEN led 3 won`t even come on.
_CONFIG _CONFIG1, _CP_OFF & _CCP1_RB0 & _DEBUG_OFF & _WRT_PROTECT_OFF & _CPD_OFF & _LVP_OFF & _BODEN_OFF & _MCLR_ON & _PWRTE_ON & _WDT_OFF & _HS_OSC 🔗 External reference