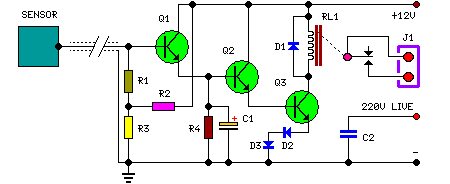
Nature simulator with 555 circuit

The circuit operates using an integrated circuit (IC) NE555 along with resistors R, RP, and capacitor C3, forming an astable multivibrator configuration. The output from pin 3 of the IC generates a square wave oscillation signal, which is passed through a current-limiting resistor R2 to control the TRIAC. This TRIAC is connected to an outlet, allowing it to regulate the operation of a fan based on the intermittent oscillation signal.
The circuit described utilizes the NE555 timer IC in its astable mode, which is a popular configuration for generating continuous square wave signals. In this setup, the timing components, which include resistors R and RP and capacitor C3, determine the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform. The output signal from pin 3 of the NE555 is a square wave that alternates between high and low states at a frequency defined by the values of R, RP, and C3.
The current-limiting resistor R2 is crucial as it protects the TRIAC from excessive current that could otherwise damage it. The TRIAC, a semiconductor device that can control AC loads, is connected to the output to manage the power supplied to the fan. When the NE555 outputs a high signal, the TRIAC is triggered, allowing current to flow to the fan. Conversely, when the signal is low, the TRIAC turns off, interrupting the current flow and stopping the fan.
This circuit is particularly useful for applications requiring fan control based on specific timing intervals. By adjusting the values of R, RP, and C3, the frequency of the oscillation can be modified, thus changing how frequently the fan operates. This flexibility makes the circuit suitable for various cooling and ventilation applications, where intermittent fan operation is desired to save energy or manage temperature effectively. Proper heat dissipation measures should be considered in the design to ensure reliable operation of the TRIAC and the overall circuit.Circuit works: an integrated circuit lC (NE555) and R, RP, C3 substandard elements constituting around astable multivibrator, lC 3 feet square wave oscillation signal output from the current limiting resistor R2 is added to the TRIAC vs the control terminal, connected to the outlet to control the fan inside xs make it work according to the oscillation signal intermittently
The circuit described utilizes the NE555 timer IC in its astable mode, which is a popular configuration for generating continuous square wave signals. In this setup, the timing components, which include resistors R and RP and capacitor C3, determine the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform. The output signal from pin 3 of the NE555 is a square wave that alternates between high and low states at a frequency defined by the values of R, RP, and C3.
The current-limiting resistor R2 is crucial as it protects the TRIAC from excessive current that could otherwise damage it. The TRIAC, a semiconductor device that can control AC loads, is connected to the output to manage the power supplied to the fan. When the NE555 outputs a high signal, the TRIAC is triggered, allowing current to flow to the fan. Conversely, when the signal is low, the TRIAC turns off, interrupting the current flow and stopping the fan.
This circuit is particularly useful for applications requiring fan control based on specific timing intervals. By adjusting the values of R, RP, and C3, the frequency of the oscillation can be modified, thus changing how frequently the fan operates. This flexibility makes the circuit suitable for various cooling and ventilation applications, where intermittent fan operation is desired to save energy or manage temperature effectively. Proper heat dissipation measures should be considered in the design to ensure reliable operation of the TRIAC and the overall circuit.Circuit works: an integrated circuit lC (NE555) and R, RP, C3 substandard elements constituting around astable multivibrator, lC 3 feet square wave oscillation signal output from the current limiting resistor R2 is added to the TRIAC vs the control terminal, connected to the outlet to control the fan inside xs make it work according to the oscillation signal intermittently