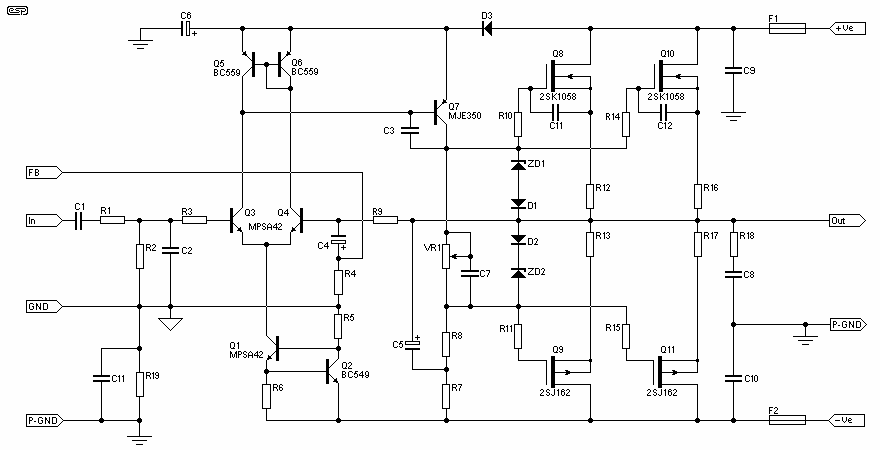
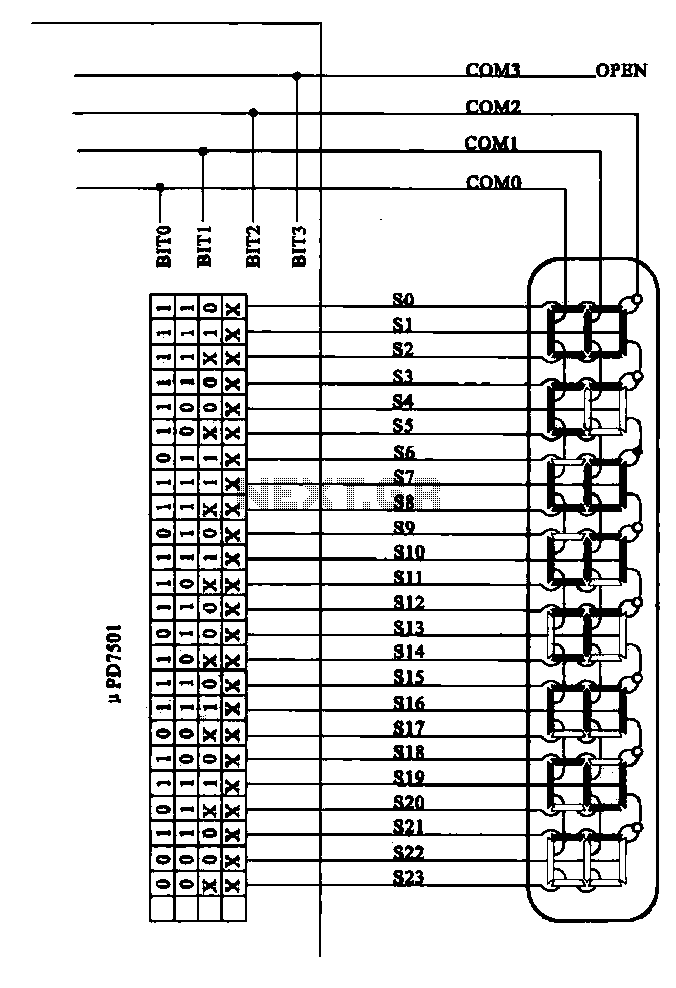
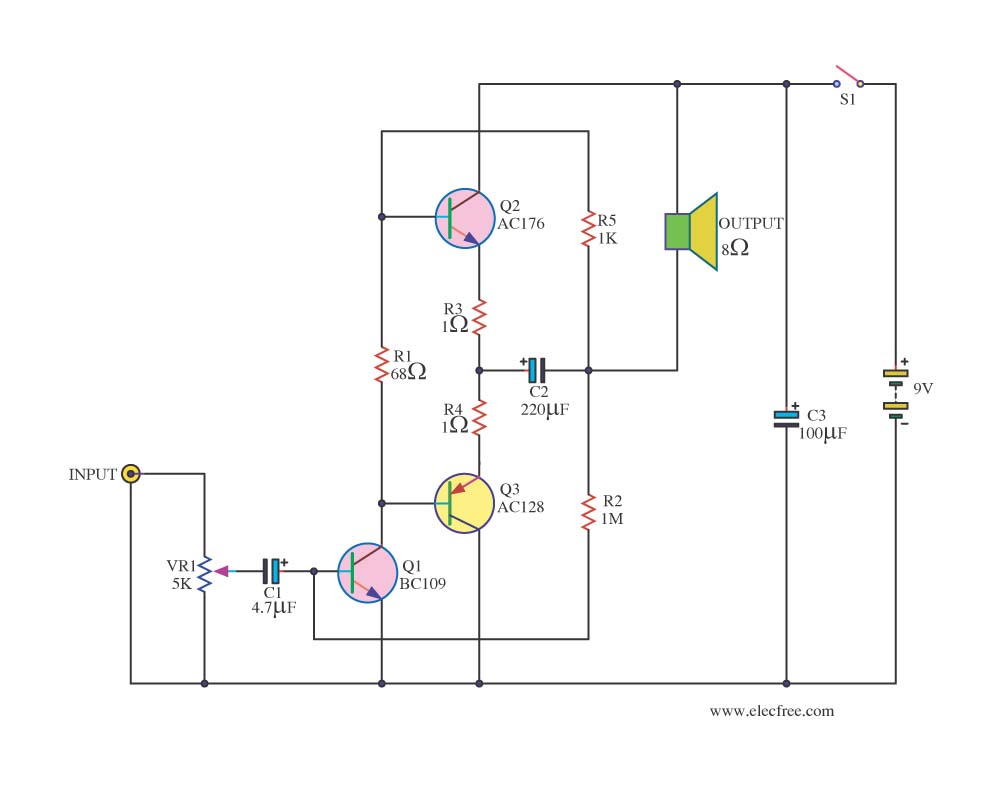
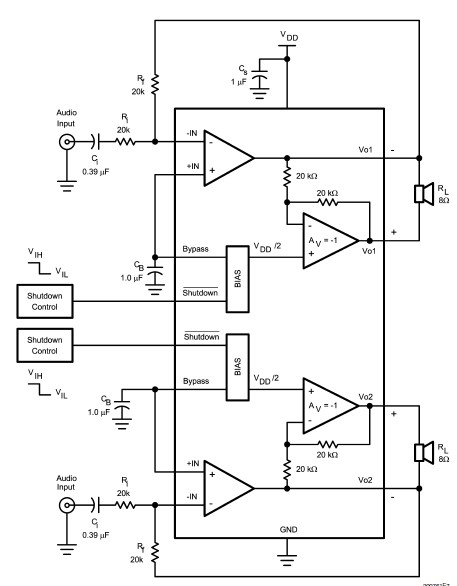
Op Amp And Two JFETs Form A Voltage-Controlled Amplifier

A simple linear voltage-controlled amplifier can be constructed with one operational amplifier (op amp) and two junction field-effect transistors (JFETs). This amplifier can achieve an 80-dB dynamic control range with less than ±0.2% linearity error for 0 V.
The described circuit utilizes a single op amp in conjunction with two JFETs to create a voltage-controlled amplifier (VCA) that operates efficiently within a specified dynamic range. The operational amplifier serves as the core component for signal amplification and control, while the JFETs function as variable resistors, modulated by an input control voltage.
In this configuration, the op amp is typically connected in a non-inverting configuration to ensure that the output maintains the same phase as the input signal. The two JFETs are arranged in a manner that allows for the adjustment of the gain based on the control voltage applied to their gates. This setup enables the amplifier to provide a wide dynamic control range of 80 dB, making it suitable for applications requiring precise amplitude control.
The linearity error of less than ±0.2% indicates that the amplifier maintains a high degree of fidelity across its operational range, which is critical for audio and signal processing applications. The low distortion ensures that the output closely resembles the input signal, barring the amplification factor.
In terms of implementation, careful selection of the op amp and JFETs is essential to achieve the desired performance characteristics. The op amp should have a high slew rate and low noise to minimize signal degradation. The JFETs must be chosen based on their transconductance and threshold voltage to ensure they operate effectively within the linear region throughout the control voltage range.
