nicd nimh battery charger circuit
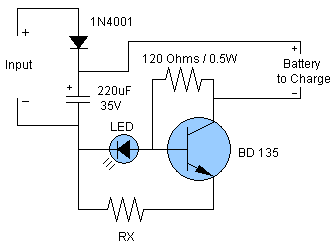
Schematic and description of a simple and easy-to-build NiCd and NiMH battery charger circuit that is capable of charging multiple NiCd and NiMH batteries.
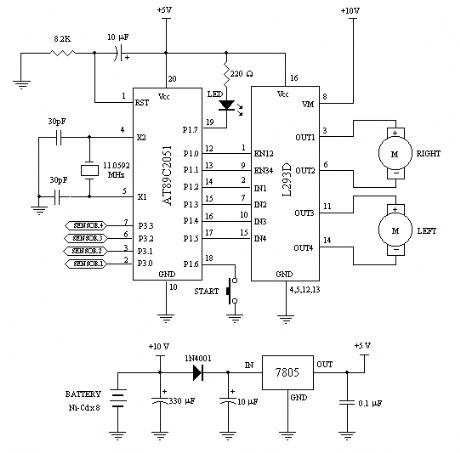
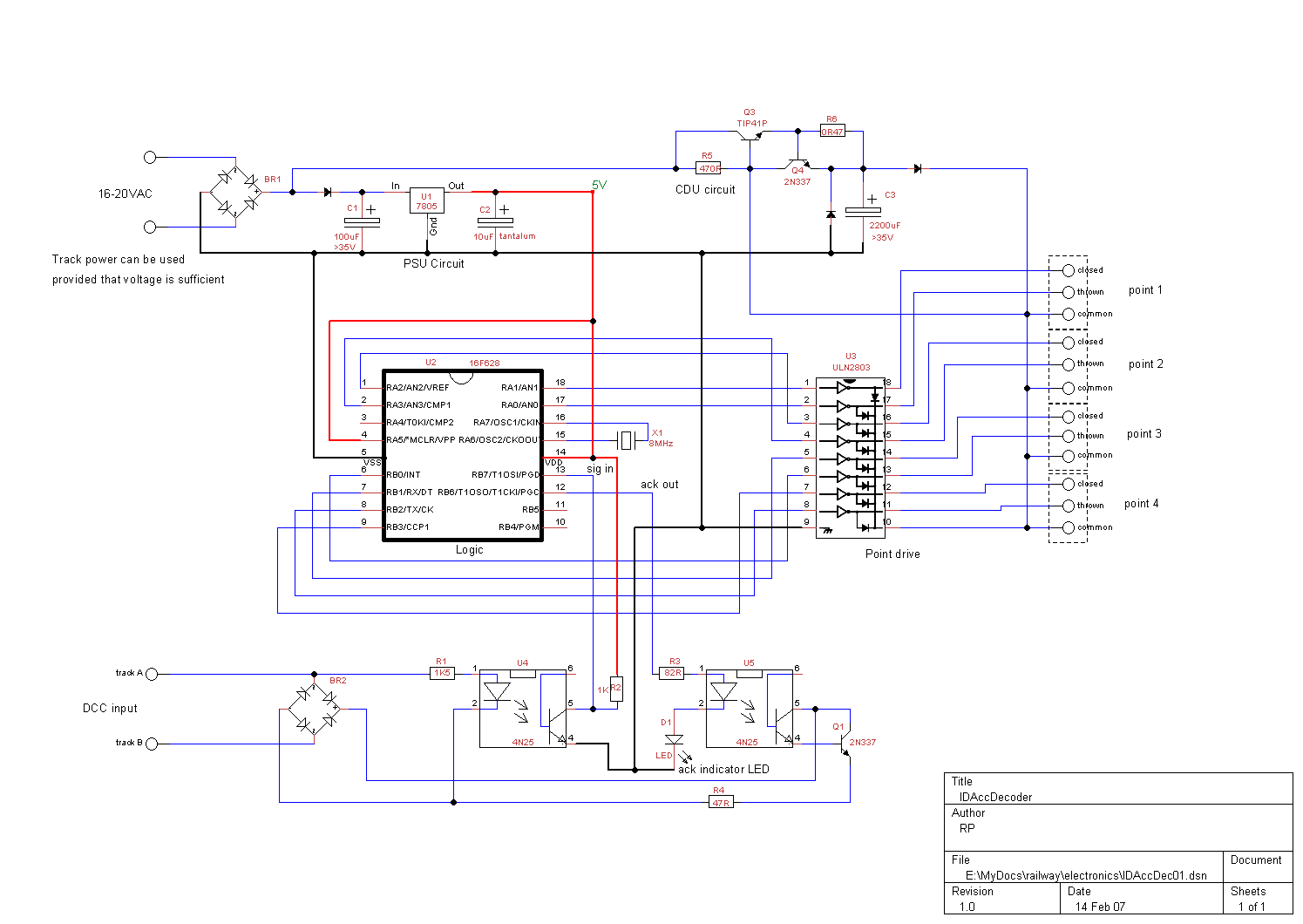
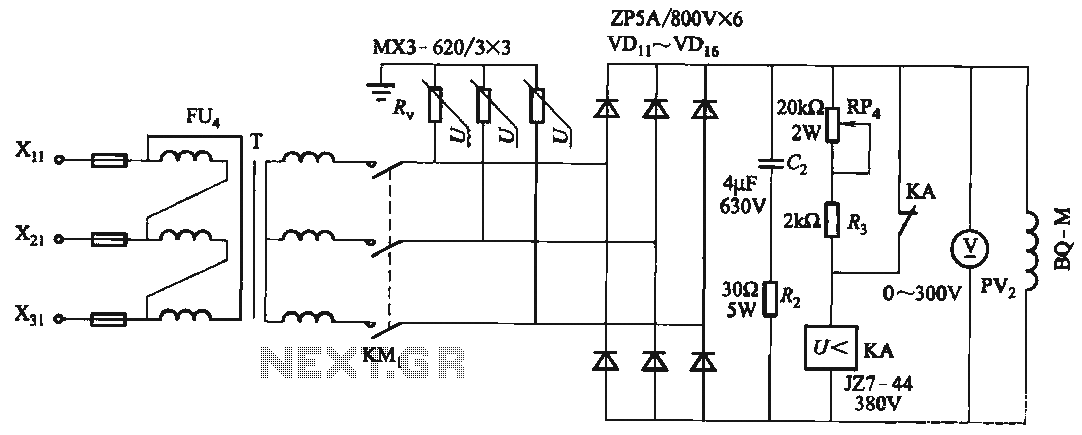
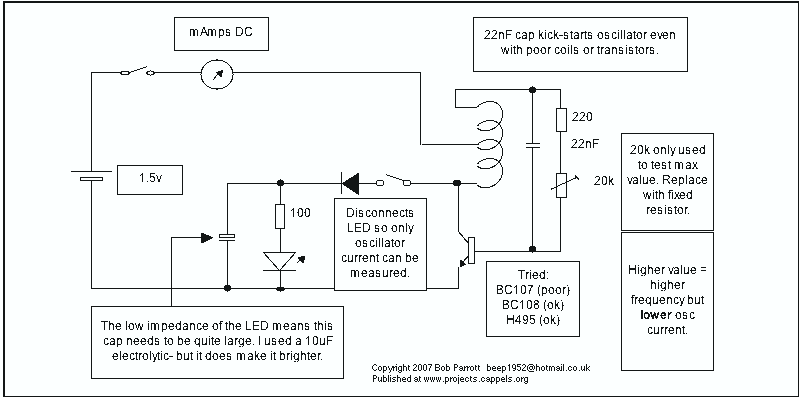
The circuit for the NiCd and NiMH battery charger is designed to be straightforward, allowing for the charging of multiple batteries simultaneously. The schematic typically includes a power supply, a charging control circuit, and battery connections.
The power supply can be a standard AC to DC adapter that provides the necessary voltage and current for charging. The charging control circuit often consists of a voltage regulator, which ensures that the output voltage remains stable and appropriate for charging NiCd and NiMH batteries.
A common configuration may include a series of resistors and diodes to manage the charging current and protect against reverse polarity. Additionally, a microcontroller or simple comparator circuit can be integrated to monitor the battery voltage and terminate charging once the batteries reach full charge, preventing overcharging and extending battery life.
Battery connections are typically made using a terminal block or soldered connections, allowing for easy attachment and detachment of the batteries. It is essential to ensure that the circuit is designed to handle the specific voltage and current ratings of the batteries being charged, with appropriate safety features such as fuses or thermal cutoffs to prevent overheating.
In summary, this charger circuit is a practical solution for charging multiple NiCd and NiMH batteries, combining simplicity in design with effective charging capabilities. Proper attention to component selection and circuit layout is crucial for optimal performance and safety.Schematic and description of a simple and easy to built NiCd and Nimh battery charger circuit which is able to charge multiple NiCd and NiMH batteries. .. 🔗 External reference
