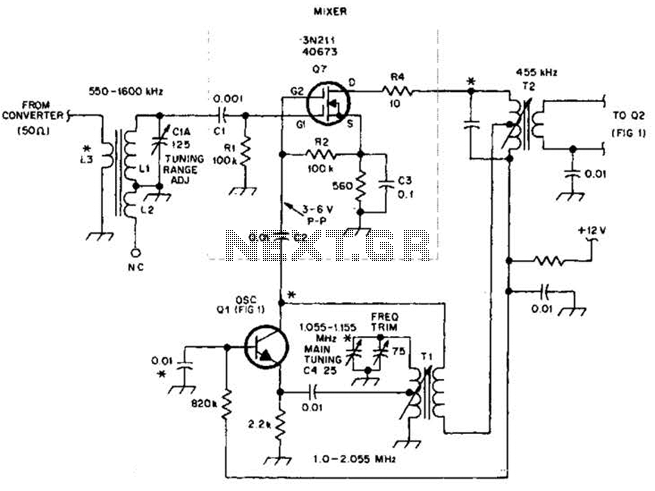
mixer
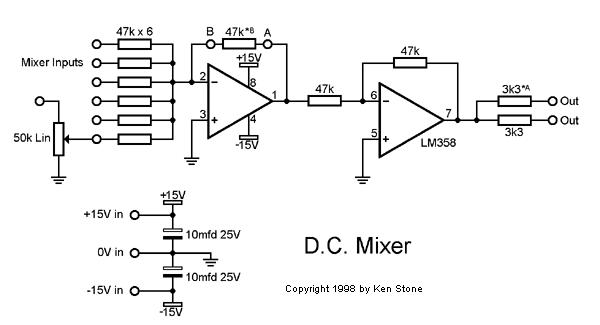
An electronic project detailing a D.C. mixer for synthesizers and various control applications.
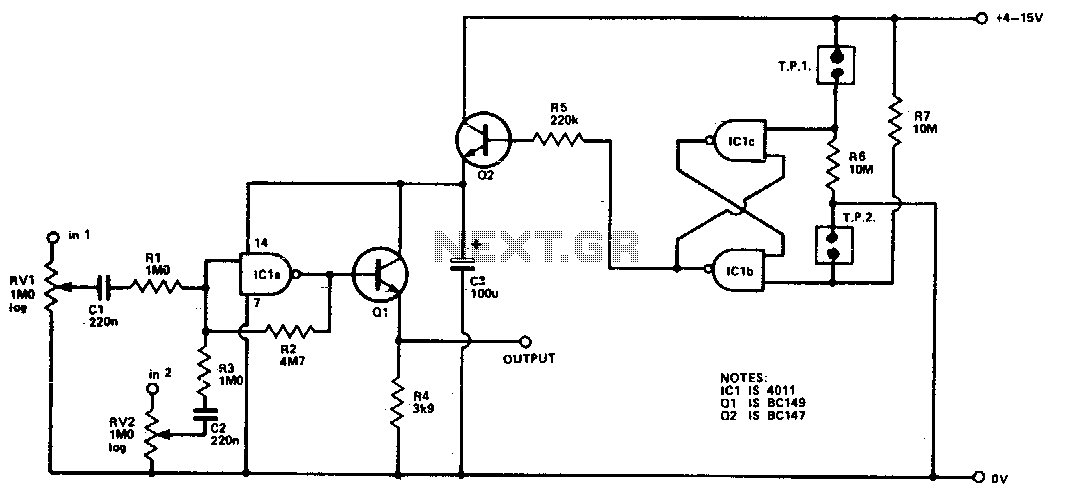
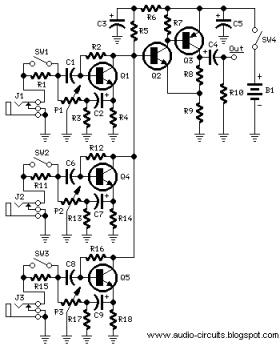
The D.C. mixer circuit is designed to combine multiple direct current (DC) signals into a single output, making it particularly useful in synthesizer applications where different control voltages need to be mixed. This circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a summing amplifier arrangement, which allows for the linear combination of input signals.
In a standard D.C. mixer, the input signals are fed into the inverting and/or non-inverting terminals of the op-amps. Resistors are used to set the gain for each input, ensuring that the output reflects the desired mix of the input voltages. The output of the mixer can then be used to control various parameters in a synthesizer, such as pitch, filter cutoff, or modulation depth.
The design may also include features such as adjustable gain for each input channel, allowing for fine-tuning of the mix according to the specific requirements of the application. Additional components like capacitors can be utilized to filter out noise, ensuring that the output signal remains clean and stable.
When implementing this circuit, careful attention must be paid to power supply requirements, as op-amps typically require a dual power supply for optimal performance. Additionally, the layout of the circuit should minimize interference and maintain signal integrity, particularly in environments with high electromagnetic interference.
Overall, the D.C. mixer serves as a fundamental building block in synthesizer design and other electronic control systems, enabling the integration of various control voltages into a cohesive output signal.Electronic project describing a D.C. Mixer for Synthesizers and other control applications.. 🔗 External reference
The D.C. mixer circuit is designed to combine multiple direct current (DC) signals into a single output, making it particularly useful in synthesizer applications where different control voltages need to be mixed. This circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a summing amplifier arrangement, which allows for the linear combination of input signals.
In a standard D.C. mixer, the input signals are fed into the inverting and/or non-inverting terminals of the op-amps. Resistors are used to set the gain for each input, ensuring that the output reflects the desired mix of the input voltages. The output of the mixer can then be used to control various parameters in a synthesizer, such as pitch, filter cutoff, or modulation depth.
The design may also include features such as adjustable gain for each input channel, allowing for fine-tuning of the mix according to the specific requirements of the application. Additional components like capacitors can be utilized to filter out noise, ensuring that the output signal remains clean and stable.
When implementing this circuit, careful attention must be paid to power supply requirements, as op-amps typically require a dual power supply for optimal performance. Additionally, the layout of the circuit should minimize interference and maintain signal integrity, particularly in environments with high electromagnetic interference.
Overall, the D.C. mixer serves as a fundamental building block in synthesizer design and other electronic control systems, enabling the integration of various control voltages into a cohesive output signal.Electronic project describing a D.C. Mixer for Synthesizers and other control applications.. 🔗 External reference