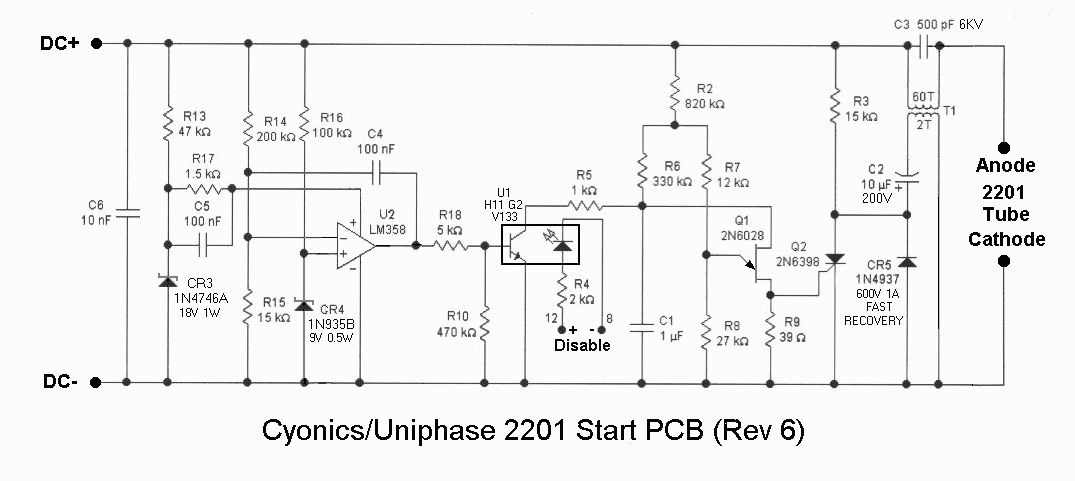
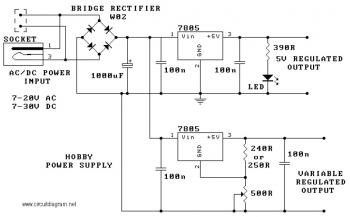
notebook power car adapter 19 volt

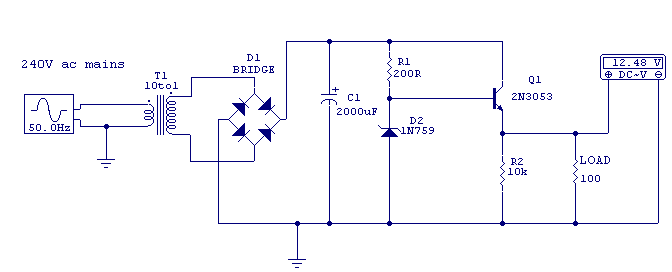
The car cigarette lighter outputs a DC voltage of 12 V, which does not exceed 13.8 V even when the engine is running. A voltage of 19 V is lower than the normally required levels.
The car cigarette lighter circuit is designed to provide a stable DC voltage output, primarily 12 V, which is suitable for powering various automotive accessories such as phone chargers, GPS devices, and other electronic gadgets. The voltage remains consistent at 12 V under normal operating conditions, ensuring compatibility with devices that require this specific voltage for proper functionality.
When the vehicle's engine is running, the voltage at the cigarette lighter may increase slightly but will not exceed 13.8 V. This characteristic is crucial for protecting sensitive electronic devices from overvoltage conditions, which could lead to damage or malfunction. The circuit typically includes a fuse to prevent excessive current draw, thereby ensuring safety and reliability.
The design of the cigarette lighter socket includes a spring-loaded mechanism that allows for easy insertion and removal of plugs. The socket is usually connected to the vehicle's battery through a wiring harness that is capable of handling the current required by the accessories. The wiring must be adequately sized to prevent voltage drop and overheating, which could compromise the performance and safety of the connected devices.
In summary, the car cigarette lighter circuit provides a reliable and safe means of delivering DC power to automotive accessories, with built-in protections against voltage spikes and excessive current. This makes it an essential component in modern vehicles, facilitating the use of a wide range of electronic devices while on the road.Car cigarette lighter output DC voltage is 12 V, even when the engine is running will not exceed 13 .8 V, 19 V voltage lower than the normally required of.. 🔗 External reference
The car cigarette lighter circuit is designed to provide a stable DC voltage output, primarily 12 V, which is suitable for powering various automotive accessories such as phone chargers, GPS devices, and other electronic gadgets. The voltage remains consistent at 12 V under normal operating conditions, ensuring compatibility with devices that require this specific voltage for proper functionality.
When the vehicle's engine is running, the voltage at the cigarette lighter may increase slightly but will not exceed 13.8 V. This characteristic is crucial for protecting sensitive electronic devices from overvoltage conditions, which could lead to damage or malfunction. The circuit typically includes a fuse to prevent excessive current draw, thereby ensuring safety and reliability.
The design of the cigarette lighter socket includes a spring-loaded mechanism that allows for easy insertion and removal of plugs. The socket is usually connected to the vehicle's battery through a wiring harness that is capable of handling the current required by the accessories. The wiring must be adequately sized to prevent voltage drop and overheating, which could compromise the performance and safety of the connected devices.
In summary, the car cigarette lighter circuit provides a reliable and safe means of delivering DC power to automotive accessories, with built-in protections against voltage spikes and excessive current. This makes it an essential component in modern vehicles, facilitating the use of a wide range of electronic devices while on the road.Car cigarette lighter output DC voltage is 12 V, even when the engine is running will not exceed 13 .8 V, 19 V voltage lower than the normally required of.. 🔗 External reference