Motorola Hi-Fi power amplifiers
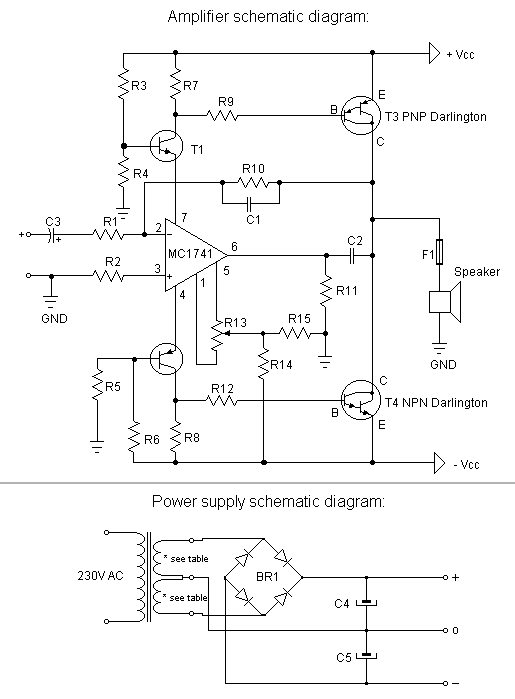
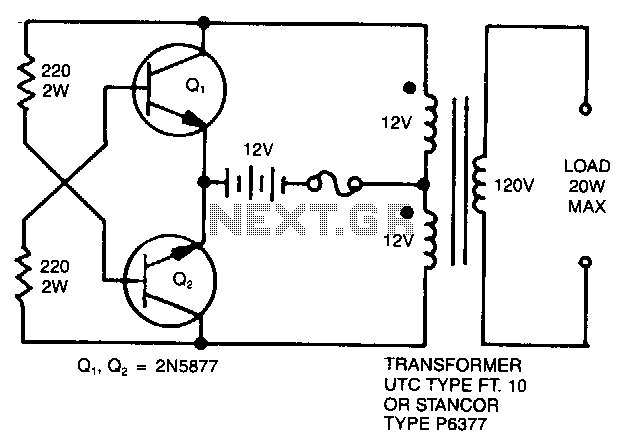
This is a very simple, low-cost, Hi-Fi quality power amplifier. It can be built in five different configurations, as shown in the table, ranging from 20 W to 80 W RMS.
The Hi-Fi quality power amplifier circuit is designed to deliver high fidelity audio output while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The amplifier can be configured in five distinct ways to accommodate various power requirements, allowing for an output range from 20 watts to 80 watts RMS.
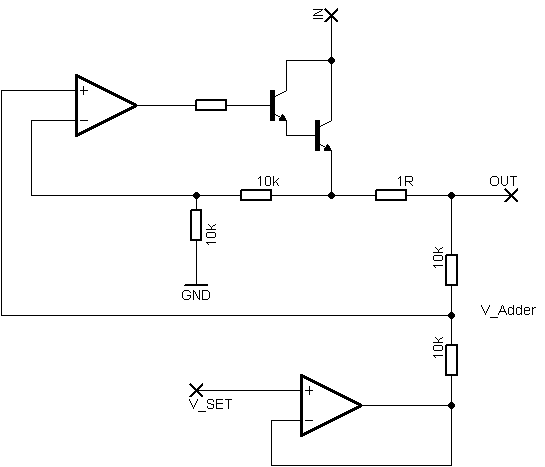
The core of the amplifier typically consists of a complementary push-pull output stage, which enhances efficiency and linearity, minimizing distortion while maximizing sound quality. The design may incorporate a voltage gain stage, often utilizing operational amplifiers or transistors, which can be adjusted based on the desired output power.