The circuit for the NiCd and NiMH battery charger is designed to be straightforward, allowing for the charging of multiple batteries simultaneously. The schematic typically includes a power supply, a charging control circuit, and battery connections.
The power supply can be a standard AC to DC adapter that provides the necessary voltage and current for charging. The charging control circuit often consists of a voltage regulator, which ensures that the output voltage remains stable and appropriate for charging NiCd and NiMH batteries.
A common configuration may include a series of resistors and diodes to manage the charging current and protect against reverse polarity. Additionally, a microcontroller or simple comparator circuit can be integrated to monitor the battery voltage and terminate charging once the batteries reach full charge, preventing overcharging and extending battery life.
Battery connections are typically made using a terminal block or soldered connections, allowing for easy attachment and detachment of the batteries. It is essential to ensure that the circuit is designed to handle the specific voltage and current ratings of the batteries being charged, with appropriate safety features such as fuses or thermal cutoffs to prevent overheating.
In summary, this charger circuit is a practical solution for charging multiple NiCd and NiMH batteries, combining simplicity in design with effective charging capabilities. Proper attention to component selection and circuit layout is crucial for optimal performance and safety.Schematic and description of a simple and easy to built NiCd and Nimh battery charger circuit which is able to charge multiple NiCd and NiMH batteries. .. 🔗 External reference