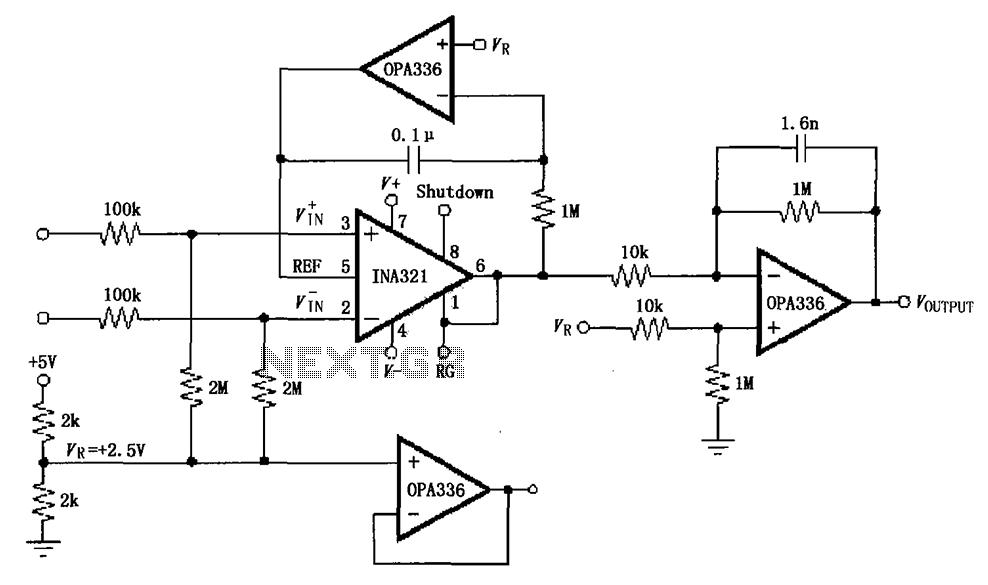
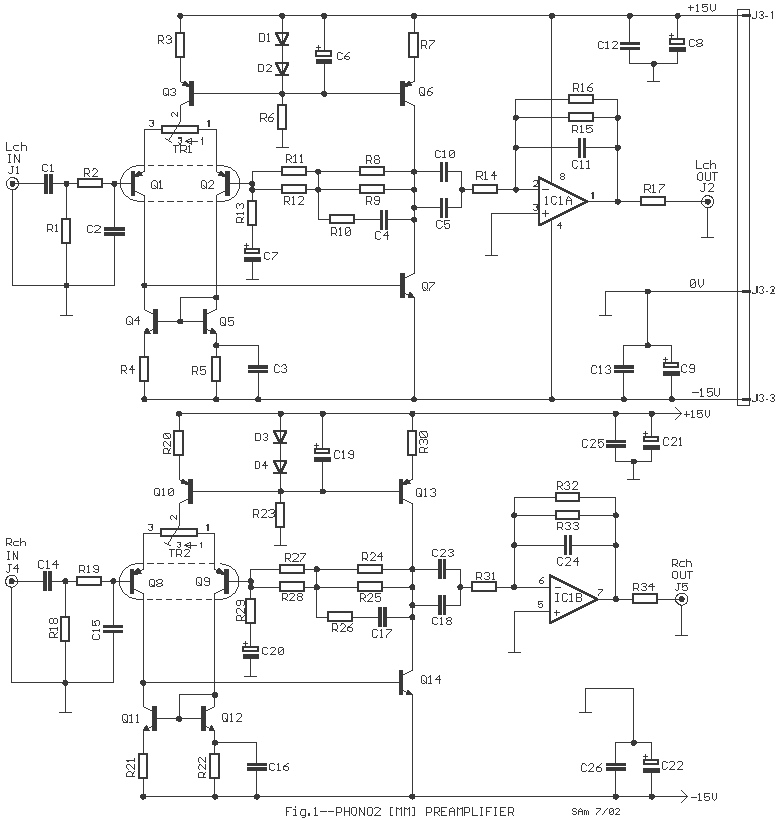
OP90 Micropower Instrumentation Amplifier
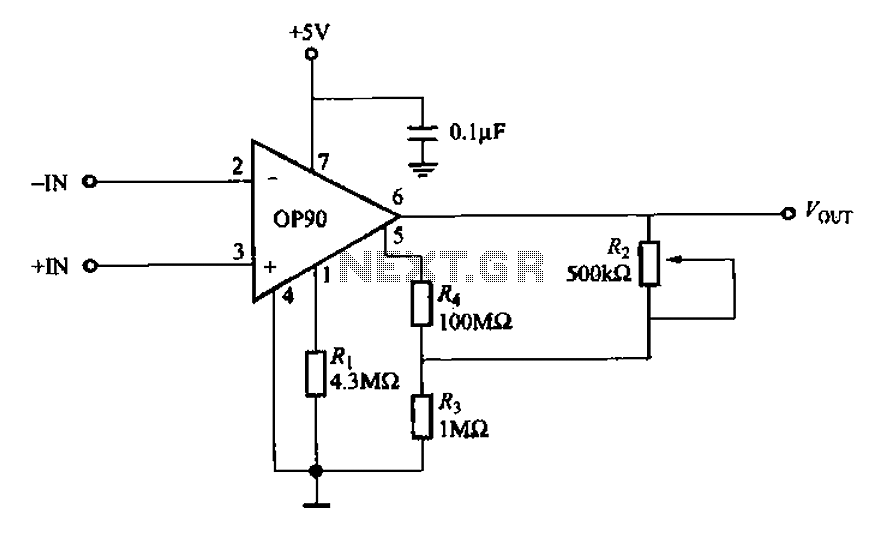
Compared to other operational amplifiers, the OP90 has a significant advantage in low power consumption. Its low power requirements allow for a wide range of power supply voltages (from 1.6V to 18V, and it can also operate with dual supplies from a single supply), making it suitable for portable or battery-powered devices. An example of this is the OP90 configured as a micropower instrumentation amplifier.
The OP90 operational amplifier is designed for applications where low power consumption is critical, particularly in battery-operated devices. Its ability to operate within a wide voltage range enhances its versatility, allowing it to be utilized in various configurations, including single-supply and dual-supply setups.
When configured as a micropower instrumentation amplifier, the OP90 demonstrates its capability to amplify small signals while maintaining low power usage. This configuration typically involves using three OP90 units: two for the differential inputs and one for the output stage.
The input stage typically employs resistors to set the gain of the amplifier, while additional passive components may be included to filter noise and improve stability. The use of low-power resistors ensures that the overall power consumption remains minimal, which is essential for prolonging battery life in portable applications.
In terms of performance, the OP90 offers a low input offset voltage and high input impedance, which are crucial for accurate signal amplification without loading the source. The output stage can drive loads directly or can be coupled to additional stages if further processing is required.
Overall, the OP90's design and characteristics make it an excellent choice for low-power applications, particularly in portable instrumentation and sensor interfacing, where efficiency and performance are paramount. Compared to other operational amplifier, OP90 significant advantage in low power consumption. With its low power consumption, the power supply voltage adapted to a wide range ( 1 6.36V; or 0.8-18V, both can also work in a dual supply from a single supply) and to show their talents in a portable or battery-powered devices. As shown for the OP90 configuration micropower instrumentation amplifier.
