Noisy Regen Receiver
The following circuit illustrates a Noisy Regenerative Receiver Circuit Diagram. Features include a Noisy Regenerative Receiver Circuit, which simplifies the process of...
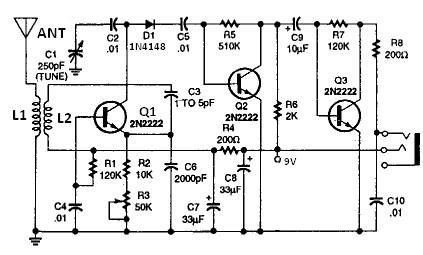
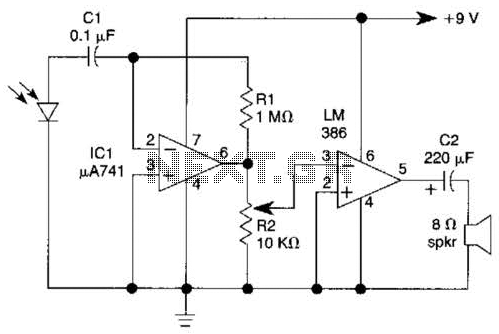
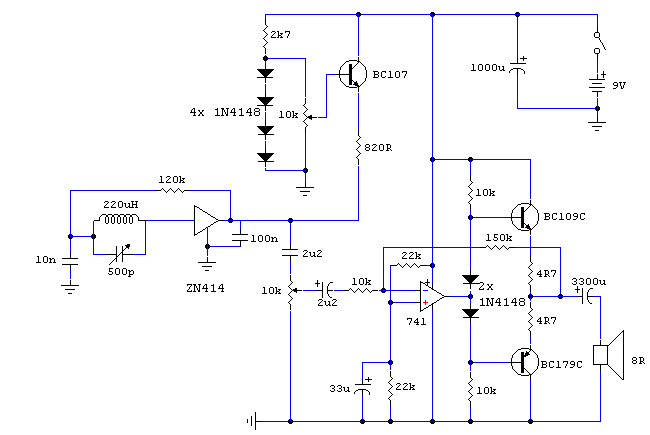
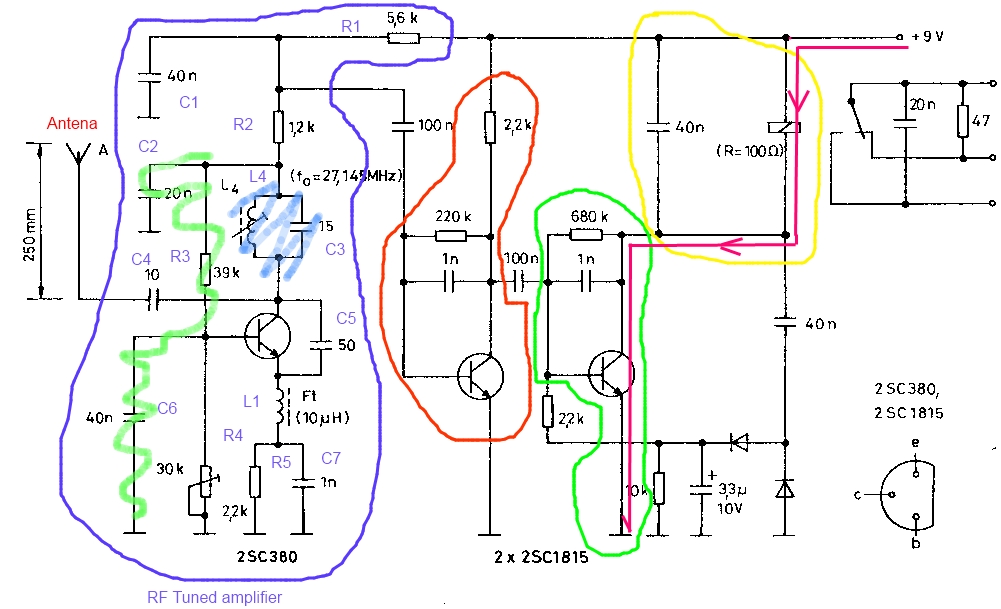
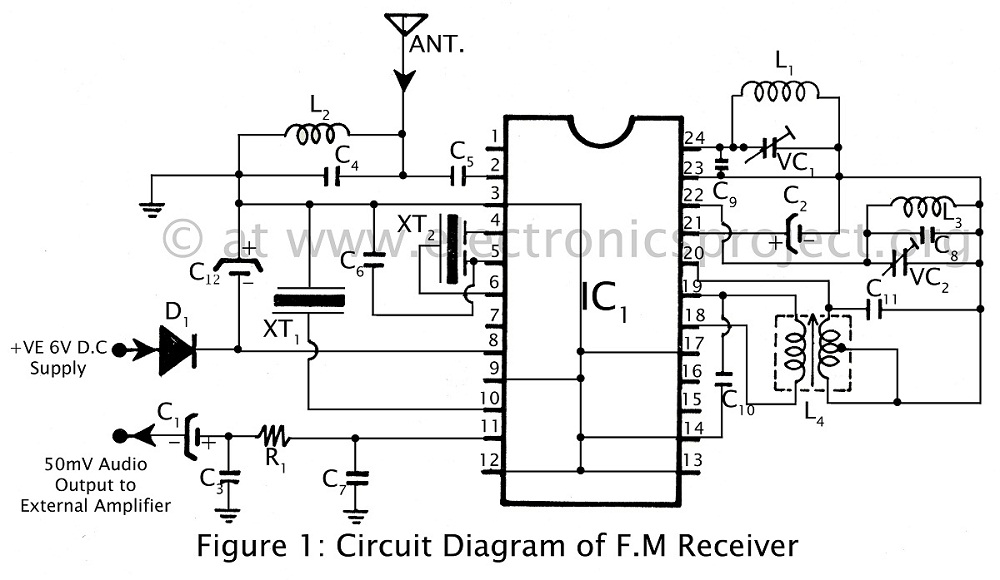
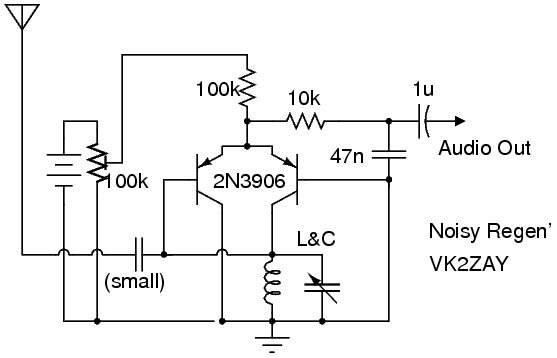
The Noisy Regenerative Receiver Circuit is designed to amplify weak radio frequency signals while also incorporating a regenerative feedback mechanism. This type of circuit is particularly useful in scenarios where signal strength is low, allowing for improved reception of distant radio stations.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a transistor or operational amplifier, resistors, capacitors, and an inductor, which acts as part of the tuning element. The regenerative aspect is achieved by feeding a portion of the output signal back to the input, which enhances the gain and sensitivity of the circuit.
In this configuration, the input signal is first filtered through a tuned circuit, composed of the inductor and capacitors, to select the desired frequency. The amplified output is then fed back into the input via a feedback resistor, which is crucial for maintaining stability and preventing oscillations.
The design allows for adjustments to be made to the feedback loop, enabling the user to control the gain and bandwidth of the receiver. This flexibility makes the Noisy Regenerative Receiver Circuit an excellent choice for applications in amateur radio and experimental electronics, where signal clarity and reception range are paramount.
Proper layout and component selection are essential for minimizing noise and maximizing performance. Careful consideration should be given to the placement of components to reduce interference, and the use of shielded cables can further enhance the circuit's effectiveness. Overall, the Noisy Regenerative Receiver Circuit is a valuable tool for enhancing radio signal reception in various applications.The following circuit shows about Noisy Regen Receiver Circuit Diagram. Features: Noisy Regenerative Receiver Circuit, making it easier to .. 🔗 External reference
