Optical transmission detection circuit

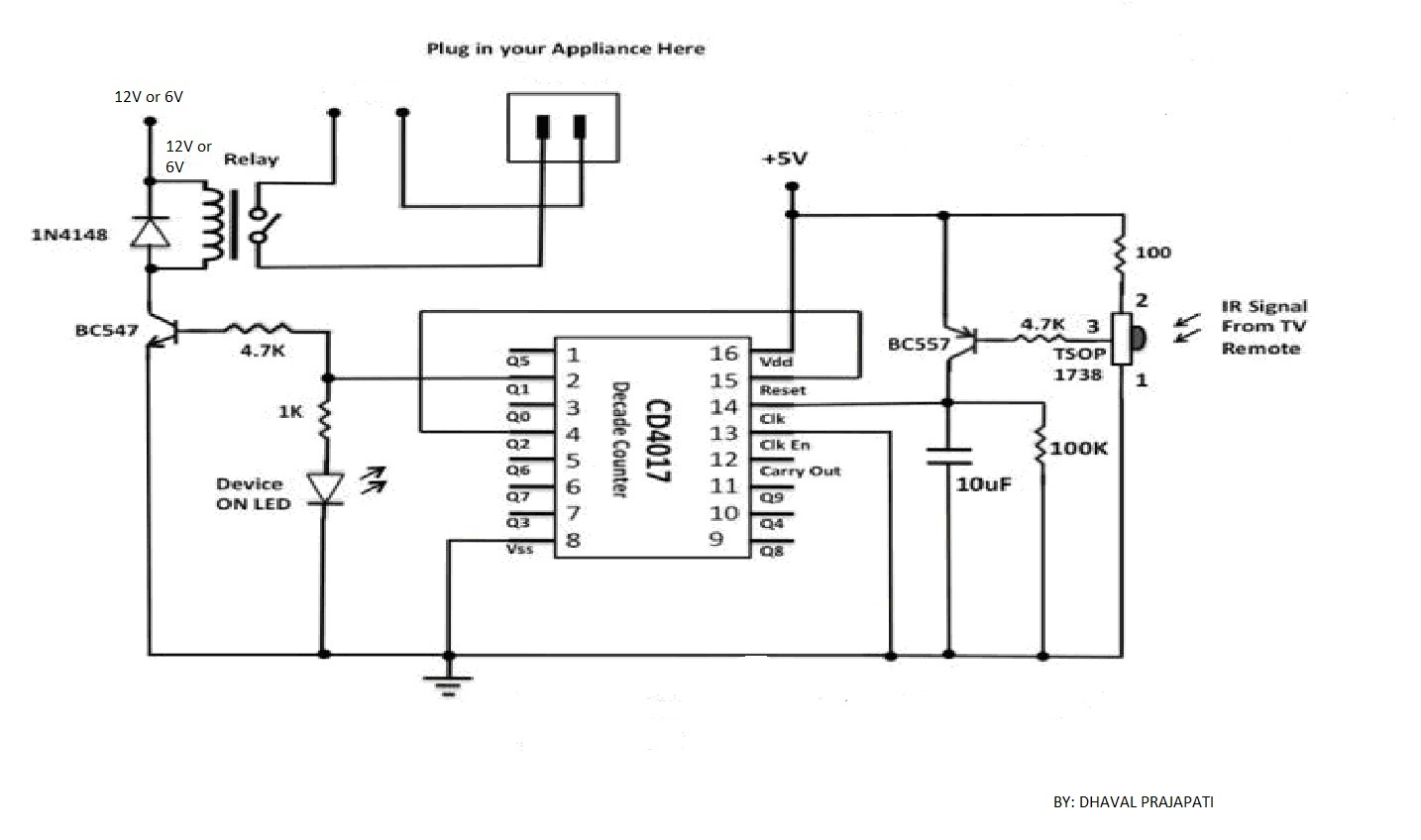
This circuit employs a phototransistor along with four operational amplifiers to function as a total energy detector. It is designed to measure the total energy of optical pulses transmitted through an optical cable communication system. When the light intensity of the signal source is consistent, this circuit can be utilized to test and compare the conditions of optical fibers.
The circuit consists of a phototransistor that converts the incoming optical signals into electrical signals. The output from the phototransistor is fed into a series of four operational amplifiers configured to amplify the signal for further processing. Each operational amplifier can be set up in different configurations, such as inverting, non-inverting, or differential, depending on the desired characteristics of the output signal.
The operational amplifiers play a crucial role in enhancing the sensitivity and accuracy of the total energy detection. By adjusting the gain of each amplifier, the circuit can be fine-tuned to respond appropriately to varying light intensities, ensuring reliable performance under different conditions. The amplified signal can then be processed to determine the total energy of the optical pulse, allowing for effective monitoring and evaluation of the optical fiber's performance.
In practical applications, this total energy detector can be used in conjunction with diagnostic equipment to assess the integrity of optical fibers in communication systems. By comparing the detected energy levels with known standards, it is possible to identify potential issues such as attenuation or signal degradation, thereby facilitating timely maintenance and ensuring optimal communication efficiency.In this circuit, phototransistor and four operational amplifier take the action of total energy detector, to detect the total energy of pulse optical transported by the optical cable communication system. If the light intensity of singal source remains the same, then this circuit can be used to test and compare the situation of optical fiber, it also can b..
🔗 External reference
The circuit consists of a phototransistor that converts the incoming optical signals into electrical signals. The output from the phototransistor is fed into a series of four operational amplifiers configured to amplify the signal for further processing. Each operational amplifier can be set up in different configurations, such as inverting, non-inverting, or differential, depending on the desired characteristics of the output signal.
The operational amplifiers play a crucial role in enhancing the sensitivity and accuracy of the total energy detection. By adjusting the gain of each amplifier, the circuit can be fine-tuned to respond appropriately to varying light intensities, ensuring reliable performance under different conditions. The amplified signal can then be processed to determine the total energy of the optical pulse, allowing for effective monitoring and evaluation of the optical fiber's performance.
In practical applications, this total energy detector can be used in conjunction with diagnostic equipment to assess the integrity of optical fibers in communication systems. By comparing the detected energy levels with known standards, it is possible to identify potential issues such as attenuation or signal degradation, thereby facilitating timely maintenance and ensuring optimal communication efficiency.In this circuit, phototransistor and four operational amplifier take the action of total energy detector, to detect the total energy of pulse optical transported by the optical cable communication system. If the light intensity of singal source remains the same, then this circuit can be used to test and compare the situation of optical fiber, it also can b..
🔗 External reference