Nicad Battery Charger circuit
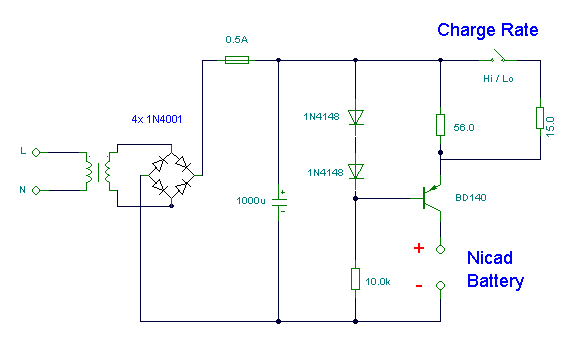
This simple charger utilizes a single transistor as a constant current source. The voltage across the pair of 1N4148 diodes biases the base of the BD140 medium power transistor.
The circuit operates by employing the BD140 transistor to regulate the charging current delivered to the load. The 1N4148 diodes serve as a reference voltage source, establishing a stable voltage level that is necessary for the proper biasing of the transistor. This configuration ensures that the charging current remains constant, regardless of variations in the load or supply voltage.
In this design, the base-emitter junction of the BD140 is activated by the voltage drop across the two 1N4148 diodes, which typically amounts to approximately 1.4V when forward-biased. This biasing allows the transistor to operate in its active region, maintaining a constant current output. The output current can be adjusted by changing the value of the resistor connected to the emitter of the BD140, thereby allowing for flexibility in the charging current based on the specific requirements of the application.
The overall circuit is efficient and straightforward, making it suitable for various low-power charging applications. It is important to ensure that the transistor's maximum ratings are not exceeded during operation, and appropriate heat sinking may be required depending on the load conditions. Additionally, the choice of diodes and their placement within the circuit can affect the overall performance and stability of the charger.his simple charger uses a single transistor as a constant current source. The voltage across the pair of 1N4148 diodes biases the base of the BD140 medium power transistor.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by employing the BD140 transistor to regulate the charging current delivered to the load. The 1N4148 diodes serve as a reference voltage source, establishing a stable voltage level that is necessary for the proper biasing of the transistor. This configuration ensures that the charging current remains constant, regardless of variations in the load or supply voltage.
In this design, the base-emitter junction of the BD140 is activated by the voltage drop across the two 1N4148 diodes, which typically amounts to approximately 1.4V when forward-biased. This biasing allows the transistor to operate in its active region, maintaining a constant current output. The output current can be adjusted by changing the value of the resistor connected to the emitter of the BD140, thereby allowing for flexibility in the charging current based on the specific requirements of the application.
The overall circuit is efficient and straightforward, making it suitable for various low-power charging applications. It is important to ensure that the transistor's maximum ratings are not exceeded during operation, and appropriate heat sinking may be required depending on the load conditions. Additionally, the choice of diodes and their placement within the circuit can affect the overall performance and stability of the charger.his simple charger uses a single transistor as a constant current source. The voltage across the pair of 1N4148 diodes biases the base of the BD140 medium power transistor.. 🔗 External reference