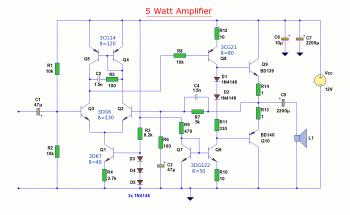
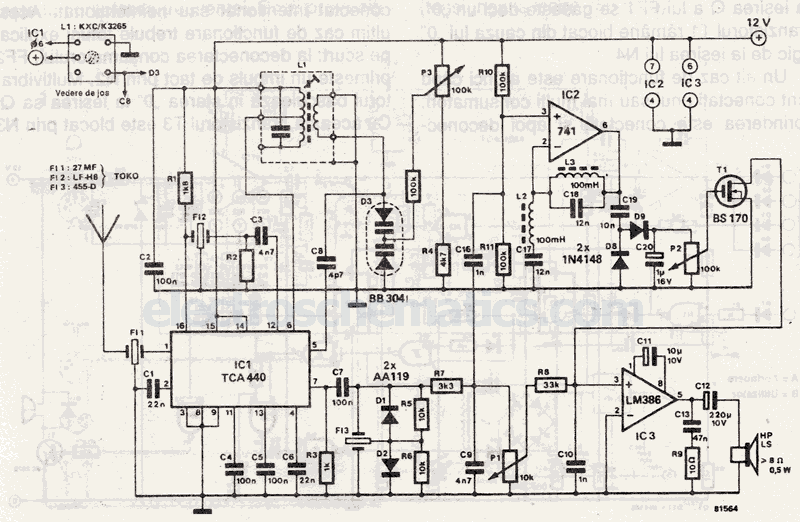
Speech amplifier circuit
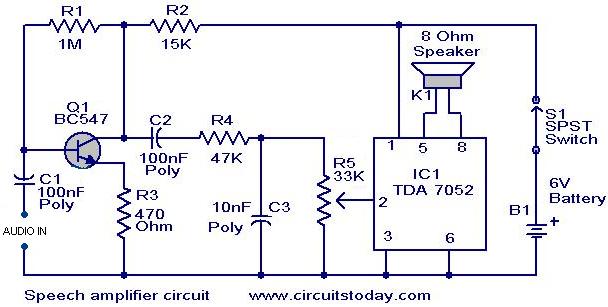
This circuit can be housed within a box containing a speaker to create a convenient microphone amplifier. It is suitable for use by teachers, guides, lecturers, and others in crowded or noisy environments. The design is based on the audio power amplifier integrated circuit (IC) TDA 7052, which can deliver a maximum power output of 1.2 W at a 6V supply. The audio signal from the microphone is pre-amplified by a transistor amplifier (Q1, BC 547) before being fed into pin 2 of IC1. The potentiometer (POTR5) functions as a volume control. Capacitor C3 is employed to bypass higher frequencies, helping to prevent the Larsen effect, which occurs when the microphone picks up the speaker output and causes feedback.
The microphone amplifier circuit utilizes the TDA 7052 IC, which is well-suited for audio amplification applications due to its low distortion and high efficiency. The circuit's architecture includes a pre-amplification stage using the BC 547 transistor, which serves to amplify the weak audio signals from the microphone before they reach the main amplifier IC. This pre-amplification is critical in ensuring that the subsequent amplification stage operates effectively, particularly in environments with significant background noise.
The potentiometer (POTR5) allows for user-adjustable volume control, enabling the operator to tailor the output level to suit the specific environment and audience size. This feature is essential for maintaining clarity and preventing audio distortion, especially in dynamic settings where ambient noise levels may fluctuate.
Capacitor C3 plays a pivotal role in maintaining sound quality by filtering out unwanted high-frequency signals that could lead to feedback loops, commonly referred to as the Larsen effect. By bypassing these frequencies, the circuit minimizes the risk of howling and ensures a smoother audio experience for both the speaker and the audience.
Overall, the design of this microphone amplifier circuit is practical and efficient, making it an ideal solution for enhancing audio delivery in various public speaking scenarios. Its compact design allows for easy integration with portable speaker systems, ensuring that users can effectively communicate even in challenging acoustic environments.This circuit given here can be housed in the box containing the speaker to form a handy microphone amplifier. The device can be used by teachers, guides, lecturers etc for speaking in a crowdy or noisy environment.
The circuit is designed base on the audio power amplifier IC TDA 7052. The IC can deliver a maximum power output of 1. 2 W at a 6V supply. T he audio signal from the microphone is pre amplified by the amplifier based on Q1 (BC 547) and give to the input of IC1 (pin 2). The POTR5 acts as a volume control. The capacitor C3 is used to bye pass the upper frequencies in order to avoid the Larsen`s effect(the microphone picking up speaker output to cause howls).
🔗 External reference
The microphone amplifier circuit utilizes the TDA 7052 IC, which is well-suited for audio amplification applications due to its low distortion and high efficiency. The circuit's architecture includes a pre-amplification stage using the BC 547 transistor, which serves to amplify the weak audio signals from the microphone before they reach the main amplifier IC. This pre-amplification is critical in ensuring that the subsequent amplification stage operates effectively, particularly in environments with significant background noise.
The potentiometer (POTR5) allows for user-adjustable volume control, enabling the operator to tailor the output level to suit the specific environment and audience size. This feature is essential for maintaining clarity and preventing audio distortion, especially in dynamic settings where ambient noise levels may fluctuate.
Capacitor C3 plays a pivotal role in maintaining sound quality by filtering out unwanted high-frequency signals that could lead to feedback loops, commonly referred to as the Larsen effect. By bypassing these frequencies, the circuit minimizes the risk of howling and ensures a smoother audio experience for both the speaker and the audience.
Overall, the design of this microphone amplifier circuit is practical and efficient, making it an ideal solution for enhancing audio delivery in various public speaking scenarios. Its compact design allows for easy integration with portable speaker systems, ensuring that users can effectively communicate even in challenging acoustic environments.This circuit given here can be housed in the box containing the speaker to form a handy microphone amplifier. The device can be used by teachers, guides, lecturers etc for speaking in a crowdy or noisy environment.
The circuit is designed base on the audio power amplifier IC TDA 7052. The IC can deliver a maximum power output of 1. 2 W at a 6V supply. T he audio signal from the microphone is pre amplified by the amplifier based on Q1 (BC 547) and give to the input of IC1 (pin 2). The POTR5 acts as a volume control. The capacitor C3 is used to bye pass the upper frequencies in order to avoid the Larsen`s effect(the microphone picking up speaker output to cause howls).
🔗 External reference