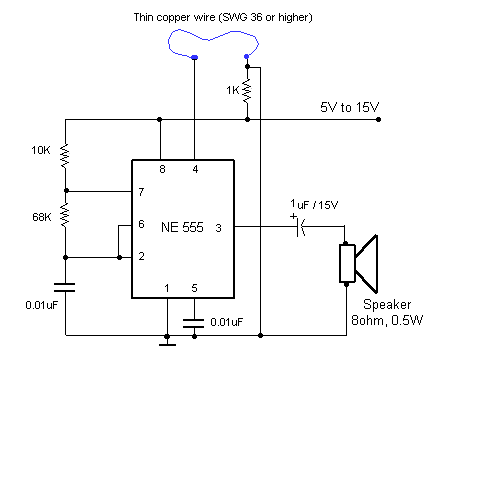
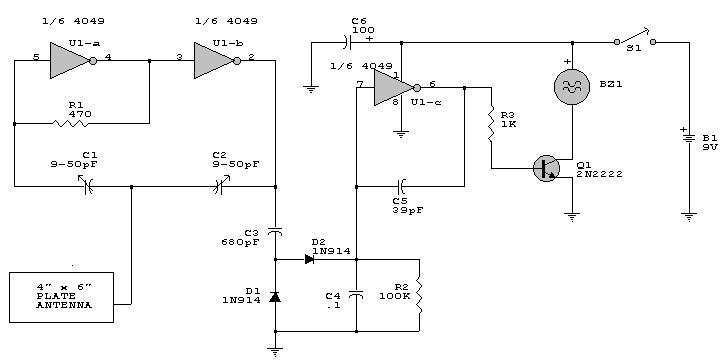
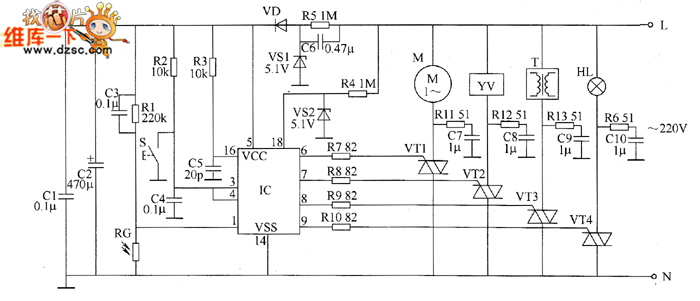
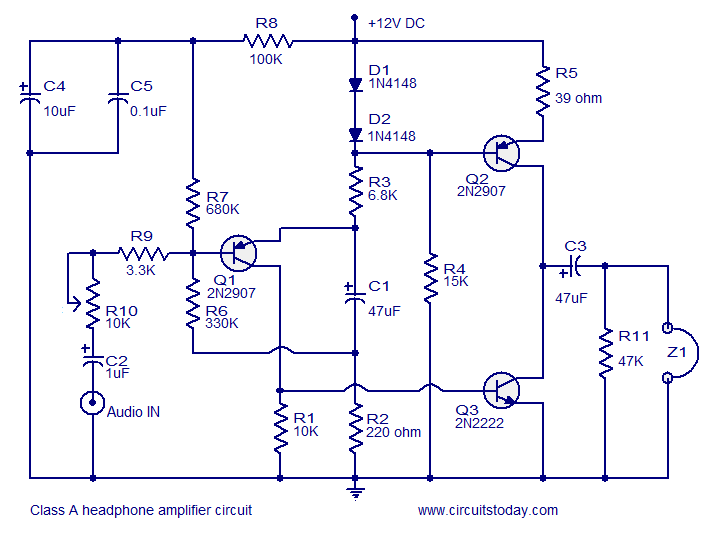
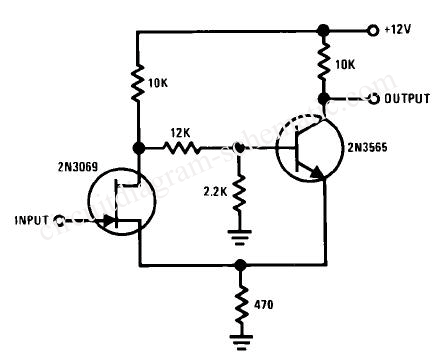
Monostable circuit diagram composed of two 555
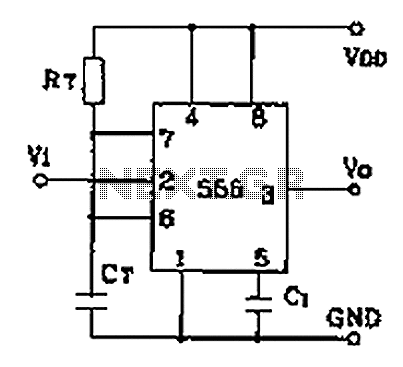
Common monostable circuit in two configurations: manual start type and start pulse type. It generates a single-shot pulse upon activation.
