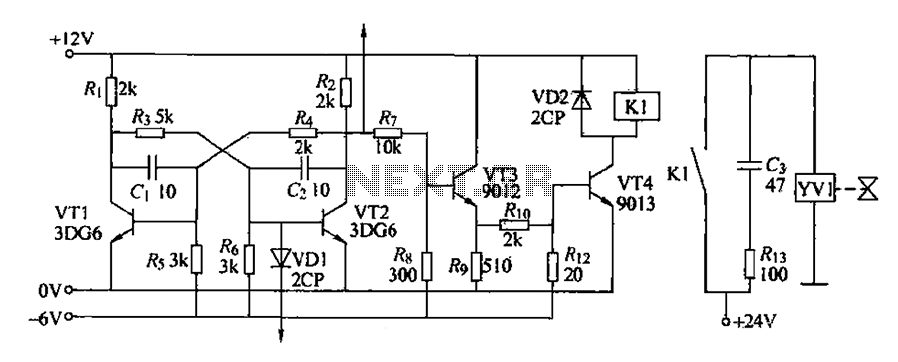
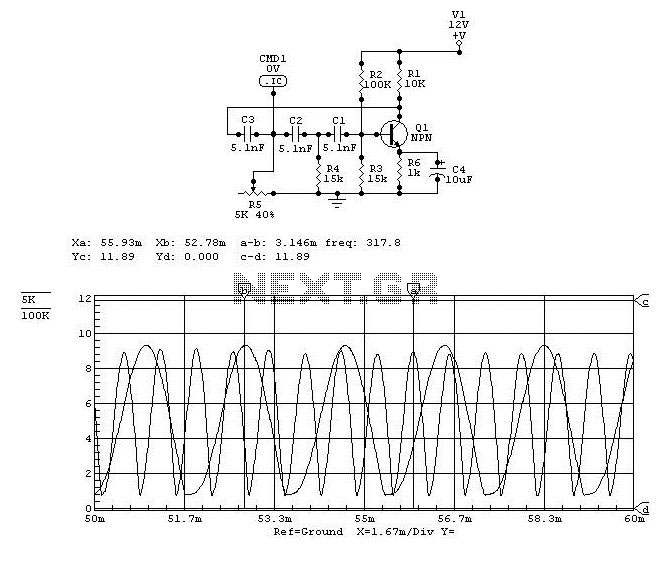
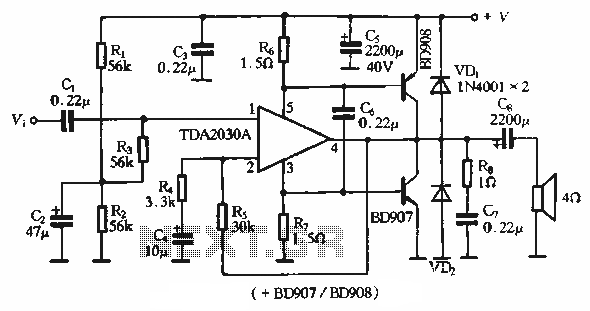
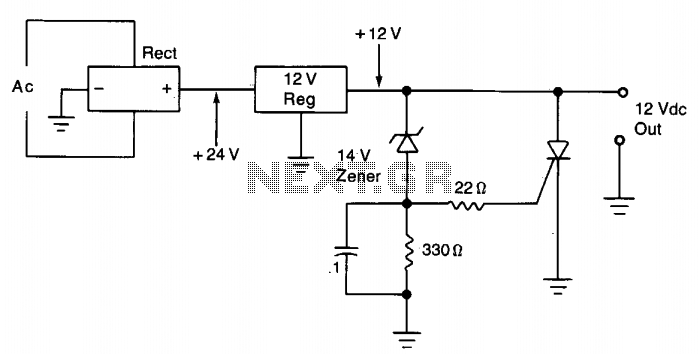
Octave Equalizer Circuit
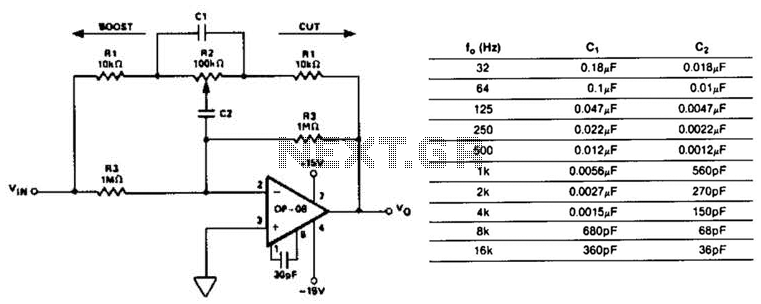
This circuit represents a section of an octave equalizer utilized in audio systems. The table outlines the values of C1 and C2 required to achieve specific center frequencies. This circuit can provide a boost or cut of 12 dB, which is determined by the position of R2. Due to the low input bias current of the OP-08 operational amplifier, the resistors can be scaled up by a factor of 10, allowing for a reduction in the values of C1 and C2 at the lower frequency range. Furthermore, a total of 10 sections will draw a maximum combined supply current of 6 mA.
