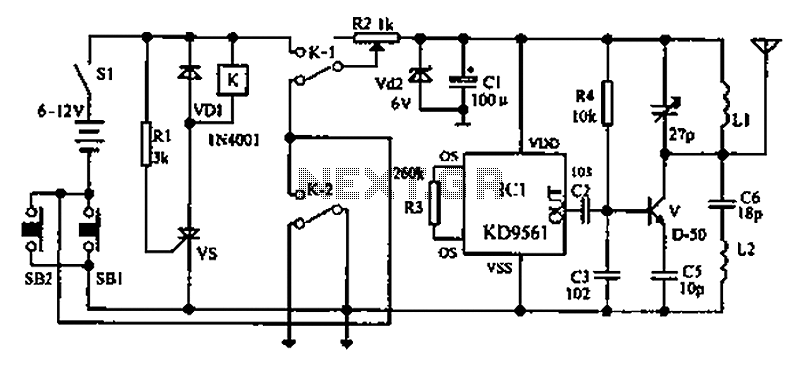
Monostable Multivibrator I Circuit
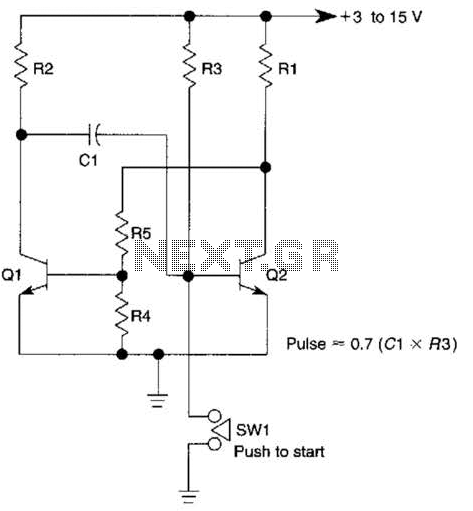
This circuit is activated when switch SW1 is pressed, grounding the base of transistor Q2. The pulse rate is approximately equal to 0.7 multiplied by the product of resistor R3 and capacitor C1.
The described circuit features a transistor Q2, which acts as a switch or amplifier, depending on the configuration. When switch SW1 is pressed, it creates a path to ground for the base of Q2, causing the transistor to enter a conductive state. This activation allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, thus controlling the load connected to the circuit.
The pulse rate of the circuit is determined by the time constant formed by resistor R3 and capacitor C1. The formula provided indicates that the pulse rate is approximately 0.7 times the product of these two components, which suggests that the circuit is likely configured as an astable multivibrator or a similar timing circuit. The values of R3 and C1 will dictate the frequency of the pulses generated.
In practical applications, the choice of R3 and C1 will affect the duration of the high and low states of the output signal. A larger resistance or capacitance will result in a slower pulse rate, while a smaller resistance or capacitance will produce a faster pulse rate. Additionally, the circuit may include other components such as diodes for protection, additional transistors for amplification, or operational amplifiers for signal conditioning, depending on the intended application.
Overall, this circuit can be utilized in various applications, including timers, pulse generators, or as part of a larger control system where timed events are necessary. Proper selection of components and careful layout design will ensure reliable operation and desired performance. This circuit is activated when SW1 is pushed to ground the base of transistor Q2. The pulse rate is approximately equal to 0.7(R3xCl).
The described circuit features a transistor Q2, which acts as a switch or amplifier, depending on the configuration. When switch SW1 is pressed, it creates a path to ground for the base of Q2, causing the transistor to enter a conductive state. This activation allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, thus controlling the load connected to the circuit.
The pulse rate of the circuit is determined by the time constant formed by resistor R3 and capacitor C1. The formula provided indicates that the pulse rate is approximately 0.7 times the product of these two components, which suggests that the circuit is likely configured as an astable multivibrator or a similar timing circuit. The values of R3 and C1 will dictate the frequency of the pulses generated.
In practical applications, the choice of R3 and C1 will affect the duration of the high and low states of the output signal. A larger resistance or capacitance will result in a slower pulse rate, while a smaller resistance or capacitance will produce a faster pulse rate. Additionally, the circuit may include other components such as diodes for protection, additional transistors for amplification, or operational amplifiers for signal conditioning, depending on the intended application.
Overall, this circuit can be utilized in various applications, including timers, pulse generators, or as part of a larger control system where timed events are necessary. Proper selection of components and careful layout design will ensure reliable operation and desired performance. This circuit is activated when SW1 is pushed to ground the base of transistor Q2. The pulse rate is approximately equal to 0.7(R3xCl).