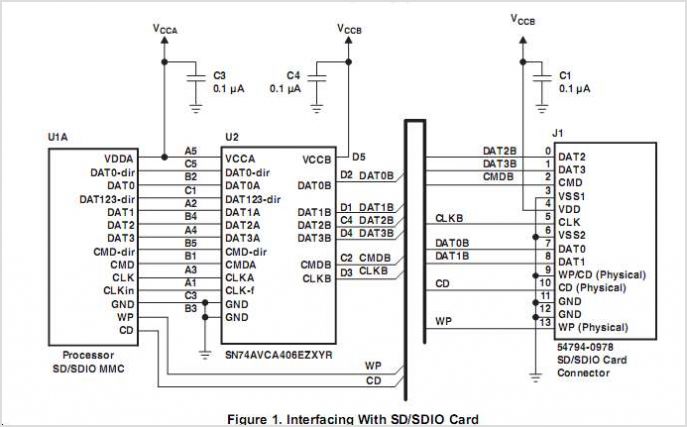
SD card IO
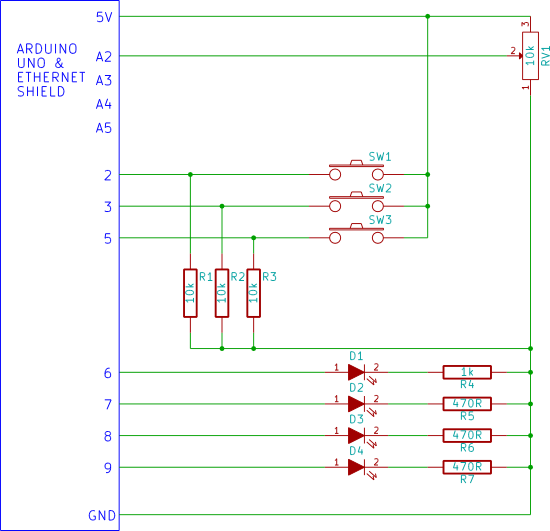
Input and output (I/O) on the Arduino web server using the SD card. Arduino inputs (analog inputs, switches) are displayed on a web page. Arduino outputs (LEDs) are controlled from a web page. Uses Ajax for flicker-free loading.
The described circuit involves an Arduino microcontroller interfacing with an SD card to create a web server that can handle both input and output operations. The system utilizes analog inputs, such as sensors or potentiometers, and digital inputs from switches, which are monitored by the Arduino. The status of these inputs is then displayed on a web page, allowing users to view real-time data.
For output control, the circuit includes LEDs that can be turned on or off via commands sent from the web interface. This interaction is facilitated through the use of Ajax, which allows for asynchronous communication between the web page and the Arduino server. This technology ensures that the web page updates without the need to refresh, providing a seamless user experience.
The Arduino is connected to the SD card module, which stores the HTML and JavaScript files necessary for the web interface. The SD card module is typically connected to the Arduino using the SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) protocol, which involves connecting the MOSI, MISO, SCK, and CS pins appropriately.
The inputs from the analog sensors are read using the Arduino's analog pins, while digital inputs from switches are read using the digital pins. The state of these inputs is processed by the Arduino code, which then updates the web page content dynamically.
For output control, the LEDs are connected to digital pins on the Arduino. The web interface includes buttons that send commands to the Arduino to change the state of these LEDs. The use of Ajax allows these commands to be sent without reloading the entire page, ensuring a flicker-free user experience.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines input and output functionalities within an Arduino web server context, utilizing an SD card for storage and Ajax for a responsive interface, thereby enabling real-time monitoring and control of connected devices.Input and output (I/O) on the Arduino web server using the SD card. Arduino inputs (analogue inputs, switches) are displayed on a web page. Arduino outputs (LEDs) are controlled from a web page. Uses Ajax for flicker free loading.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit involves an Arduino microcontroller interfacing with an SD card to create a web server that can handle both input and output operations. The system utilizes analog inputs, such as sensors or potentiometers, and digital inputs from switches, which are monitored by the Arduino. The status of these inputs is then displayed on a web page, allowing users to view real-time data.
For output control, the circuit includes LEDs that can be turned on or off via commands sent from the web interface. This interaction is facilitated through the use of Ajax, which allows for asynchronous communication between the web page and the Arduino server. This technology ensures that the web page updates without the need to refresh, providing a seamless user experience.
The Arduino is connected to the SD card module, which stores the HTML and JavaScript files necessary for the web interface. The SD card module is typically connected to the Arduino using the SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) protocol, which involves connecting the MOSI, MISO, SCK, and CS pins appropriately.
The inputs from the analog sensors are read using the Arduino's analog pins, while digital inputs from switches are read using the digital pins. The state of these inputs is processed by the Arduino code, which then updates the web page content dynamically.
For output control, the LEDs are connected to digital pins on the Arduino. The web interface includes buttons that send commands to the Arduino to change the state of these LEDs. The use of Ajax allows these commands to be sent without reloading the entire page, ensuring a flicker-free user experience.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines input and output functionalities within an Arduino web server context, utilizing an SD card for storage and Ajax for a responsive interface, thereby enabling real-time monitoring and control of connected devices.Input and output (I/O) on the Arduino web server using the SD card. Arduino inputs (analogue inputs, switches) are displayed on a web page. Arduino outputs (LEDs) are controlled from a web page. Uses Ajax for flicker free loading.. 🔗 External reference