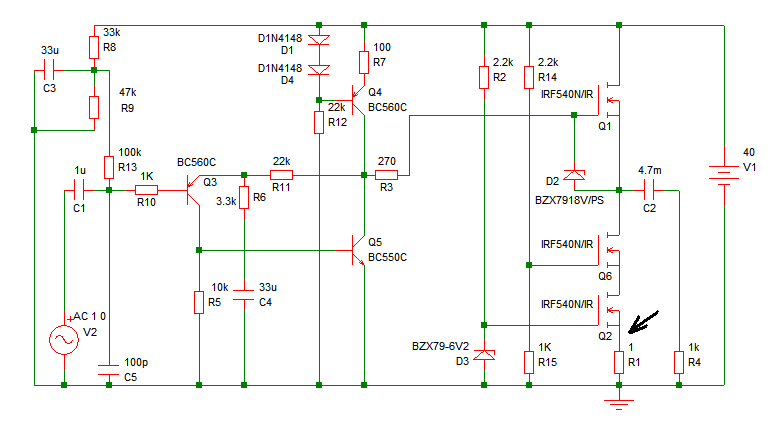
On After Delay with Mosfet

This is an On After Delay Circuit that utilizes a MOSFET for delay, which is simpler than using a transistor. The operation of the circuit is triggered when switch S1 is pressed.
The On After Delay Circuit is designed to provide a delay in the activation of a load after a switch is pressed. The core component of this circuit is a MOSFET, which is preferred over a traditional bipolar junction transistor (BJT) due to its efficiency and ease of use in delay applications.
When switch S1 is pressed, it initiates the delay mechanism. The circuit typically includes a resistor-capacitor (RC) timing network that determines the length of the delay. The capacitor charges through the resistor when S1 is activated, and the voltage across the capacitor rises gradually. Once the voltage reaches a certain threshold, the MOSFET turns on, allowing current to flow to the load.
The MOSFET's gate is connected to the junction of the resistor and capacitor, ensuring that it remains off until the capacitor's voltage is sufficient to exceed the gate-source threshold voltage. This arrangement provides a reliable and adjustable delay, which can be modified by changing the values of the resistor and capacitor.
To ensure proper operation, it is important to select a MOSFET with suitable specifications for the load current and voltage. Additionally, the circuit can incorporate a pull-down resistor to ensure that the MOSFET remains off when S1 is not pressed, preventing false triggering due to noise or floating voltages.
Overall, this On After Delay Circuit is a versatile solution for applications requiring delayed activation, such as in lighting systems, alarms, or other electronic devices where a time delay is beneficial.That be On After Delay Circuit. I uses mosfet in the circuit for delay easy more than the transistor. By have the work of the circuit be when press , S1 ,. 🔗 External reference
The On After Delay Circuit is designed to provide a delay in the activation of a load after a switch is pressed. The core component of this circuit is a MOSFET, which is preferred over a traditional bipolar junction transistor (BJT) due to its efficiency and ease of use in delay applications.
When switch S1 is pressed, it initiates the delay mechanism. The circuit typically includes a resistor-capacitor (RC) timing network that determines the length of the delay. The capacitor charges through the resistor when S1 is activated, and the voltage across the capacitor rises gradually. Once the voltage reaches a certain threshold, the MOSFET turns on, allowing current to flow to the load.
The MOSFET's gate is connected to the junction of the resistor and capacitor, ensuring that it remains off until the capacitor's voltage is sufficient to exceed the gate-source threshold voltage. This arrangement provides a reliable and adjustable delay, which can be modified by changing the values of the resistor and capacitor.
To ensure proper operation, it is important to select a MOSFET with suitable specifications for the load current and voltage. Additionally, the circuit can incorporate a pull-down resistor to ensure that the MOSFET remains off when S1 is not pressed, preventing false triggering due to noise or floating voltages.
Overall, this On After Delay Circuit is a versatile solution for applications requiring delayed activation, such as in lighting systems, alarms, or other electronic devices where a time delay is beneficial.That be On After Delay Circuit. I uses mosfet in the circuit for delay easy more than the transistor. By have the work of the circuit be when press , S1 ,. 🔗 External reference