motorola hi fi power
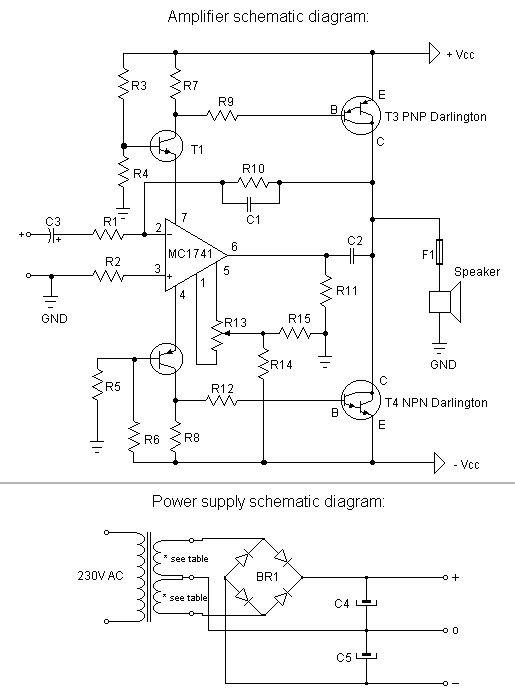
The first step is to measure the amplification factor of the end transistors (T3 and T4), known as the hfe. If their difference exceeds 30%, the amplifier will produce unclear sound. In this case, MJ3001 and MJ2501 transistors were used, and the discrepancy was approximately 5%. Before the initial power-up, it is necessary to short-circuit the amplifier's input and connect a milliampere meter to the output. After turning on the amplifier, adjust the R13 potentiometer to reduce the DC output current to a few microamperes or, ideally, to zero. A reduction to 10 microamperes was achieved.
To ensure optimal performance of the amplifier circuit, it is crucial to accurately measure the hfe values of the transistors T3 and T4. The hfe, or current gain, is a vital parameter that influences the overall gain and fidelity of the amplifier. When selecting transistors, a tolerance of less than 30% between the hfe values is recommended to maintain sound clarity. The use of MJ3001 and MJ2501 transistors, known for their reliability in audio applications, resulted in a minimal deviation of approximately 5%, which is acceptable for high-quality sound reproduction.
Prior to powering the amplifier, it is essential to short-circuit the input to prevent any unwanted signals from affecting the initial measurements. Connecting a milliampere meter to the output allows for precise monitoring of the DC output current. Upon powering the amplifier, the R13 potentiometer must be adjusted carefully. This adjustment is critical for minimizing the DC offset at the output, which could otherwise lead to distortion or damage to connected speakers. The goal is to achieve a DC output current as low as possible, ideally reaching zero. In this case, a successful adjustment was made, reducing the current to 10 microamperes, which indicates that the amplifier is functioning correctly without significant DC offset.
In summary, following these procedures ensures the amplifier operates within its designed specifications, contributing to clear and accurate sound reproduction. Proper transistor matching and meticulous adjustment of the output current are essential steps in the amplifier setup process.The first thing that you must do, is to measure the end transistors (T3 and T4) amplifying coefficient, the hfe or ². If their disagreement is bigger than 30 %, the amplifier would not give a clear sound. I used MJ3001 and MJ2501 transistors, and this disagreement was around 5%. - Before the first ½turning on ½ you must short circuit the input s of the amp, and put a mA-meter on the output, than turn the amplifier on, and tune the R13 pot, to decrease the DC current on the output, to some uA-s, or in a lucky situation to zero. I was able to decrease it to 10 uA. 🔗 External reference
To ensure optimal performance of the amplifier circuit, it is crucial to accurately measure the hfe values of the transistors T3 and T4. The hfe, or current gain, is a vital parameter that influences the overall gain and fidelity of the amplifier. When selecting transistors, a tolerance of less than 30% between the hfe values is recommended to maintain sound clarity. The use of MJ3001 and MJ2501 transistors, known for their reliability in audio applications, resulted in a minimal deviation of approximately 5%, which is acceptable for high-quality sound reproduction.
Prior to powering the amplifier, it is essential to short-circuit the input to prevent any unwanted signals from affecting the initial measurements. Connecting a milliampere meter to the output allows for precise monitoring of the DC output current. Upon powering the amplifier, the R13 potentiometer must be adjusted carefully. This adjustment is critical for minimizing the DC offset at the output, which could otherwise lead to distortion or damage to connected speakers. The goal is to achieve a DC output current as low as possible, ideally reaching zero. In this case, a successful adjustment was made, reducing the current to 10 microamperes, which indicates that the amplifier is functioning correctly without significant DC offset.
In summary, following these procedures ensures the amplifier operates within its designed specifications, contributing to clear and accurate sound reproduction. Proper transistor matching and meticulous adjustment of the output current are essential steps in the amplifier setup process.The first thing that you must do, is to measure the end transistors (T3 and T4) amplifying coefficient, the hfe or ². If their disagreement is bigger than 30 %, the amplifier would not give a clear sound. I used MJ3001 and MJ2501 transistors, and this disagreement was around 5%. - Before the first ½turning on ½ you must short circuit the input s of the amp, and put a mA-meter on the output, than turn the amplifier on, and tune the R13 pot, to decrease the DC current on the output, to some uA-s, or in a lucky situation to zero. I was able to decrease it to 10 uA. 🔗 External reference