One thyristor incandescent dimming circuit
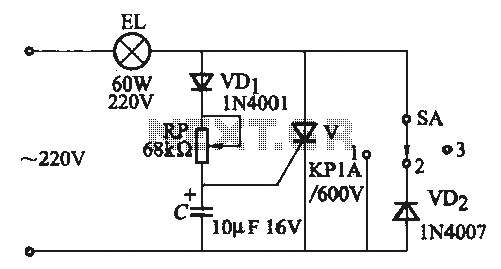
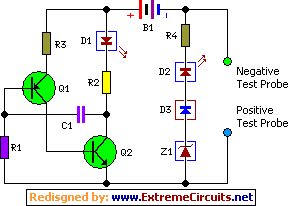
A thyristor-based incandescent dimming circuit is illustrated in Figure 2-66. Figure 2-66 (a) depicts a thyristor half-wave controlled dimmer combined with a diode approach. When switch SA is set to position "3," the adjustment potentiometer RP allows the voltage across the lamp to vary from 20V to 100V. Setting switch SA to position "2" results in the light bulb emitting approximately 1/4 of its rated power. In position "1," all bulbs are fully illuminated. Figure 2-66 (b) shows a dimmer that utilizes only a thyristor for operation, designed for a bulb rated at 110V.
The thyristor incandescent dimming circuit is a sophisticated electronic control system designed to manage the brightness of incandescent lamps by regulating the power delivered to the load. The core component of this circuit is the thyristor, which functions as a controlled rectifier. It allows current to flow through the load only when triggered, effectively controlling the average power delivered to the lamp.
In the configuration shown in Figure 2-66 (a), the circuit incorporates a half-wave control method. The thyristor is connected in series with the lamp, and a diode is used to provide additional control and protection. The adjustment potentiometer RP is crucial for varying the voltage across the lamp, enabling fine-tuning of the brightness. By adjusting RP while the switch SA is set to position "3," users can achieve a voltage range from 20V to 100V, allowing for a broad spectrum of brightness levels.
Switch SA has three positions, each corresponding to a different brightness setting. In position "2," the circuit limits the power to the lamp to approximately 1/4 of its rated capacity, providing a significant reduction in brightness for applications requiring lower light levels. Position "1" allows full power to the lamp, ensuring maximum brightness.
Figure 2-66 (b) simplifies the design by employing only a thyristor for dimming control, suitable for a 110V rated bulb. This design emphasizes the versatility of thyristors in controlling incandescent lighting while maintaining efficiency and reliability. The circuit's design can be adapted for various applications, from residential lighting to industrial settings, where precise light control is essential. Overall, this thyristor-based dimming circuit exemplifies an effective solution for managing incandescent lamp brightness with ease and precision.(1) using thyristor incandescent dimming circuit one circuit is shown in Figure 2-66. Figure 2-66 (a) using thyristor half- wave controlled dimmer and dimmer with diode approach. When the switch SA hit when "3" position, the adjustment potentiometer RP, the voltage across the lamp varies from 20-100V; when SA hit the "2" position, the light bulb brightness light-emitting rated power of about 1/4; when SA hit the "1" bits set when, all light bulbs. Figure 2-66 (b) using only product thyristor dimmer, use rated voltage lloV bulb.
The thyristor incandescent dimming circuit is a sophisticated electronic control system designed to manage the brightness of incandescent lamps by regulating the power delivered to the load. The core component of this circuit is the thyristor, which functions as a controlled rectifier. It allows current to flow through the load only when triggered, effectively controlling the average power delivered to the lamp.
In the configuration shown in Figure 2-66 (a), the circuit incorporates a half-wave control method. The thyristor is connected in series with the lamp, and a diode is used to provide additional control and protection. The adjustment potentiometer RP is crucial for varying the voltage across the lamp, enabling fine-tuning of the brightness. By adjusting RP while the switch SA is set to position "3," users can achieve a voltage range from 20V to 100V, allowing for a broad spectrum of brightness levels.
Switch SA has three positions, each corresponding to a different brightness setting. In position "2," the circuit limits the power to the lamp to approximately 1/4 of its rated capacity, providing a significant reduction in brightness for applications requiring lower light levels. Position "1" allows full power to the lamp, ensuring maximum brightness.
Figure 2-66 (b) simplifies the design by employing only a thyristor for dimming control, suitable for a 110V rated bulb. This design emphasizes the versatility of thyristors in controlling incandescent lighting while maintaining efficiency and reliability. The circuit's design can be adapted for various applications, from residential lighting to industrial settings, where precise light control is essential. Overall, this thyristor-based dimming circuit exemplifies an effective solution for managing incandescent lamp brightness with ease and precision.(1) using thyristor incandescent dimming circuit one circuit is shown in Figure 2-66. Figure 2-66 (a) using thyristor half- wave controlled dimmer and dimmer with diode approach. When the switch SA hit when "3" position, the adjustment potentiometer RP, the voltage across the lamp varies from 20-100V; when SA hit the "2" position, the light bulb brightness light-emitting rated power of about 1/4; when SA hit the "1" bits set when, all light bulbs. Figure 2-66 (b) using only product thyristor dimmer, use rated voltage lloV bulb.