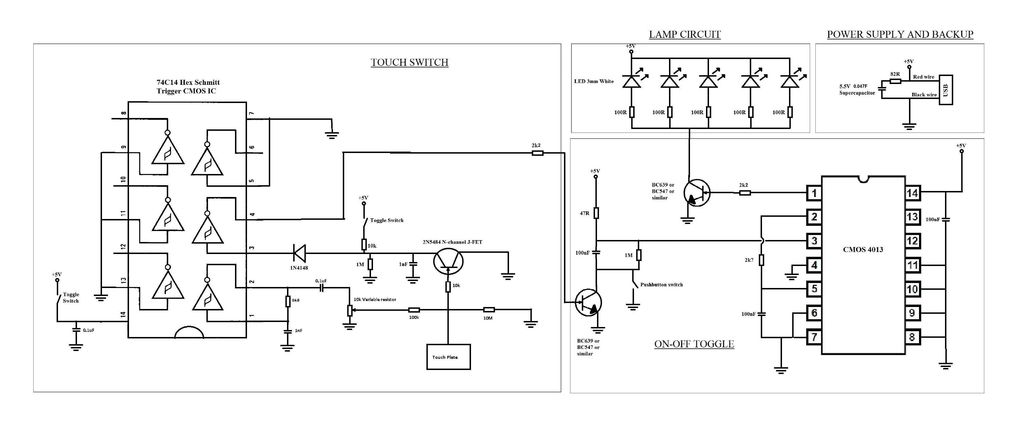
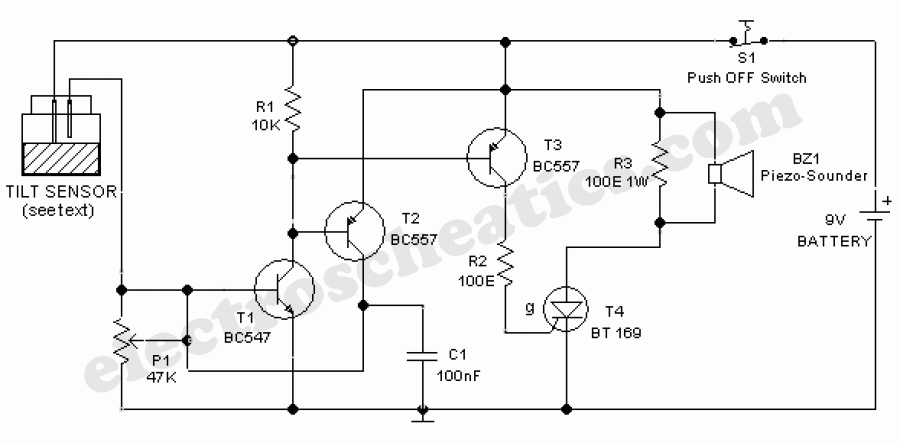
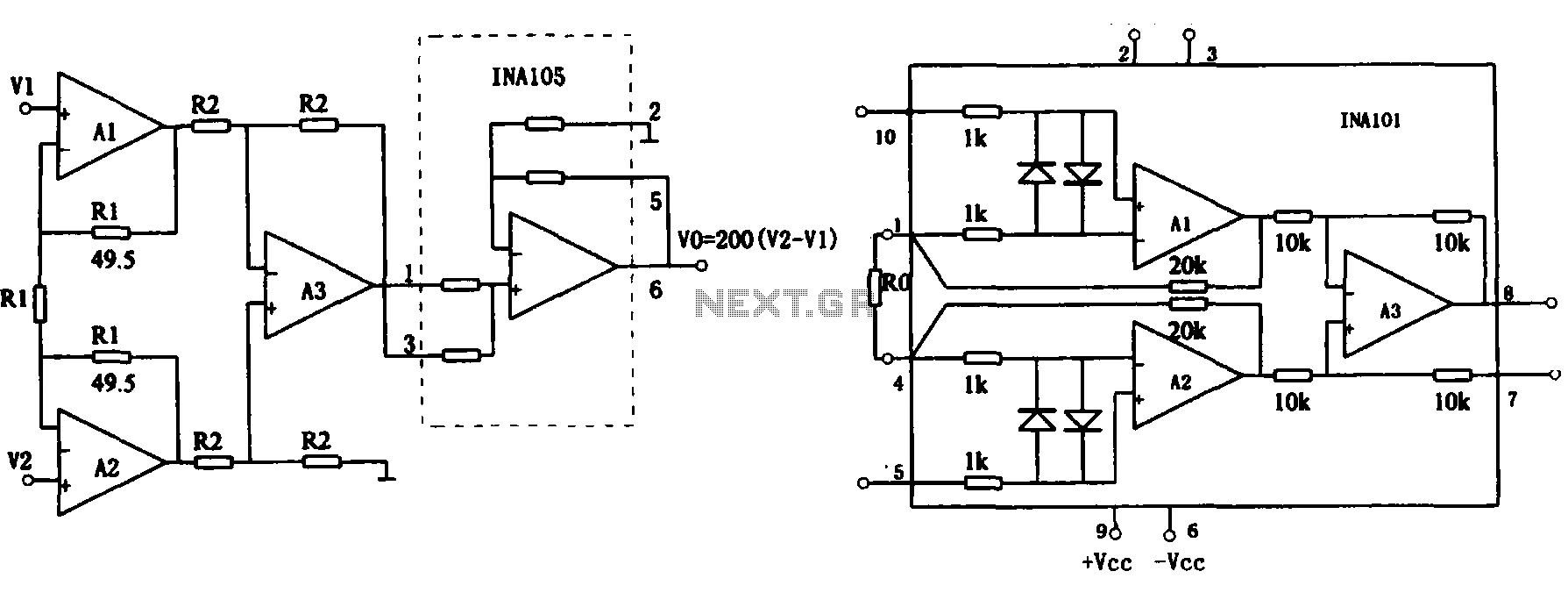
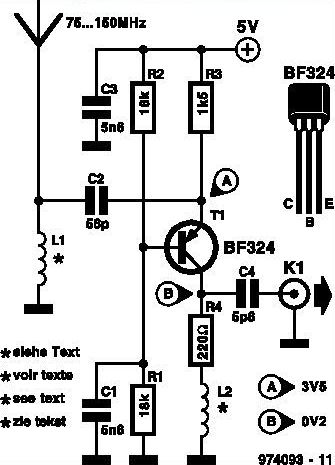
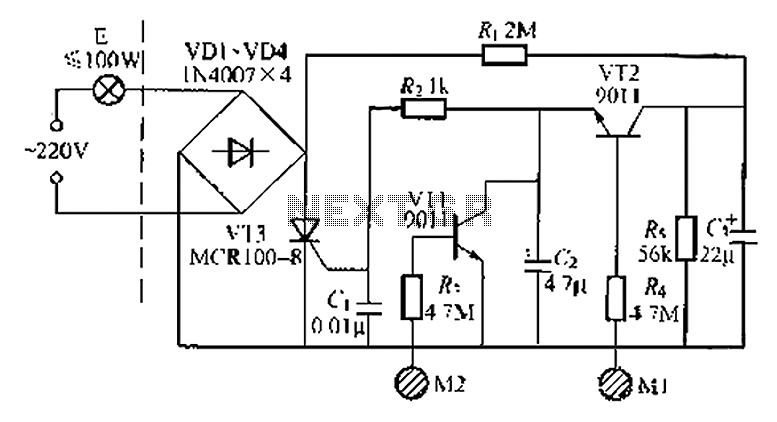
Separately excited DC motor reversing circuit
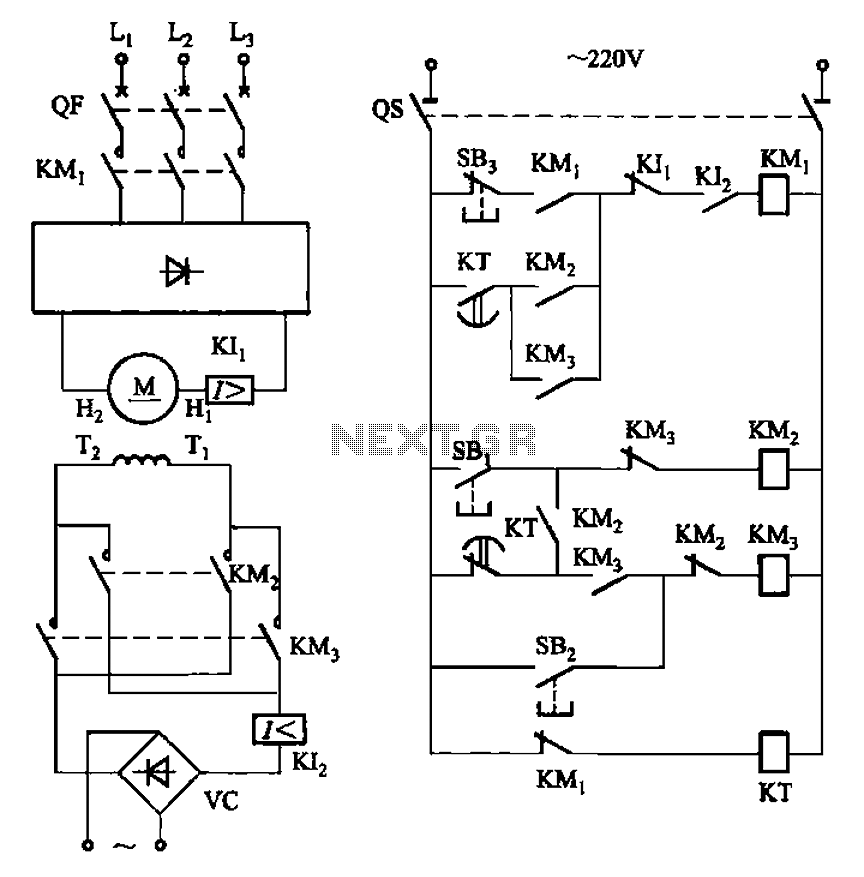
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-193 illustrates a separately excited DC motor. The brake circuit is not activated; therefore, positive reversals occur alternately using a delay action relay, ensuring that the motor reverses direction after coming to a stop.
The schematic involves a separately excited DC motor, which is powered by an external voltage source that is independent of the armature circuit. This configuration allows for better control over the motor speed and torque.
In the circuit, a relay is employed to manage the motor's operation. The delay action relay is crucial for controlling the timing of the motor's reversal. When the motor is commanded to stop, the relay introduces a predefined delay before reversing the motor's direction. This delay is necessary to allow the motor to come to a complete stop before engaging the opposite polarity, thereby preventing mechanical stress and potential damage.
