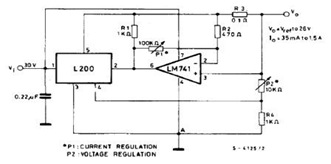
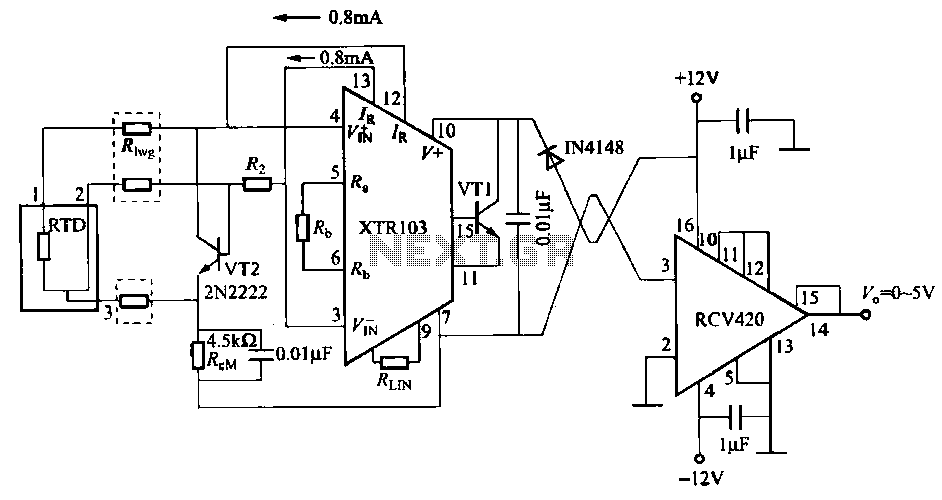
OP90 4 mA to 20 mA Current Loop Transmitter
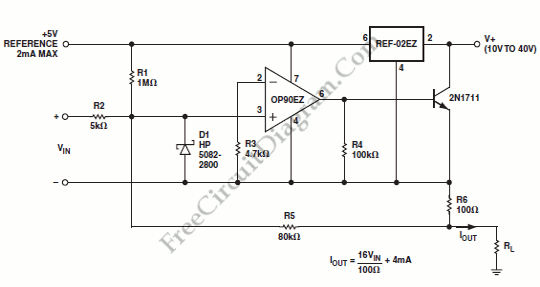
An output of 4 mA to 20 mA that is linearly proportional to the input voltage is provided by the current transmitter. Line rejection is included.
The current transmitter operates within a specified range, providing an output current that is directly proportional to the input voltage. This is typically used in industrial applications for process control, where it translates varying voltage levels into a standardized current signal for further processing or monitoring.
The output range of 4 mA to 20 mA is a common standard in industrial automation, allowing for easy integration with various control systems and devices. The lower limit of 4 mA usually indicates a zero input voltage, while the upper limit of 20 mA corresponds to the maximum input voltage. This linear relationship ensures that any changes in the input voltage result in a corresponding change in the output current, which can be easily measured and interpreted by downstream devices.
Line rejection refers to the ability of the current transmitter to filter out noise and interference from the power supply or other external sources. This ensures that the output signal remains stable and accurate, even in environments with fluctuating electrical conditions. Effective line rejection is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the signal, particularly in applications where precision is essential.
The schematic of the current transmitter would typically include components such as operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors configured to achieve the desired gain and linearity. The input stage may include a differential amplifier to accurately measure the input voltage, while the output stage would be designed to convert this voltage into the specified current output, often utilizing a transistor or a current loop driver.
Overall, this current transmitter is an essential component in many electronic systems, providing reliable and accurate signal conversion for various applications.An output of 4 mA to 20 mA that is linearly proportional to the input voltage is provided by the current transmitter on figure below. Line rejection is. 🔗 External reference
The current transmitter operates within a specified range, providing an output current that is directly proportional to the input voltage. This is typically used in industrial applications for process control, where it translates varying voltage levels into a standardized current signal for further processing or monitoring.
The output range of 4 mA to 20 mA is a common standard in industrial automation, allowing for easy integration with various control systems and devices. The lower limit of 4 mA usually indicates a zero input voltage, while the upper limit of 20 mA corresponds to the maximum input voltage. This linear relationship ensures that any changes in the input voltage result in a corresponding change in the output current, which can be easily measured and interpreted by downstream devices.
Line rejection refers to the ability of the current transmitter to filter out noise and interference from the power supply or other external sources. This ensures that the output signal remains stable and accurate, even in environments with fluctuating electrical conditions. Effective line rejection is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the signal, particularly in applications where precision is essential.
The schematic of the current transmitter would typically include components such as operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors configured to achieve the desired gain and linearity. The input stage may include a differential amplifier to accurately measure the input voltage, while the output stage would be designed to convert this voltage into the specified current output, often utilizing a transistor or a current loop driver.
Overall, this current transmitter is an essential component in many electronic systems, providing reliable and accurate signal conversion for various applications.An output of 4 mA to 20 mA that is linearly proportional to the input voltage is provided by the current transmitter on figure below. Line rejection is. 🔗 External reference