The Noisy Regenerative Receiver Circuit is designed to amplify weak radio frequency signals while also incorporating a regenerative feedback mechanism. This type of circuit is particularly useful in scenarios where signal strength is low, allowing for improved reception of distant radio stations.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a transistor or operational amplifier, resistors, capacitors, and an inductor, which acts as part of the tuning element. The regenerative aspect is achieved by feeding a portion of the output signal back to the input, which enhances the gain and sensitivity of the circuit.
In this configuration, the input signal is first filtered through a tuned circuit, composed of the inductor and capacitors, to select the desired frequency. The amplified output is then fed back into the input via a feedback resistor, which is crucial for maintaining stability and preventing oscillations.
The design allows for adjustments to be made to the feedback loop, enabling the user to control the gain and bandwidth of the receiver. This flexibility makes the Noisy Regenerative Receiver Circuit an excellent choice for applications in amateur radio and experimental electronics, where signal clarity and reception range are paramount.
Proper layout and component selection are essential for minimizing noise and maximizing performance. Careful consideration should be given to the placement of components to reduce interference, and the use of shielded cables can further enhance the circuit's effectiveness. Overall, the Noisy Regenerative Receiver Circuit is a valuable tool for enhancing radio signal reception in various applications.The following circuit shows about Noisy Regen Receiver Circuit Diagram. Features: Noisy Regenerative Receiver Circuit, making it easier to .. 🔗 External reference