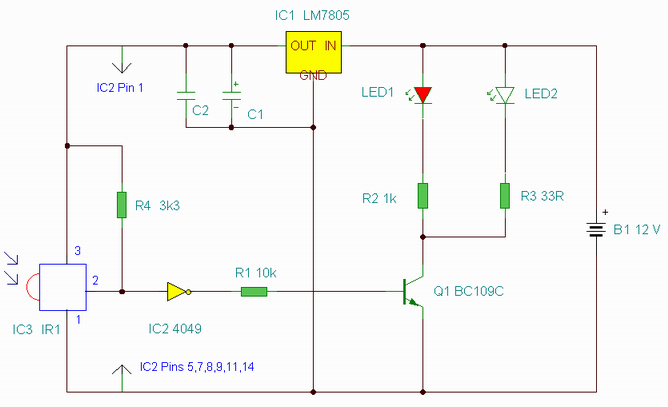
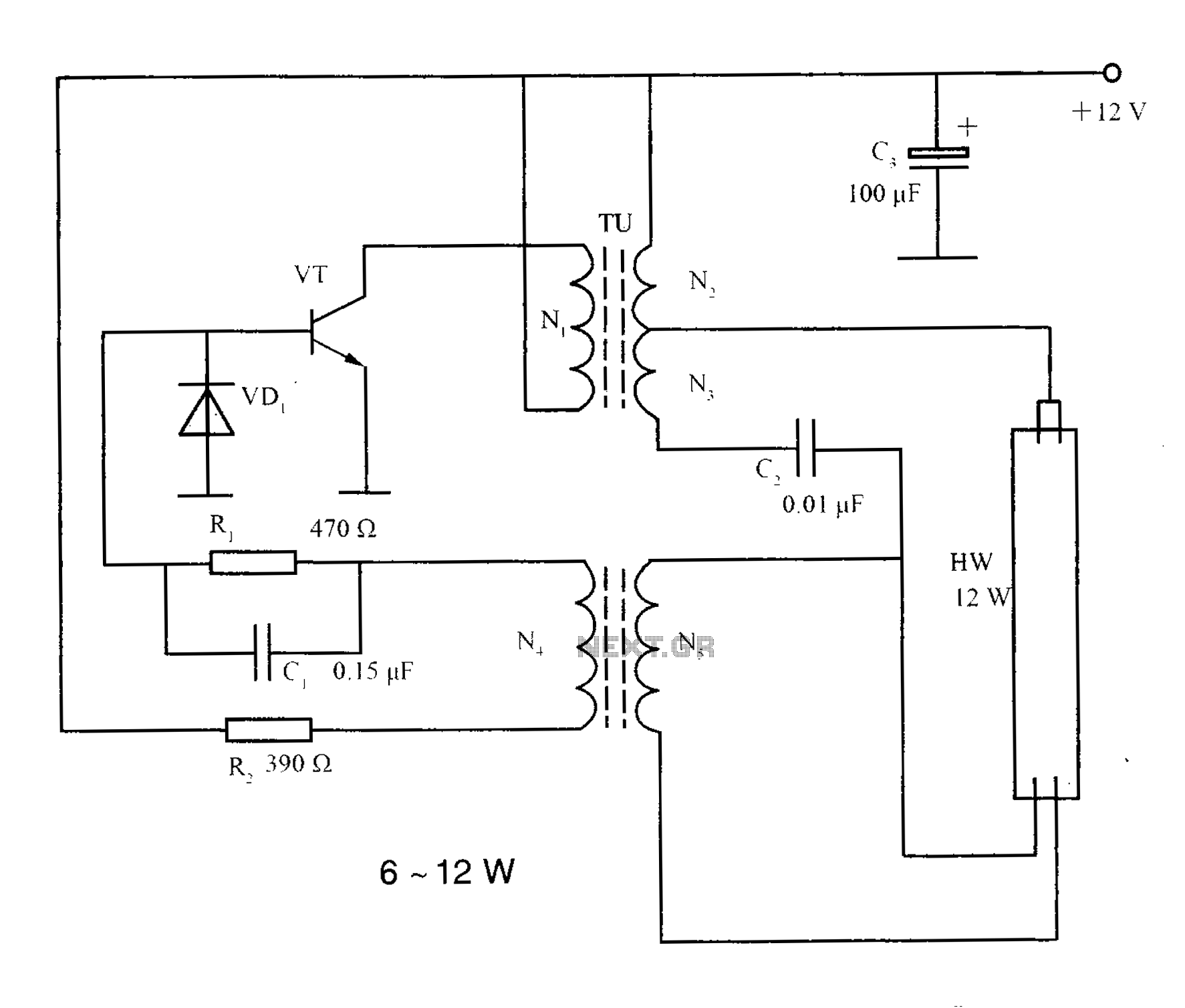
nicd battery charger circuit
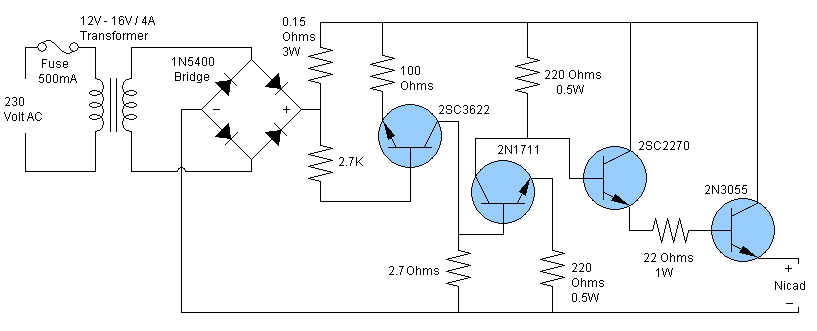
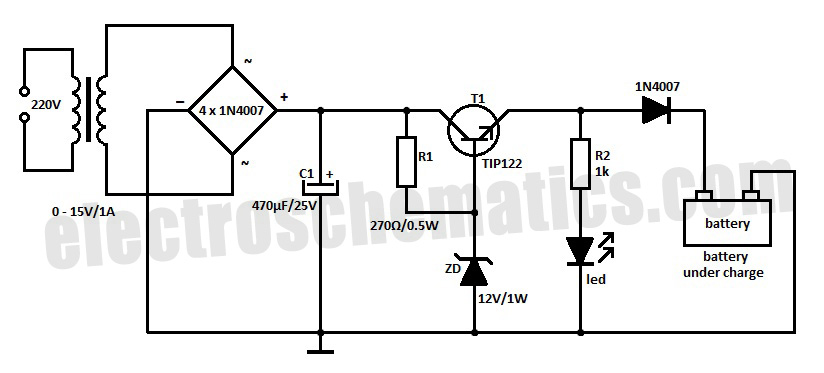
NiCd battery charger schematic and description. This NiCd battery charger circuit can charge 12V, 6V, and 9V battery packs.
The NiCd battery charger circuit is designed to efficiently charge nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries, specifically those with voltage ratings of 12V, 6V, and 9V. The circuit typically consists of a transformer, rectifier, voltage regulator, and additional components such as resistors and capacitors to ensure stable operation.
The transformer steps down the mains voltage to a suitable level for charging the batteries. After the transformer, a rectifier converts the alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). The rectified output is then smoothed using capacitors to reduce voltage ripples, ensuring a more stable charging voltage.
A voltage regulator may be included to maintain the charging voltage at an appropriate level for the specific battery voltage being charged. This is crucial because overcharging can lead to battery damage and reduced lifespan. Additional components, such as diodes, may be employed to prevent reverse current flow, protecting the circuit and the batteries.
To accommodate different battery voltages, the circuit may feature selectable configurations or a variable resistor that allows the user to adjust the charging voltage as needed. Safety features, such as thermal protection and current limiting, are also essential to prevent overheating and overcurrent conditions during the charging process.
