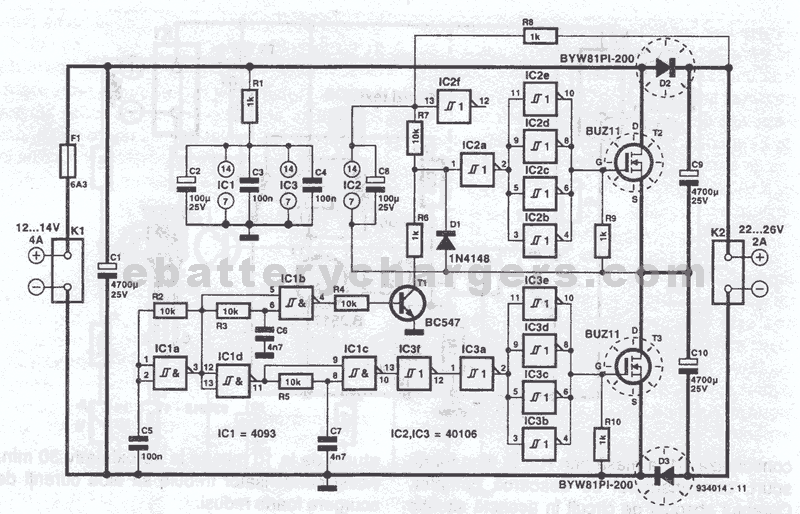
audio level meter circuit using lm3915

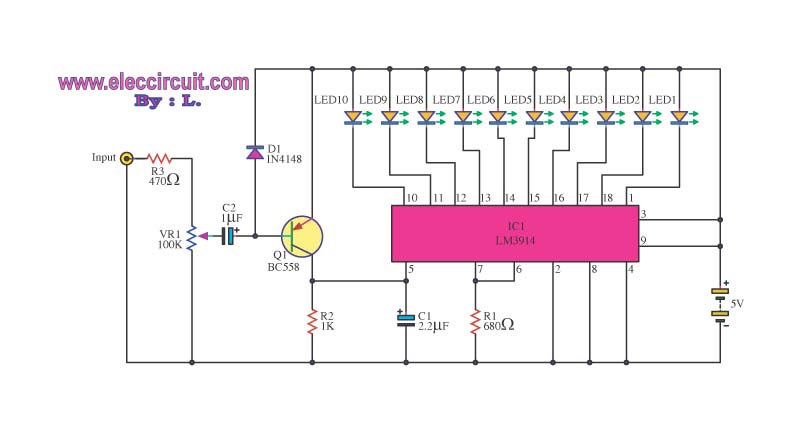
This is a simple design of an audio level meter. The circuit utilizes a single integrated circuit (IC) and a minimal number of external components. It is based on the LM3915, which functions as the controller for the audio level meter circuit. The circuit displays the audio level using ten LEDs. The input voltage can range from 12V to 20V, with a suggested operating voltage of 12V. The LM3915 is a monolithic integrated circuit that detects analog voltage levels and drives ten LEDs, providing a logarithmic 3 dB/step analog display. The LED current drive is regulated and programmable, which eliminates the need for current limiting resistors. The IC includes an adjustable voltage reference and a precise ten-step voltage divider. The high-impedance input buffer can accept signals down to ground and up to within 1.5V of the positive supply, requiring no protection against inputs of 35V. The input buffer drives ten individual comparators that are referenced to the precision divider, with accuracy typically better than 1 dB.
The audio level meter circuit designed using the LM3915 is a straightforward and efficient solution for visualizing audio signal levels. The LM3915 IC operates in bar graph mode, illuminating a series of LEDs that represent the amplitude of the audio signal. This feature is particularly useful in audio engineering, sound mixing, and various applications where monitoring audio levels is crucial to prevent distortion or clipping.
The circuit's design can be broken down into several key components. The LM3915 serves as the heart of the meter, where it processes the incoming audio signal. The input stage includes a high-impedance buffer, which is essential for preventing loading effects on the audio source. This feature allows the circuit to accurately sense low-level signals without introducing distortion or altering the signal characteristics.
