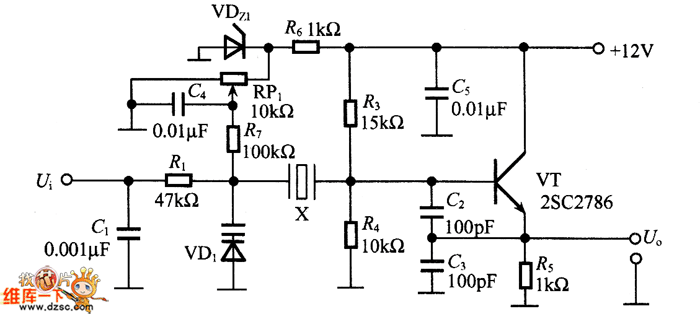
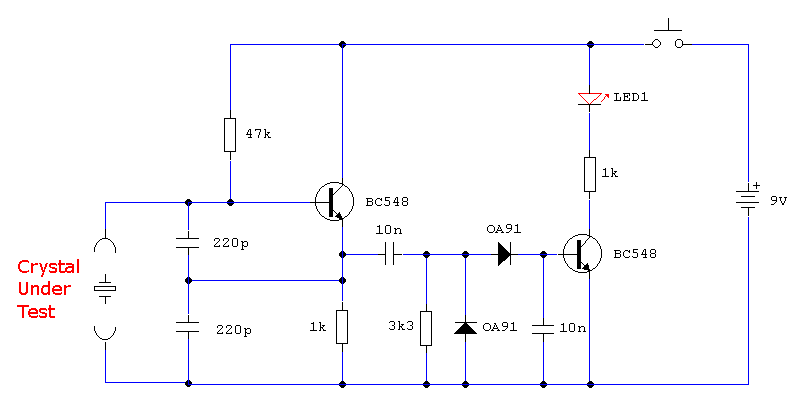
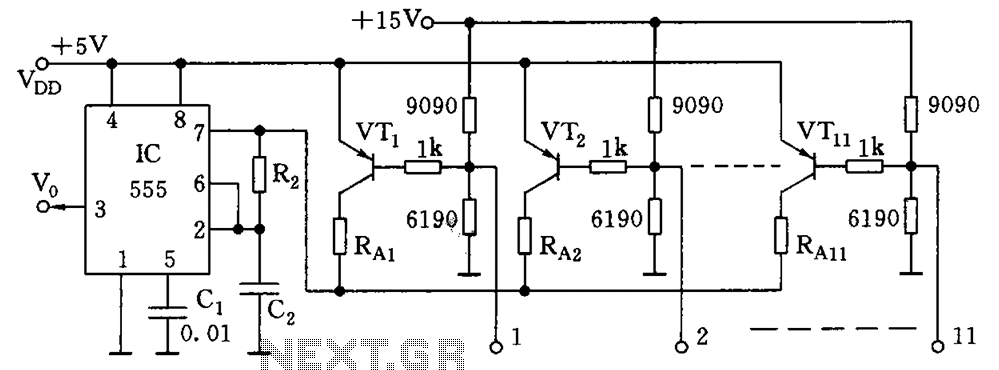
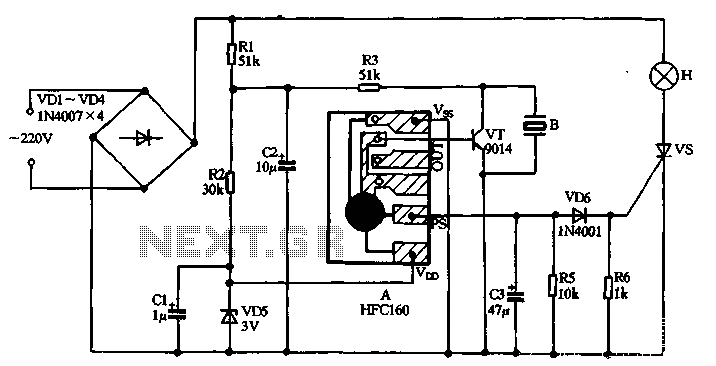
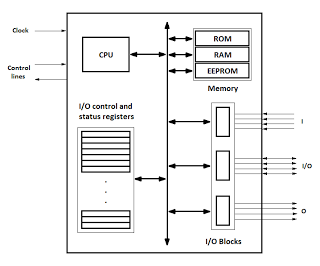
Oscillator astable multi-vibrator with Crystal controller
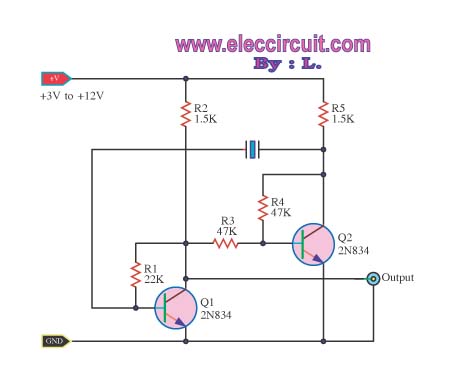
An oscillator circuit of this nature is often utilized as a clock circuit. This circuit employs a crystal frequency control with a stability of one million hertz.
An oscillator circuit designed for clock applications typically generates a periodic signal, which can be used to synchronize the operation of digital systems. The circuit's fundamental component is a crystal oscillator, which uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal to create an accurate frequency output. In this case, the specified frequency is one million hertz (1 MHz), which is a common standard for various digital clocks and timing applications.
The crystal used in the oscillator provides high stability and precision, making it suitable for applications requiring consistent timing signals. The oscillator circuit may include additional components such as capacitors and resistors that help in defining the oscillation characteristics, ensuring that the output signal maintains its frequency and shape over time.
In a typical configuration, the oscillator circuit may consist of an amplifier stage that boosts the signal generated by the crystal. Feedback components are employed to sustain oscillation, allowing the circuit to produce a continuous square wave or sine wave output. This output can then be further processed or divided down for use in various digital devices, such as microcontrollers or frequency dividers.
Overall, the oscillator circuit serves a critical role in electronic systems, providing the necessary timing signals for operation, and its design emphasizes stability, accuracy, and reliability.An oscillator circuit of this nature. Often used as a clock circuit. This circuit uses a million crystal frequency control with stability. And.. 🔗 External reference
An oscillator circuit designed for clock applications typically generates a periodic signal, which can be used to synchronize the operation of digital systems. The circuit's fundamental component is a crystal oscillator, which uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal to create an accurate frequency output. In this case, the specified frequency is one million hertz (1 MHz), which is a common standard for various digital clocks and timing applications.
The crystal used in the oscillator provides high stability and precision, making it suitable for applications requiring consistent timing signals. The oscillator circuit may include additional components such as capacitors and resistors that help in defining the oscillation characteristics, ensuring that the output signal maintains its frequency and shape over time.
In a typical configuration, the oscillator circuit may consist of an amplifier stage that boosts the signal generated by the crystal. Feedback components are employed to sustain oscillation, allowing the circuit to produce a continuous square wave or sine wave output. This output can then be further processed or divided down for use in various digital devices, such as microcontrollers or frequency dividers.
Overall, the oscillator circuit serves a critical role in electronic systems, providing the necessary timing signals for operation, and its design emphasizes stability, accuracy, and reliability.An oscillator circuit of this nature. Often used as a clock circuit. This circuit uses a million crystal frequency control with stability. And.. 🔗 External reference