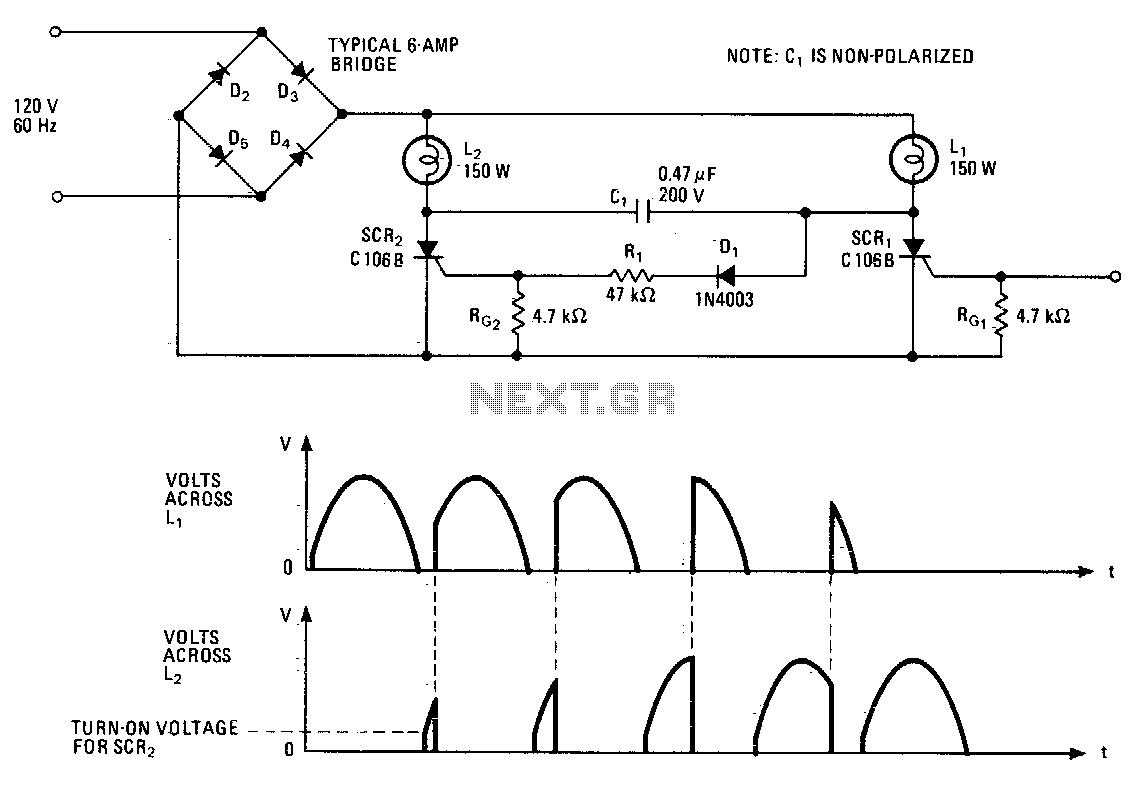
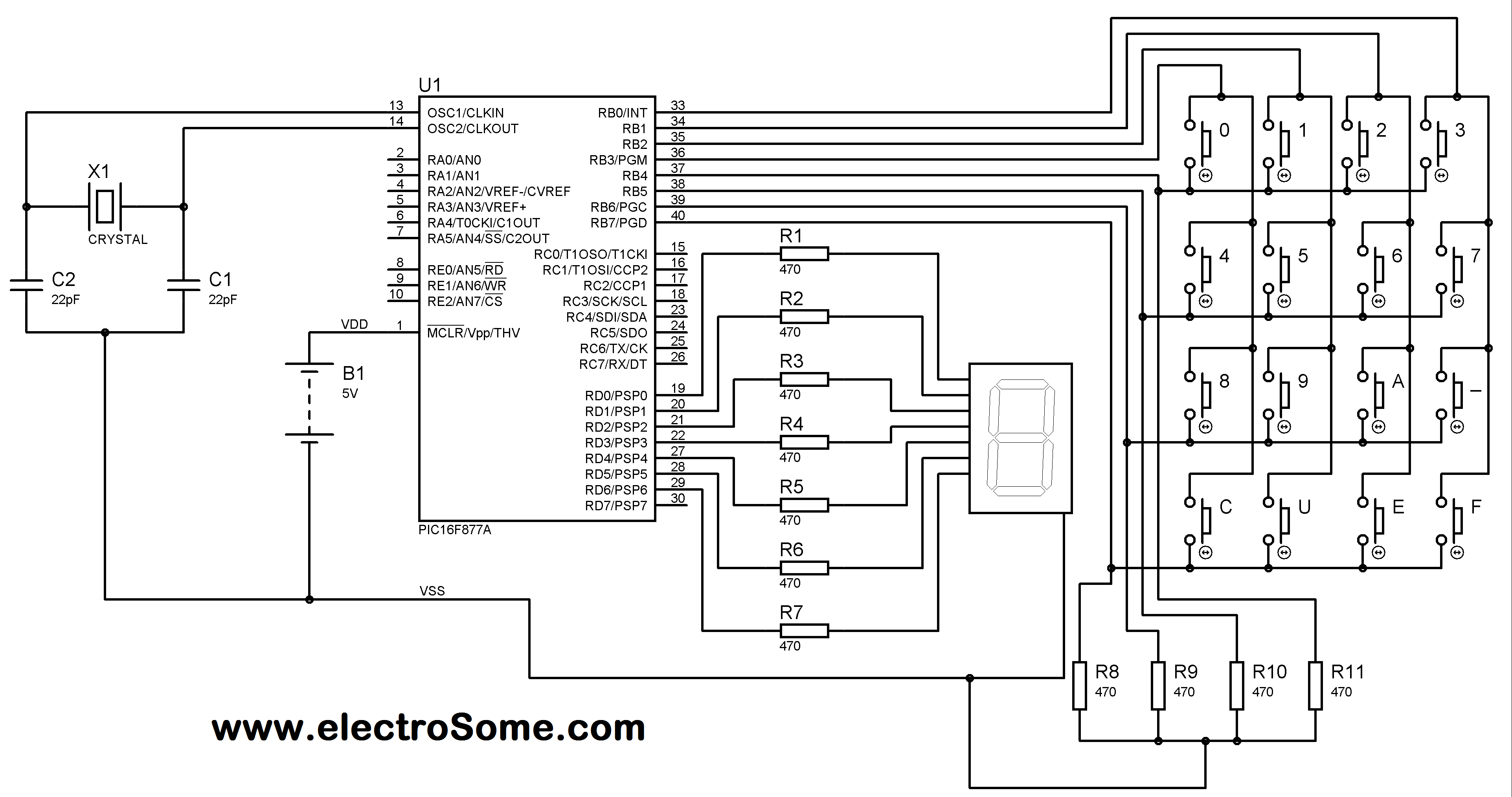
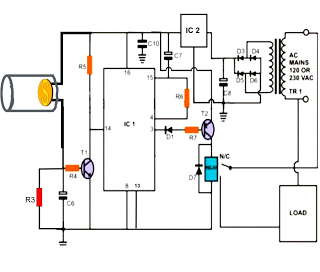
Motor Speed Control Using PWM
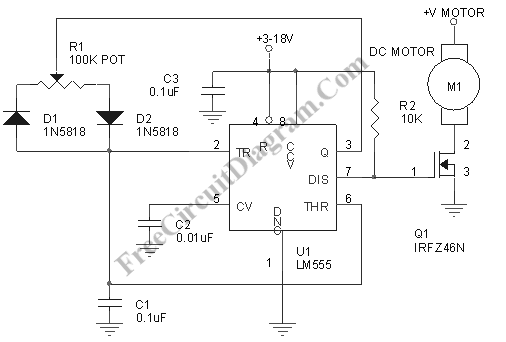
Pulse width modulation, commonly referred to as PWM, is utilized to regulate the power supplied to a load without sacrificing efficiency. This technique is often employed in controlling the speed of an electric motor.
PWM operates by varying the width of the pulses in a signal while maintaining a constant frequency. This method allows for precise control of the average power delivered to an electrical device by adjusting the duty cycle, which is the ratio of the "on" time to the total cycle time. For instance, a 50% duty cycle means the signal is on half of the time and off the other half, resulting in an average power output that is half of the maximum.
In practical applications, PWM is widely used in motor speed control, dimming of lights, and in various power supply circuits. The implementation of PWM in motor control enables smooth acceleration and deceleration, reduces mechanical wear, and enhances energy efficiency. The use of high-frequency PWM signals minimizes audible noise in motors, as the switching frequency is typically above the audible range.
To design a PWM circuit for motor control, a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM controller can be employed. The microcontroller generates the PWM signal based on the desired speed input, which can be adjusted via a potentiometer or a digital interface. The PWM signal is then fed into a power stage, typically comprising a MOSFET or an IGBT, which acts as a switch that controls the motor's power supply.
The circuit should include protective components such as diodes to prevent back EMF from damaging the switching elements, as well as capacitors to filter voltage spikes. Feedback mechanisms, such as tachometers or encoders, can be integrated to provide real-time speed data, allowing for closed-loop control and further refinement of the PWM signal based on the motor's performance.