The programmable LED current drive feature of the LM3915 allows for customization of brightness levels, enhancing visibility under different lighting conditions. By adjusting the reference voltage, the user can calibrate the meter to suit specific application requirements, ensuring precise readings across various audio levels.
The ten-step voltage divider within the IC enables the display of audio levels in a logarithmic scale, which is more representative of human hearing perception. This logarithmic response is crucial for applications such as live sound reinforcement, where audio levels can vary significantly.
Additionally, the circuit can operate safely with input voltages up to 35V, making it robust for various environments. This characteristic, combined with the IC's accuracy of better than 1 dB, positions the audio level meter as a reliable tool for audio professionals. The simplicity of the design, requiring only a few external components, further enhances its appeal, allowing for easy integration into larger audio systems or standalone applications.This is a simple design of audio level meter. This circuit uses just one IC and a very few number of external components. This circuit is based on LM3915 as controller in the operation of the audio level meter circuit. It displays the audio level in terms of 10 LEDs. This is the figure of the circuit. The input voltage can vary from 12V to 20V, bu t suggested voltage is 12V. The LM3915 is a monolithic integrated circuit that senses analog voltage levels and drives ten LEDs providing a logarithmic 3 dB/step analog display. LED current drive is regulated and programmable, eliminating the need for current limiting resistors.
The IC contains an adjustable voltage reference and an accurate ten-step voltage divider. The high-impedance input buffer accepts signals down to ground and up to within 1. 5V of the positive supply. Further, it needs no protection against inputs of 35V. The input buffer drives 10 individual comparators referenced to the precision divider. Accuracy is typically better than 1 dB. 🔗 External reference
The audio level meter circuit designed using the LM3915 is a straightforward and efficient solution for visualizing audio signal levels. The LM3915 IC operates in bar graph mode, illuminating a series of LEDs that represent the amplitude of the audio signal. This feature is particularly useful in audio engineering, sound mixing, and various applications where monitoring audio levels is crucial to prevent distortion or clipping.
The circuit's design can be broken down into several key components. The LM3915 serves as the heart of the meter, where it processes the incoming audio signal. The input stage includes a high-impedance buffer, which is essential for preventing loading effects on the audio source. This feature allows the circuit to accurately sense low-level signals without introducing distortion or altering the signal characteristics.
The programmable LED current drive feature of the LM3915 allows for customization of brightness levels, enhancing visibility under different lighting conditions. By adjusting the reference voltage, the user can calibrate the meter to suit specific application requirements, ensuring precise readings across various audio levels.
The ten-step voltage divider within the IC enables the display of audio levels in a logarithmic scale, which is more representative of human hearing perception. This logarithmic response is crucial for applications such as live sound reinforcement, where audio levels can vary significantly.
Additionally, the circuit can operate safely with input voltages up to 35V, making it robust for various environments. This characteristic, combined with the IC's accuracy of better than 1 dB, positions the audio level meter as a reliable tool for audio professionals. The simplicity of the design, requiring only a few external components, further enhances its appeal, allowing for easy integration into larger audio systems or standalone applications.This is a simple design of audio level meter. This circuit uses just one IC and a very few number of external components. This circuit is based on LM3915 as controller in the operation of the audio level meter circuit. It displays the audio level in terms of 10 LEDs. This is the figure of the circuit. The input voltage can vary from 12V to 20V, bu t suggested voltage is 12V. The LM3915 is a monolithic integrated circuit that senses analog voltage levels and drives ten LEDs providing a logarithmic 3 dB/step analog display. LED current drive is regulated and programmable, eliminating the need for current limiting resistors.
The IC contains an adjustable voltage reference and an accurate ten-step voltage divider. The high-impedance input buffer accepts signals down to ground and up to within 1. 5V of the positive supply. Further, it needs no protection against inputs of 35V. The input buffer drives 10 individual comparators referenced to the precision divider. Accuracy is typically better than 1 dB. 🔗 External reference