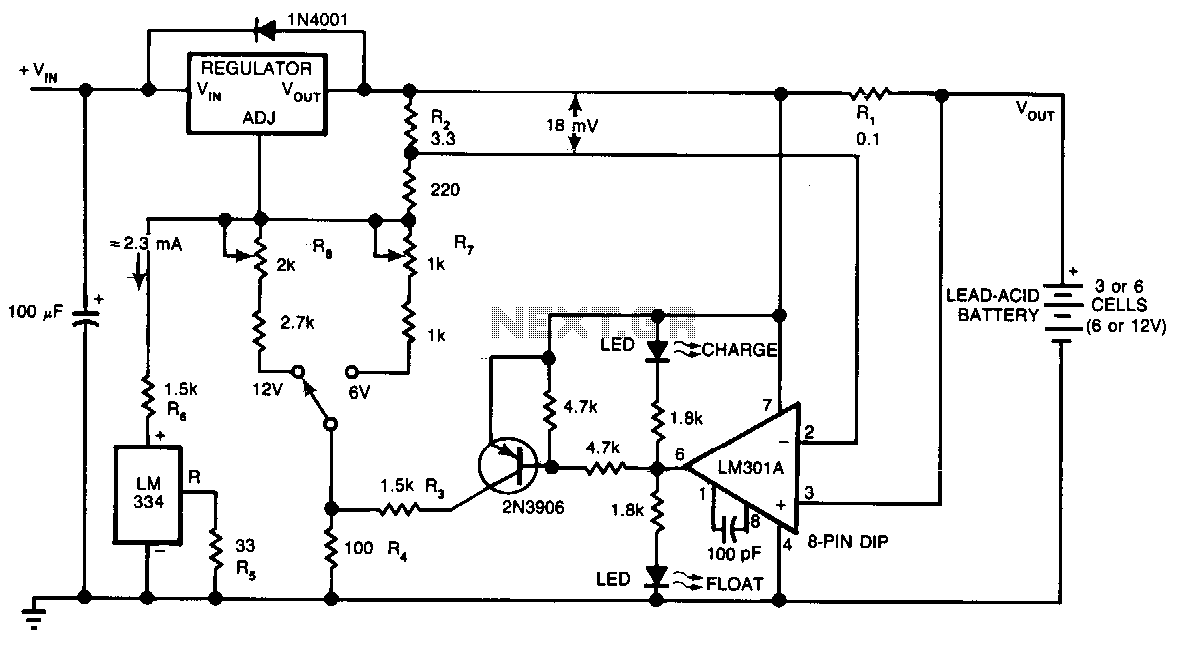
nicd battery charger with reverse polarity protection

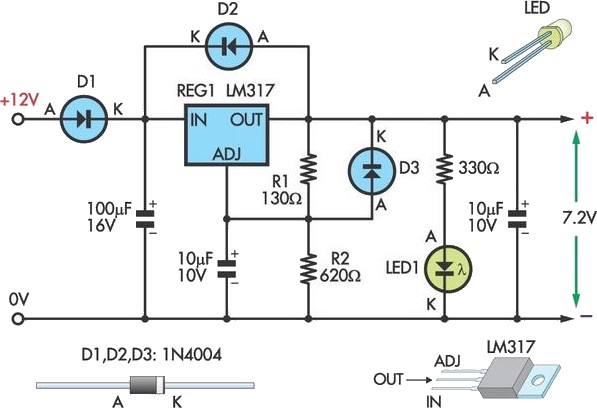
This NiCd battery charger is capable of charging up to seven NiCd batteries connected in series. The number of batteries can be increased if the power supply voltage is raised by 1.65V for each additional battery. When Q2 is mounted on an appropriate heatsink, the input voltage can be maximally increased to 25V. Unlike many commercial NiCd chargers available in the market, this charger features reverse polarity protection. Another notable advantage is that it does not discharge the battery when the charger is disconnected from the power supply.
The NiCd battery charger operates by utilizing a series configuration to efficiently charge multiple batteries simultaneously. The design allows for a scalable charging solution, accommodating additional batteries as long as the power supply voltage is adjusted accordingly. Each additional battery requires an increase of 1.65V, ensuring that the charger can maintain effective charging conditions.
Incorporating Q2, a critical component in this circuit, allows for the input voltage to be increased to a maximum of 25V when adequately cooled with a heatsink. This feature enhances the charger's versatility, enabling it to handle various configurations and battery counts without compromising performance.
The reverse polarity protection is implemented to safeguard the circuit against incorrect connections, a common issue in battery charging applications. This feature significantly enhances the reliability and safety of the charger, making it suitable for both novice and experienced users.
Moreover, the charger is designed to prevent battery discharge when disconnected from the power supply, which is a crucial aspect for maintaining battery life and performance. This characteristic ensures that the batteries remain charged and ready for use without the risk of self-discharge, providing an added layer of convenience for users.
In summary, this NiCd battery charger combines scalability, safety, and efficiency, making it a robust solution for charging multiple NiCd batteries in various configurations. The careful consideration of component specifications and features ensures reliable operation and user-friendly experience.This NiCd battery Charger can charge up to 7 NiCd batteries connected in series. This number can be increased if the power supply is increased with 1.65V for each supplementary battery. If Q2 is mounted on a proper heatsink, the input voltage can be increased at a maximum of 25V. Unlike most of comercial NiCd chargers available on the market, this charger has a reverse polarity protection.
Another great quality is that it does not discharge the battery if the charger is disconnected from the power supply.. 🔗 External reference
The NiCd battery charger operates by utilizing a series configuration to efficiently charge multiple batteries simultaneously. The design allows for a scalable charging solution, accommodating additional batteries as long as the power supply voltage is adjusted accordingly. Each additional battery requires an increase of 1.65V, ensuring that the charger can maintain effective charging conditions.
Incorporating Q2, a critical component in this circuit, allows for the input voltage to be increased to a maximum of 25V when adequately cooled with a heatsink. This feature enhances the charger's versatility, enabling it to handle various configurations and battery counts without compromising performance.
The reverse polarity protection is implemented to safeguard the circuit against incorrect connections, a common issue in battery charging applications. This feature significantly enhances the reliability and safety of the charger, making it suitable for both novice and experienced users.
Moreover, the charger is designed to prevent battery discharge when disconnected from the power supply, which is a crucial aspect for maintaining battery life and performance. This characteristic ensures that the batteries remain charged and ready for use without the risk of self-discharge, providing an added layer of convenience for users.
In summary, this NiCd battery charger combines scalability, safety, and efficiency, making it a robust solution for charging multiple NiCd batteries in various configurations. The careful consideration of component specifications and features ensures reliable operation and user-friendly experience.This NiCd battery Charger can charge up to 7 NiCd batteries connected in series. This number can be increased if the power supply is increased with 1.65V for each supplementary battery. If Q2 is mounted on a proper heatsink, the input voltage can be increased at a maximum of 25V. Unlike most of comercial NiCd chargers available on the market, this charger has a reverse polarity protection.
Another great quality is that it does not discharge the battery if the charger is disconnected from the power supply.. 🔗 External reference