The OP90 operational amplifier is designed for applications where low power consumption is critical, particularly in battery-operated devices. Its ability to operate within a wide voltage range enhances its versatility, allowing it to be utilized in various configurations, including single-supply and dual-supply setups.
When configured as a micropower instrumentation amplifier, the OP90 demonstrates its capability to amplify small signals while maintaining low power usage. This configuration typically involves using three OP90 units: two for the differential inputs and one for the output stage.
The input stage typically employs resistors to set the gain of the amplifier, while additional passive components may be included to filter noise and improve stability. The use of low-power resistors ensures that the overall power consumption remains minimal, which is essential for prolonging battery life in portable applications.
In terms of performance, the OP90 offers a low input offset voltage and high input impedance, which are crucial for accurate signal amplification without loading the source. The output stage can drive loads directly or can be coupled to additional stages if further processing is required.
Overall, the OP90's design and characteristics make it an excellent choice for low-power applications, particularly in portable instrumentation and sensor interfacing, where efficiency and performance are paramount. Compared to other operational amplifier, OP90 significant advantage in low power consumption. With its low power consumption, the power supply voltage adapted to a wide range ( 1 6.36V; or 0.8-18V, both can also work in a dual supply from a single supply) and to show their talents in a portable or battery-powered devices. As shown for the OP90 configuration micropower instrumentation amplifier.