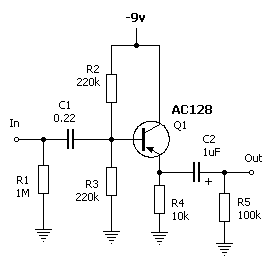
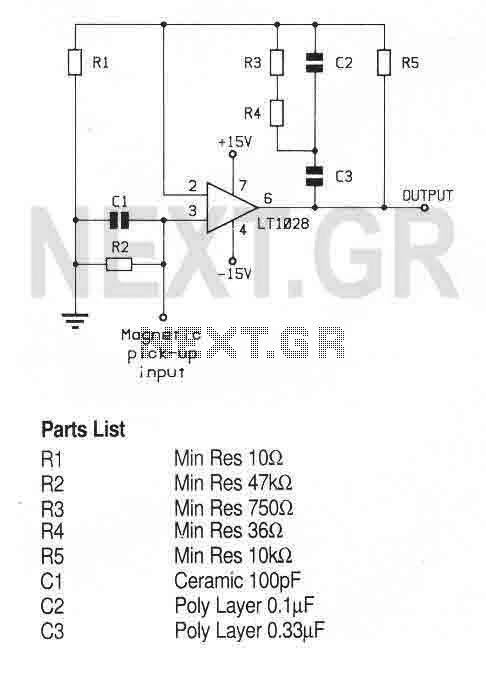
modular class a buffer preamplifier
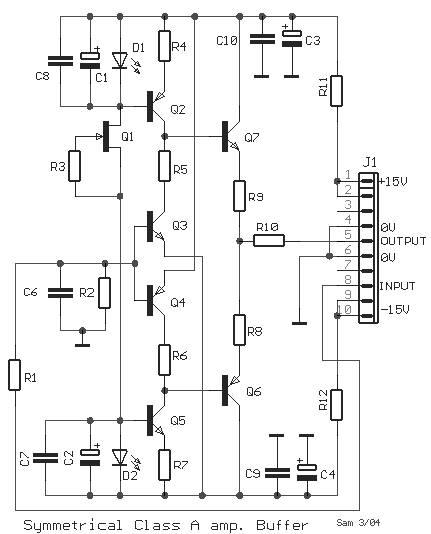
A unit that is often very useful for isolating two stages in sound circuits. This circuit includes an amplification unit with a gain of X1. Total negative feedback is not employed; instead, only local feedback is used, resulting in very low distortion levels. Careful matching is required for the types of transistors and the resistor between them.
This circuit serves as an isolation amplifier designed to connect two stages of audio processing while minimizing interaction between them. The key feature of this unit is its gain configuration, set to X1, which ensures that the signal level remains consistent without amplification, thereby preserving the integrity of the audio signal.
The use of local negative feedback rather than total feedback is crucial in maintaining low distortion levels. Local feedback allows for better control over the immediate amplification process, reducing the likelihood of signal degradation that can occur with more extensive feedback systems. This characteristic is particularly important in high-fidelity audio applications where sound quality is paramount.
Transistor selection is critical in this design, as the performance and characteristics of the transistors directly influence the overall behavior of the circuit. It is essential to match the transistors not only in terms of gain but also in their frequency response and thermal characteristics. This ensures that they operate harmoniously, providing consistent performance across the audio spectrum.
The resistor used between the transistors plays a vital role in setting the correct biasing conditions and stabilizing the circuit. Proper resistor values must be calculated to achieve the desired operating point for the transistors, allowing for optimal performance with minimal distortion. Additionally, attention must be paid to the resistor's tolerance and temperature coefficient to ensure reliability under varying conditions.
In summary, this isolation amplifier circuit is designed for use in sound applications where low distortion and high fidelity are required. Its careful design considerations, including gain configuration, local feedback, and component matching, contribute to its effectiveness in isolating audio stages while maintaining sound quality.A unit which is often very useful, if we need to isolate, in sound circuits, two stage between them. Then we can use this circuit which has an amplified unit, which gain X1, we do not use total negative feedback, only local, with the result that distortion remains at a very low level. Matching must be done with great care to the types of transistors, resistor between them.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit serves as an isolation amplifier designed to connect two stages of audio processing while minimizing interaction between them. The key feature of this unit is its gain configuration, set to X1, which ensures that the signal level remains consistent without amplification, thereby preserving the integrity of the audio signal.
The use of local negative feedback rather than total feedback is crucial in maintaining low distortion levels. Local feedback allows for better control over the immediate amplification process, reducing the likelihood of signal degradation that can occur with more extensive feedback systems. This characteristic is particularly important in high-fidelity audio applications where sound quality is paramount.
Transistor selection is critical in this design, as the performance and characteristics of the transistors directly influence the overall behavior of the circuit. It is essential to match the transistors not only in terms of gain but also in their frequency response and thermal characteristics. This ensures that they operate harmoniously, providing consistent performance across the audio spectrum.
The resistor used between the transistors plays a vital role in setting the correct biasing conditions and stabilizing the circuit. Proper resistor values must be calculated to achieve the desired operating point for the transistors, allowing for optimal performance with minimal distortion. Additionally, attention must be paid to the resistor's tolerance and temperature coefficient to ensure reliability under varying conditions.
In summary, this isolation amplifier circuit is designed for use in sound applications where low distortion and high fidelity are required. Its careful design considerations, including gain configuration, local feedback, and component matching, contribute to its effectiveness in isolating audio stages while maintaining sound quality.A unit which is often very useful, if we need to isolate, in sound circuits, two stage between them. Then we can use this circuit which has an amplified unit, which gain X1, we do not use total negative feedback, only local, with the result that distortion remains at a very low level. Matching must be done with great care to the types of transistors, resistor between them.. 🔗 External reference