Overall, this linear voltage-controlled amplifier design offers a robust solution for applications that require precise control over signal amplification while maintaining high linearity and low distortion.A simple linear voltage-controlled amplifier can be constructed with one op amp and two JFETs (see the figure). The amplifier can achieve an 80-dB dynamic control range with less than ±0.2% linearity error for 0 V .
🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a single op amp in conjunction with two JFETs to create a voltage-controlled amplifier (VCA) that operates efficiently within a specified dynamic range. The operational amplifier serves as the core component for signal amplification and control, while the JFETs function as variable resistors, modulated by an input control voltage.
In this configuration, the op amp is typically connected in a non-inverting configuration to ensure that the output maintains the same phase as the input signal. The two JFETs are arranged in a manner that allows for the adjustment of the gain based on the control voltage applied to their gates. This setup enables the amplifier to provide a wide dynamic control range of 80 dB, making it suitable for applications requiring precise amplitude control.
The linearity error of less than ±0.2% indicates that the amplifier maintains a high degree of fidelity across its operational range, which is critical for audio and signal processing applications. The low distortion ensures that the output closely resembles the input signal, barring the amplification factor.
In terms of implementation, careful selection of the op amp and JFETs is essential to achieve the desired performance characteristics. The op amp should have a high slew rate and low noise to minimize signal degradation. The JFETs must be chosen based on their transconductance and threshold voltage to ensure they operate effectively within the linear region throughout the control voltage range.
Overall, this linear voltage-controlled amplifier design offers a robust solution for applications that require precise control over signal amplification while maintaining high linearity and low distortion.A simple linear voltage-controlled amplifier can be constructed with one op amp and two JFETs (see the figure). The amplifier can achieve an 80-dB dynamic control range with less than ±0.2% linearity error for 0 V .
🔗 External reference