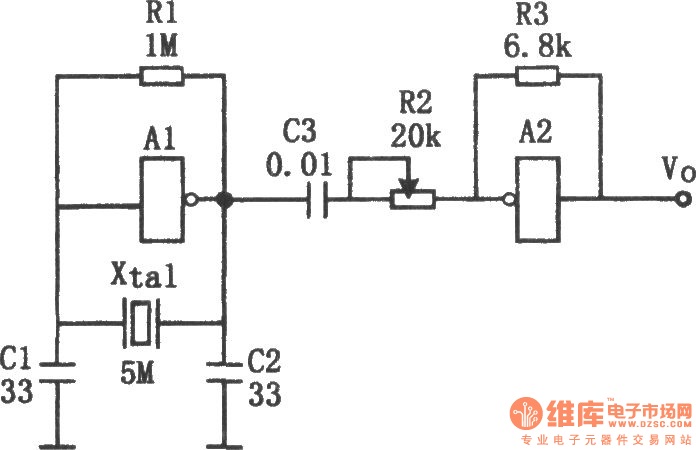
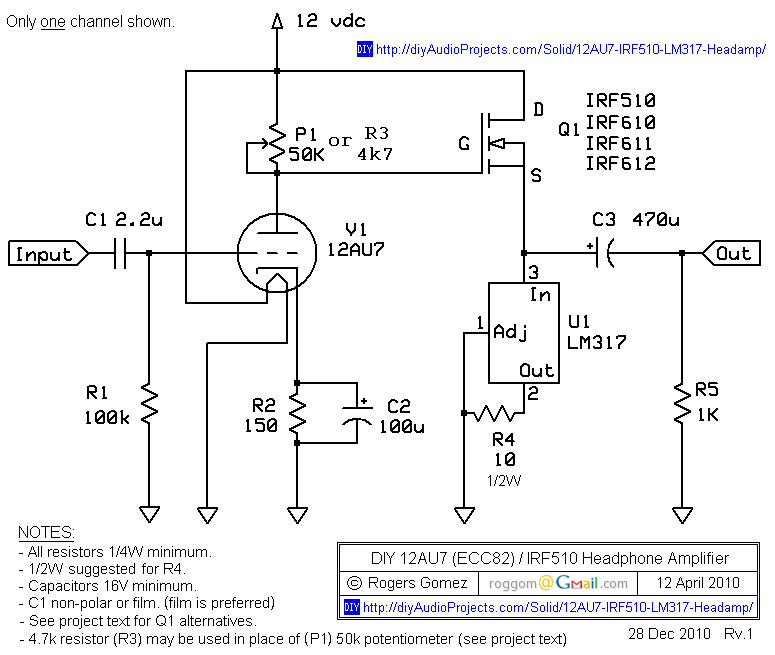
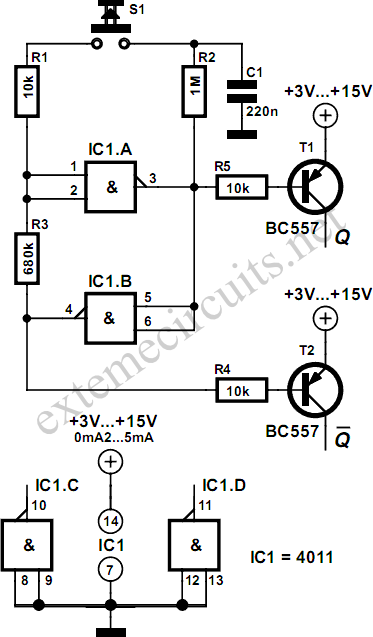
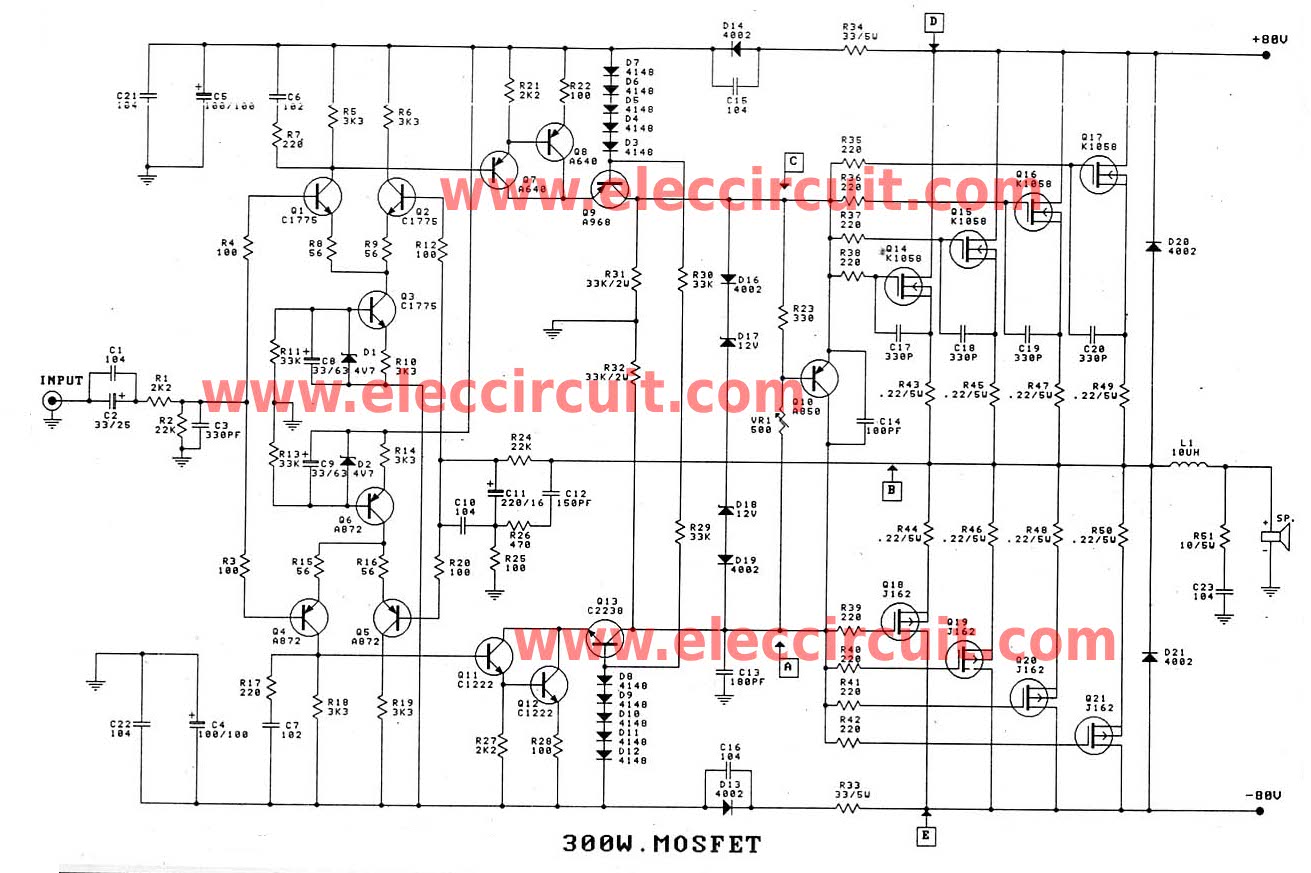
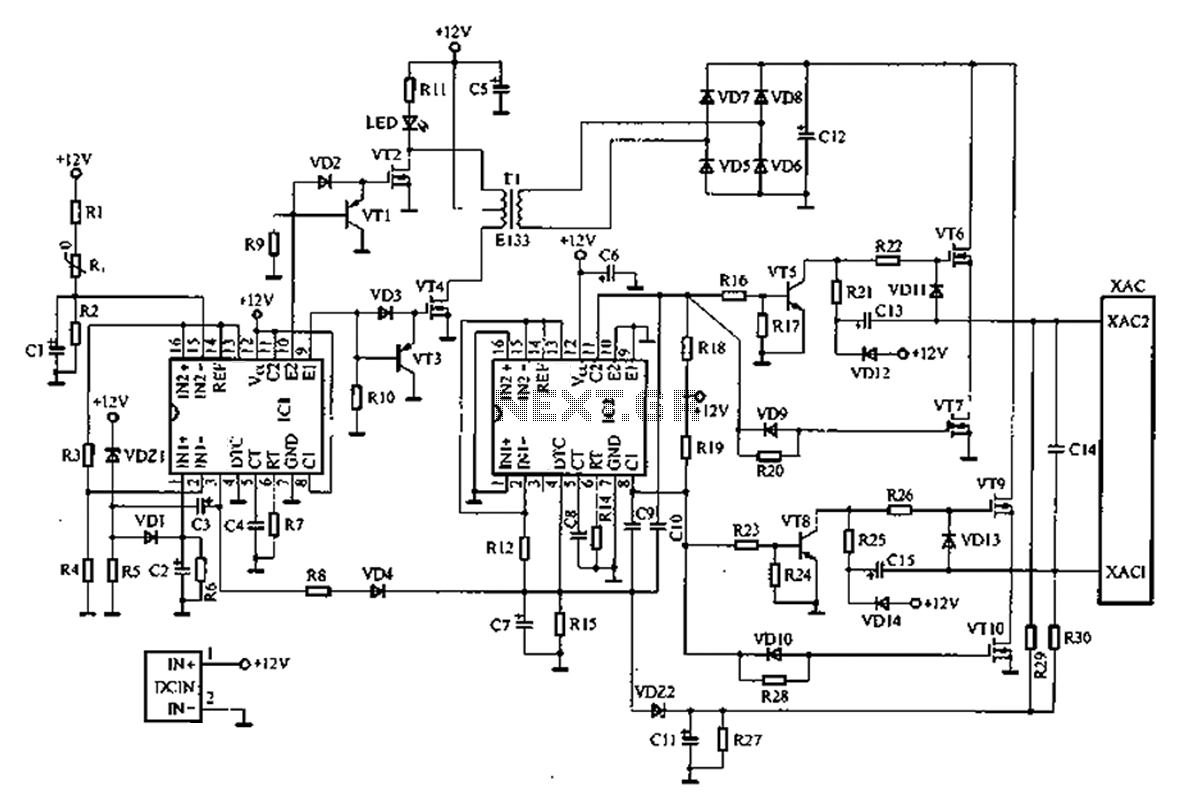
MOS FET inverter
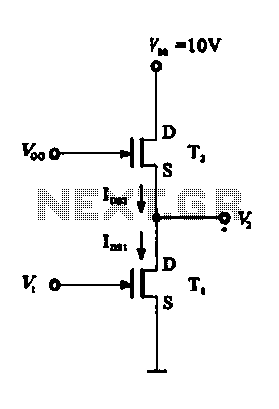
A Field Effect Transistor (FET) can function as a linear amplifier, and it can also be utilized to create a logic gate circuit.
FETs are semiconductor devices that control the flow of current using an electric field. Due to their high input impedance and low output impedance, FETs are well-suited for linear amplification applications. In a linear amplifier configuration, the FET operates in the active region, where it can amplify small input signals. The output signal is a scaled version of the input, maintaining the waveform shape, which is essential for audio and RF applications.
In addition to their role in amplification, FETs can be employed in digital circuits as logic gates. For example, a simple inverter can be constructed using a single FET. In this configuration, when