The octave equalizer circuit is designed to enhance audio signals by allowing specific frequency bands to be adjusted independently. Each section of the equalizer corresponds to a specific octave band, enabling precise control over the audio spectrum. The operational amplifier used in this design, the OP-08, exhibits low input bias current, which is advantageous for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing distortion.
The capacitors C1 and C2 are crucial for determining the center frequencies of each octave band. By selecting appropriate values for these capacitors, the circuit can be tuned to target specific frequencies, thus allowing the user to boost or cut audio levels as desired. The resistor R2 acts as a variable element in the circuit, enabling the adjustment of gain and attenuation. When R2 is positioned to allow maximum resistance, the circuit can achieve a 12 dB cut, while a lower resistance setting will provide a 12 dB boost.
The ability to scale resistors by a factor of 10 is particularly beneficial for low-frequency applications. This scaling reduces the necessary capacitance values, which can help in minimizing the physical size of the components and improving the overall performance of the circuit. Additionally, the low supply current requirement of 6 mA for 10 sections makes this design efficient, allowing it to be integrated into various audio systems without significant power consumption.
Overall, this octave equalizer circuit provides a versatile solution for audio signal processing, enabling users to tailor sound characteristics to their preferences while maintaining high fidelity and low power consumption. This circuit is one section of an octave equalizer used in audio systems. The table shows the values of CI and C2 that are needed to achieve the given center frequencies. This circuit is capable of 12 dB boost or cut, as determined by the position of R2. Because of the low input bias current of the OP-08, the resistors could be scaled up by a factor of 10, and thereby reduce the values of CI and C2 at the low-frequency end. In addition, 10 sections will only draw a combined supply current of 6 mA maximum.
The octave equalizer circuit is designed to enhance audio signals by allowing specific frequency bands to be adjusted independently. Each section of the equalizer corresponds to a specific octave band, enabling precise control over the audio spectrum. The operational amplifier used in this design, the OP-08, exhibits low input bias current, which is advantageous for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing distortion.
The capacitors C1 and C2 are crucial for determining the center frequencies of each octave band. By selecting appropriate values for these capacitors, the circuit can be tuned to target specific frequencies, thus allowing the user to boost or cut audio levels as desired. The resistor R2 acts as a variable element in the circuit, enabling the adjustment of gain and attenuation. When R2 is positioned to allow maximum resistance, the circuit can achieve a 12 dB cut, while a lower resistance setting will provide a 12 dB boost.
The ability to scale resistors by a factor of 10 is particularly beneficial for low-frequency applications. This scaling reduces the necessary capacitance values, which can help in minimizing the physical size of the components and improving the overall performance of the circuit. Additionally, the low supply current requirement of 6 mA for 10 sections makes this design efficient, allowing it to be integrated into various audio systems without significant power consumption.
Overall, this octave equalizer circuit provides a versatile solution for audio signal processing, enabling users to tailor sound characteristics to their preferences while maintaining high fidelity and low power consumption. This circuit is one section of an octave equalizer used in audio systems. The table shows the values of CI and C2 that are needed to achieve the given center frequencies. This circuit is capable of 12 dB boost or cut, as determined by the position of R2. Because of the low input bias current of the OP-08, the resistors could be scaled up by a factor of 10, and thereby reduce the values of CI and C2 at the low-frequency end. In addition, 10 sections will only draw a combined supply current of 6 mA maximum.