Modified Sine Wave Signal Generator
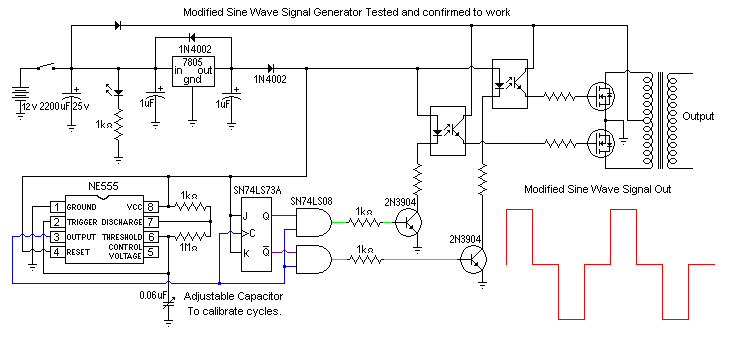
Pure sine wave inverters are optimal; however, they are costly to purchase or construct. Modified sine wave inverters can power certain equipment, while square wave inverters have more limitations.
Pure sine wave inverters are highly regarded for their ability to produce a clean and stable output waveform that closely resembles the natural sine wave produced by utility power. This quality makes them ideal for sensitive electronic devices, such as medical equipment, audio systems, and certain types of motors, which require a smooth and consistent power supply to function correctly. The primary disadvantage of pure sine wave inverters is their higher cost and complexity in design, which can make them less accessible for some users.
Modified sine wave inverters offer a more affordable alternative. They generate a waveform that approximates a sine wave but includes flat tops, leading to a more rectangular shape. While they can efficiently power many household appliances and devices, they may not be suitable for all equipment. Some sensitive electronics may experience issues such as overheating, increased noise, or reduced efficiency when powered by modified sine wave inverters.
Square wave inverters produce a waveform that is purely rectangular, lacking the smooth transitions found in sine wave outputs. These inverters are the least expensive option and are typically used for very basic applications, such as powering simple resistive loads like incandescent light bulbs or heating elements. However, their use with more complex electronic devices can lead to significant operational problems, including inefficiency, potential damage, and increased electromagnetic interference.
In summary, the choice between pure sine wave, modified sine wave, and square wave inverters depends on the specific needs of the equipment being powered, the budget available, and the importance of power quality for the intended application.Pure sine wave inverters are best, however they are expensive to buy or build. Modified sine wave inverters will power some equipment square wave inve.. 🔗 External reference
Pure sine wave inverters are highly regarded for their ability to produce a clean and stable output waveform that closely resembles the natural sine wave produced by utility power. This quality makes them ideal for sensitive electronic devices, such as medical equipment, audio systems, and certain types of motors, which require a smooth and consistent power supply to function correctly. The primary disadvantage of pure sine wave inverters is their higher cost and complexity in design, which can make them less accessible for some users.
Modified sine wave inverters offer a more affordable alternative. They generate a waveform that approximates a sine wave but includes flat tops, leading to a more rectangular shape. While they can efficiently power many household appliances and devices, they may not be suitable for all equipment. Some sensitive electronics may experience issues such as overheating, increased noise, or reduced efficiency when powered by modified sine wave inverters.
Square wave inverters produce a waveform that is purely rectangular, lacking the smooth transitions found in sine wave outputs. These inverters are the least expensive option and are typically used for very basic applications, such as powering simple resistive loads like incandescent light bulbs or heating elements. However, their use with more complex electronic devices can lead to significant operational problems, including inefficiency, potential damage, and increased electromagnetic interference.
In summary, the choice between pure sine wave, modified sine wave, and square wave inverters depends on the specific needs of the equipment being powered, the budget available, and the importance of power quality for the intended application.Pure sine wave inverters are best, however they are expensive to buy or build. Modified sine wave inverters will power some equipment square wave inve.. 🔗 External reference