the input voltage is high, the FET turns on, allowing current to flow from the drain to the source, resulting in a low output voltage. Conversely, when the input voltage is low, the FET turns off, and the output voltage becomes high. This basic principle can be expanded to create more complex logic gates such as NAND and NOR by combining multiple FETs in various configurations.
Overall, FETs serve dual purposes in electronic design, facilitating both analog signal processing through amplification and digital signal processing through logic gate implementation. Their versatility makes them integral components in modern electronic circuits.FET can be used as a linear amplifier, a logic gate circuit may also be made,
FETs are semiconductor devices that control the flow of current using an electric field. Due to their high input impedance and low output impedance, FETs are well-suited for linear amplification applications. In a linear amplifier configuration, the FET operates in the active region, where it can amplify small input signals. The output signal is a scaled version of the input, maintaining the waveform shape, which is essential for audio and RF applications.
In addition to their role in amplification, FETs can be employed in digital circuits as logic gates. For example, a simple inverter can be constructed using a single FET. In this configuration, when the input voltage is high, the FET turns on, allowing current to flow from the drain to the source, resulting in a low output voltage. Conversely, when the input voltage is low, the FET turns off, and the output voltage becomes high. This basic principle can be expanded to create more complex logic gates such as NAND and NOR by combining multiple FETs in various configurations.
Overall, FETs serve dual purposes in electronic design, facilitating both analog signal processing through amplification and digital signal processing through logic gate implementation. Their versatility makes them integral components in modern electronic circuits.FET can be used as a linear amplifier, a logic gate circuit may also be made,