Overall, this NiCd battery charger circuit provides a reliable solution for charging various battery packs while ensuring safety and efficiency.Nicd battery charger schematic and description. This Nicd battery charger circuit can charge 12V, 6V, & 9V battery packs. .. 🔗 External reference
The NiCd battery charger circuit is designed to efficiently charge nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries, specifically those with voltage ratings of 12V, 6V, and 9V. The circuit typically consists of a transformer, rectifier, voltage regulator, and additional components such as resistors and capacitors to ensure stable operation.
The transformer steps down the mains voltage to a suitable level for charging the batteries. After the transformer, a rectifier converts the alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). The rectified output is then smoothed using capacitors to reduce voltage ripples, ensuring a more stable charging voltage.
A voltage regulator may be included to maintain the charging voltage at an appropriate level for the specific battery voltage being charged. This is crucial because overcharging can lead to battery damage and reduced lifespan. Additional components, such as diodes, may be employed to prevent reverse current flow, protecting the circuit and the batteries.
To accommodate different battery voltages, the circuit may feature selectable configurations or a variable resistor that allows the user to adjust the charging voltage as needed. Safety features, such as thermal protection and current limiting, are also essential to prevent overheating and overcurrent conditions during the charging process.
Overall, this NiCd battery charger circuit provides a reliable solution for charging various battery packs while ensuring safety and efficiency.Nicd battery charger schematic and description. This Nicd battery charger circuit can charge 12V, 6V, & 9V battery packs. .. 🔗 External reference