A monostable circuit, also known as a one-shot multivibrator, is a fundamental electronic circuit that produces a single output pulse in response to an input trigger. This circuit can be configured in two primary ways: a manual start type and a start pulse type.
In the manual start configuration, the circuit is activated by a physical switch or button. When the switch is pressed, it initiates a pulse that lasts for a predetermined duration, defined by the timing components in the circuit, typically a resistor and capacitor. The output pulse will return to its stable state once the timing period elapses. This configuration is useful in applications where a user needs to manually trigger an event, such as in timers or delay circuits.
Conversely, the start pulse type configuration relies on an external pulse to trigger the monostable operation. This external pulse can come from various sources, such as a sensor output or another digital circuit. Upon receiving the pulse, the monostable circuit generates a single output pulse of a specified duration. This configuration is particularly advantageous in automated systems where triggers occur without human intervention, such as in digital signal processing or in timing applications where events must be synchronized.
Both configurations utilize similar components, including a timing capacitor, a resistor, and a trigger input. The timing characteristics of the output pulse are determined by the RC time constant, which can be calculated using the formula T = R × C, where T is the time period, R is the resistance in ohms, and C is the capacitance in farads.
The output of the monostable circuit can be connected to various loads, such as LEDs, relays, or other digital circuits, making this circuit versatile for a wide range of applications in electronics. Overall, the monostable circuit serves as a fundamental building block in digital electronics, facilitating precise timing and control in various systems. Common monostable circuit in two ways: manual start type and start pulse type. Single-shot pulse start
A monostable circuit, also known as a one-shot multivibrator, is a fundamental electronic circuit that produces a single output pulse in response to an input trigger. This circuit can be configured in two primary ways: a manual start type and a start pulse type.
In the manual start configuration, the circuit is activated by a physical switch or button. When the switch is pressed, it initiates a pulse that lasts for a predetermined duration, defined by the timing components in the circuit, typically a resistor and capacitor. The output pulse will return to its stable state once the timing period elapses. This configuration is useful in applications where a user needs to manually trigger an event, such as in timers or delay circuits.
Conversely, the start pulse type configuration relies on an external pulse to trigger the monostable operation. This external pulse can come from various sources, such as a sensor output or another digital circuit. Upon receiving the pulse, the monostable circuit generates a single output pulse of a specified duration. This configuration is particularly advantageous in automated systems where triggers occur without human intervention, such as in digital signal processing or in timing applications where events must be synchronized.
Both configurations utilize similar components, including a timing capacitor, a resistor, and a trigger input. The timing characteristics of the output pulse are determined by the RC time constant, which can be calculated using the formula T = R × C, where T is the time period, R is the resistance in ohms, and C is the capacitance in farads.
The output of the monostable circuit can be connected to various loads, such as LEDs, relays, or other digital circuits, making this circuit versatile for a wide range of applications in electronics. Overall, the monostable circuit serves as a fundamental building block in digital electronics, facilitating precise timing and control in various systems. Common monostable circuit in two ways: manual start type and start pulse type. Single-shot pulse start