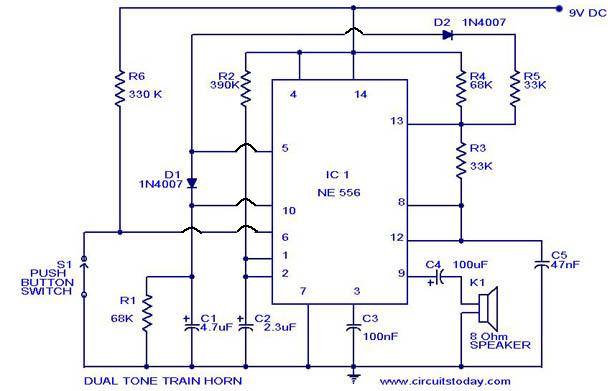
one ic two tones siren with

This circuit is designed for children's entertainment and can be installed on bicycles, battery-powered cars, motorcycles, as well as various models, games, and toys. When switch SW1 is positioned as indicated in the circuit diagram, it generates the typical dual-tone sound of police or fire brigade vehicles through the oscillation of gates IC1A and IC1B. When SW1 is set to the alternate position, it reproduces an old siren sound that increases in frequency and then gradually decreases, initiated by pressing P1, which starts the oscillation in IC1C and IC1D. The loudspeaker, driven by Q1, should be of suitable dimensions and well-encased to achieve a more realistic and louder output. The tone and period of the sound oscillations can be adjusted by changing the values of capacitors C1, C2, C5, C6, and/or their associated resistors. A power switch is not necessary; leaving SW1 in the low position (old-type siren) results in negligible circuit consumption.
This circuit utilizes a combination of integrated circuits (ICs) to produce varied audio outputs suitable for a range of applications in toys and small vehicles. The primary components include operational amplifiers or logic gates configured to oscillate at specific frequencies. The sound generation is achieved through the interaction of IC1A and IC1B for the dual-tone siren, while IC1C and IC1D are responsible for the variable frequency siren sound.
The circuit's functionality is initiated by the user-operated switch SW1, which allows for easy toggling between the two sound modes. The use of potentiometer P1 enhances user interaction by enabling dynamic adjustments to the frequency of the old siren sound, providing an engaging experience for children.
The output stage, represented by Q1, serves as an audio amplifier, ensuring that the sound produced is loud enough to be heard clearly in outdoor environments. The selection of a suitable loudspeaker is critical; it should have an adequate power rating and be housed in a case that amplifies sound without distortion.
Capacitors C1, C2, C5, and C6, along with their associated resistors, form the timing components that dictate the frequency and duration of the sound waves generated. By modifying these components, designers can tailor the sound output to specific preferences or requirements, allowing for customization in various applications.
Overall, this circuit provides a fun and interactive audio experience, making it an ideal addition to children's toys and models, while also being energy-efficient by eliminating the need for a dedicated power switch.This circuit is intended for children fun, and can be installed on bicycles, battery powered cars and motorcycles, but also on models and various games and toys. With SW1 positioned as shown in the circuit diagram, the typical dual-tone sound of Police or Fire-brigade cars is generated, by the oscillation of IC1A and IC1B gates.
With SW1 set to th e other position, the old siren sound increasing in frequency and then slowly decreasing is reproduced, by pushing on P1 that starts oscillation in IC1C and IC1D. The loudspeaker, driven by Q1, should be of reasonable dimensions and well encased, in order to obtain a more realistic and louder output.
Tone and period of the sound oscillations can be varied by changing the values of C1, C2, C5, C6 and/or associated resistors. No power switch is required: leave SW1 in the low position (old-type siren) and the circuit consumption will be negligible.
🔗 External reference
This circuit utilizes a combination of integrated circuits (ICs) to produce varied audio outputs suitable for a range of applications in toys and small vehicles. The primary components include operational amplifiers or logic gates configured to oscillate at specific frequencies. The sound generation is achieved through the interaction of IC1A and IC1B for the dual-tone siren, while IC1C and IC1D are responsible for the variable frequency siren sound.
The circuit's functionality is initiated by the user-operated switch SW1, which allows for easy toggling between the two sound modes. The use of potentiometer P1 enhances user interaction by enabling dynamic adjustments to the frequency of the old siren sound, providing an engaging experience for children.
The output stage, represented by Q1, serves as an audio amplifier, ensuring that the sound produced is loud enough to be heard clearly in outdoor environments. The selection of a suitable loudspeaker is critical; it should have an adequate power rating and be housed in a case that amplifies sound without distortion.
Capacitors C1, C2, C5, and C6, along with their associated resistors, form the timing components that dictate the frequency and duration of the sound waves generated. By modifying these components, designers can tailor the sound output to specific preferences or requirements, allowing for customization in various applications.
Overall, this circuit provides a fun and interactive audio experience, making it an ideal addition to children's toys and models, while also being energy-efficient by eliminating the need for a dedicated power switch.This circuit is intended for children fun, and can be installed on bicycles, battery powered cars and motorcycles, but also on models and various games and toys. With SW1 positioned as shown in the circuit diagram, the typical dual-tone sound of Police or Fire-brigade cars is generated, by the oscillation of IC1A and IC1B gates.
With SW1 set to th e other position, the old siren sound increasing in frequency and then slowly decreasing is reproduced, by pushing on P1 that starts oscillation in IC1C and IC1D. The loudspeaker, driven by Q1, should be of reasonable dimensions and well encased, in order to obtain a more realistic and louder output.
Tone and period of the sound oscillations can be varied by changing the values of C1, C2, C5, C6 and/or associated resistors. No power switch is required: leave SW1 in the low position (old-type siren) and the circuit consumption will be negligible.
🔗 External reference