The braking mechanism is passive in this circuit, meaning that it does not actively apply a braking force but relies on the natural inertia of the motor and the load it drives. This approach can be beneficial in applications where rapid deceleration is not critical, but it requires careful timing to ensure smooth transitions between forward and reverse operations.
Overall, the circuit design emphasizes the importance of timing and control in motor applications, particularly in scenarios where alternating direction is required. The use of a separately excited motor combined with a delay action relay provides a reliable method for achieving controlled reversals. Circuit shown in Figure 3-193. Motor is separately excited DC motor. The brake circuit does not take measures, so the positive reversals alternately using delay action time rel ay KT ensure after stopping to reverse the motor started.
The schematic involves a separately excited DC motor, which is powered by an external voltage source that is independent of the armature circuit. This configuration allows for better control over the motor speed and torque.
In the circuit, a relay is employed to manage the motor's operation. The delay action relay is crucial for controlling the timing of the motor's reversal. When the motor is commanded to stop, the relay introduces a predefined delay before reversing the motor's direction. This delay is necessary to allow the motor to come to a complete stop before engaging the opposite polarity, thereby preventing mechanical stress and potential damage.
The braking mechanism is passive in this circuit, meaning that it does not actively apply a braking force but relies on the natural inertia of the motor and the load it drives. This approach can be beneficial in applications where rapid deceleration is not critical, but it requires careful timing to ensure smooth transitions between forward and reverse operations.
Overall, the circuit design emphasizes the importance of timing and control in motor applications, particularly in scenarios where alternating direction is required. The use of a separately excited motor combined with a delay action relay provides a reliable method for achieving controlled reversals. Circuit shown in Figure 3-193. Motor is separately excited DC motor. The brake circuit does not take measures, so the positive reversals alternately using delay action time rel ay KT ensure after stopping to reverse the motor started.