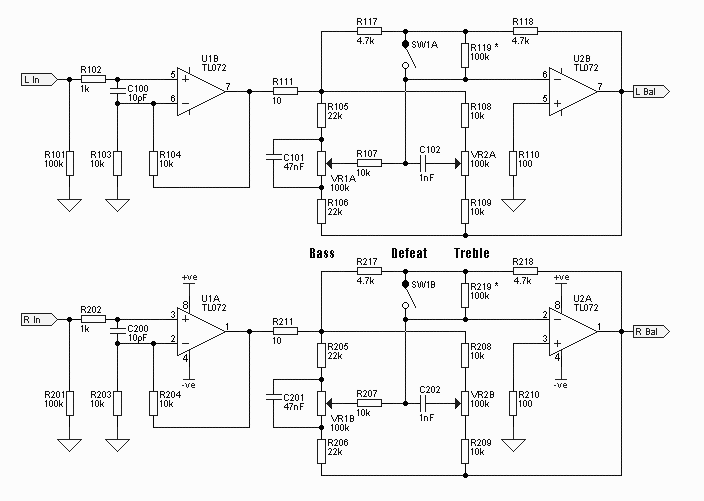
Input and output stages are crucial for the performance of the amplifier. The input stage may include capacitive coupling to block DC offset, ensuring only the AC audio signal is amplified. The output stage is designed to drive speakers effectively, with considerations for impedance matching to optimize power transfer and reduce signal loss.
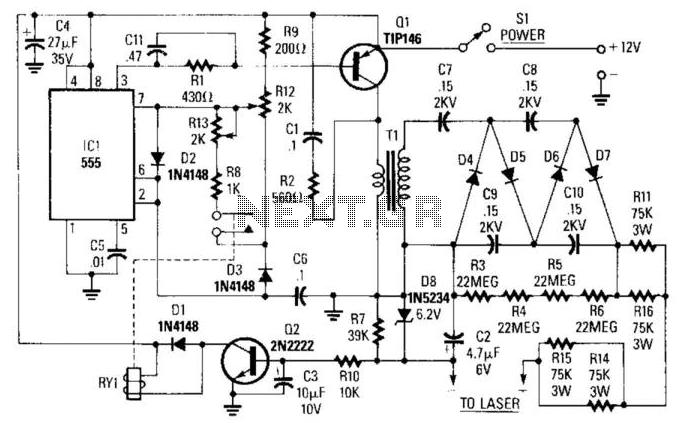
Power supply requirements for this amplifier should be considered carefully. A regulated power supply may be necessary to ensure consistent performance and avoid fluctuations that could lead to distortion or clipping during high-demand audio peaks.
Thermal management is also an essential aspect of the design. Heatsinks may be employed to dissipate heat generated by the output transistors, ensuring reliable operation over extended periods.
Overall, this amplifier circuit not only provides versatility in output power configurations but also emphasizes high-quality sound reproduction, making it suitable for various audio applications, from home audio systems to small public address systems. Properly implemented, this design can deliver impressive audio performance while remaining accessible to hobbyists and professionals alike.This is a very simple, low cost, Hi-Fi quality power amplifier. You can build it 5 ways, like it?s shown in the table (from 20 W to 80 W RMS).. 🔗 External reference
The Hi-Fi quality power amplifier circuit is designed to deliver high fidelity audio output while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The amplifier can be configured in five distinct ways to accommodate various power requirements, allowing for an output range from 20 watts to 80 watts RMS.
The core of the amplifier typically consists of a complementary push-pull output stage, which enhances efficiency and linearity, minimizing distortion while maximizing sound quality. The design may incorporate a voltage gain stage, often utilizing operational amplifiers or transistors, which can be adjusted based on the desired output power.
Input and output stages are crucial for the performance of the amplifier. The input stage may include capacitive coupling to block DC offset, ensuring only the AC audio signal is amplified. The output stage is designed to drive speakers effectively, with considerations for impedance matching to optimize power transfer and reduce signal loss.
Power supply requirements for this amplifier should be considered carefully. A regulated power supply may be necessary to ensure consistent performance and avoid fluctuations that could lead to distortion or clipping during high-demand audio peaks.
Thermal management is also an essential aspect of the design. Heatsinks may be employed to dissipate heat generated by the output transistors, ensuring reliable operation over extended periods.
Overall, this amplifier circuit not only provides versatility in output power configurations but also emphasizes high-quality sound reproduction, making it suitable for various audio applications, from home audio systems to small public address systems. Properly implemented, this design can deliver impressive audio performance while remaining accessible to hobbyists and professionals alike.This is a very simple, low cost, Hi-Fi quality power amplifier. You can build it 5 ways, like it?s shown in the table (from 20 W to 80 W RMS).. 🔗 External reference