Overall, PWM stands as a versatile and efficient method for power regulation in various electronic applications, particularly in the control of electric motors.Pulse width modulation or familiarly known as PWM is used to control the delivered power to load without loosing the efficiency. The speed of an electric motor.. 🔗 External reference
PWM operates by varying the width of the pulses in a signal while maintaining a constant frequency. This method allows for precise control of the average power delivered to an electrical device by adjusting the duty cycle, which is the ratio of the "on" time to the total cycle time. For instance, a 50% duty cycle means the signal is on half of the time and off the other half, resulting in an average power output that is half of the maximum.
In practical applications, PWM is widely used in motor speed control, dimming of lights, and in various power supply circuits. The implementation of PWM in motor control enables smooth acceleration and deceleration, reduces mechanical wear, and enhances energy efficiency. The use of high-frequency PWM signals minimizes audible noise in motors, as the switching frequency is typically above the audible range.
To design a PWM circuit for motor control, a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM controller can be employed. The microcontroller generates the PWM signal based on the desired speed input, which can be adjusted via a potentiometer or a digital interface. The PWM signal is then fed into a power stage, typically comprising a MOSFET or an IGBT, which acts as a switch that controls the motor's power supply.
The circuit should include protective components such as diodes to prevent back EMF from damaging the switching elements, as well as capacitors to filter voltage spikes. Feedback mechanisms, such as tachometers or encoders, can be integrated to provide real-time speed data, allowing for closed-loop control and further refinement of the PWM signal based on the motor's performance.
Overall, PWM stands as a versatile and efficient method for power regulation in various electronic applications, particularly in the control of electric motors.Pulse width modulation or familiarly known as PWM is used to control the delivered power to load without loosing the efficiency. The speed of an electric motor.. 🔗 External reference