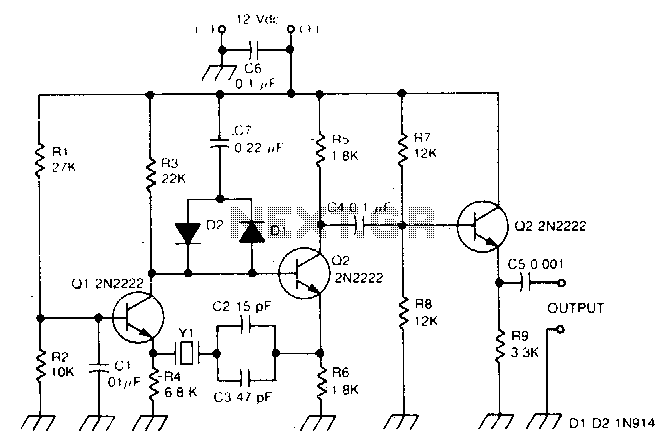
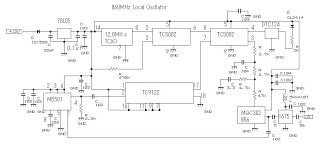
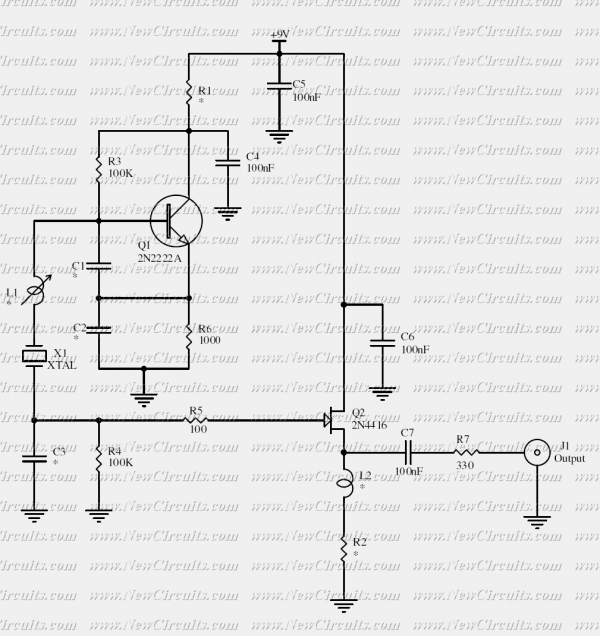
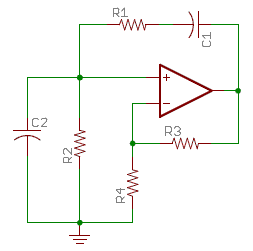
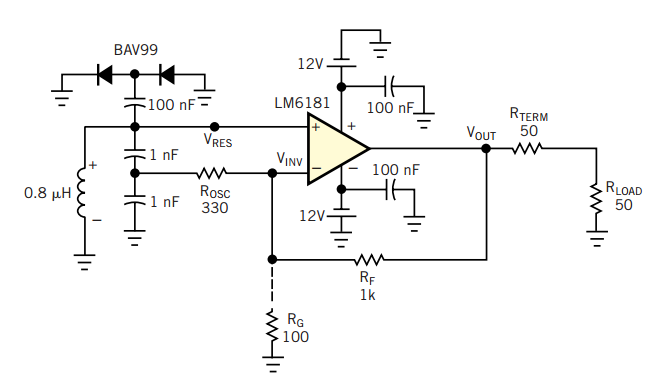
Oscillator
This is a design circuit for a linear opto-coupler circuit based on the MOC5010, which can be used to isolate a circuit from the main grid, audio interface, medical electronics, and various other applications.
The MOC5010 is a linear opto-coupler that enables electrical isolation between different circuit sections while allowing for signal transmission. This component is particularly useful in applications where it is critical to prevent high voltages or noise from affecting sensitive electronic systems.
The circuit typically consists of an LED and a phototransistor housed within a single package. The LED, when activated by an input signal, emits light that is detected by the phototransistor. The linear characteristics of the MOC5010 allow for a proportional relationship between the input and output signals, making it suitable for analog signal isolation.
In practical applications, the MOC5010 can be used to isolate audio signals, ensuring that ground loops and other interference do not compromise audio quality. In medical electronics, it provides a safe means to interface patient monitoring devices with high-voltage equipment, safeguarding against electrical shocks.
The circuit design should include appropriate resistors to limit the current through the LED and to set the gain of the phototransistor. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be included to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply. Proper layout considerations, such as minimizing trace lengths and separating high-voltage and low-voltage sections, are essential to enhance performance and reliability.
Overall, the MOC5010-based linear opto-coupler circuit is a versatile solution for achieving electrical isolation in a wide range of electronic applications, ensuring both safety and signal integrity.Here s a design circuit for linear opto coupler circuit that is based on MOC5010 and can be used to isolate a circuit from main grid, audio interface, in medical electronics and many other applications. Here s th .. 🔗 External reference
The MOC5010 is a linear opto-coupler that enables electrical isolation between different circuit sections while allowing for signal transmission. This component is particularly useful in applications where it is critical to prevent high voltages or noise from affecting sensitive electronic systems.
The circuit typically consists of an LED and a phototransistor housed within a single package. The LED, when activated by an input signal, emits light that is detected by the phototransistor. The linear characteristics of the MOC5010 allow for a proportional relationship between the input and output signals, making it suitable for analog signal isolation.
In practical applications, the MOC5010 can be used to isolate audio signals, ensuring that ground loops and other interference do not compromise audio quality. In medical electronics, it provides a safe means to interface patient monitoring devices with high-voltage equipment, safeguarding against electrical shocks.
The circuit design should include appropriate resistors to limit the current through the LED and to set the gain of the phototransistor. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be included to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply. Proper layout considerations, such as minimizing trace lengths and separating high-voltage and low-voltage sections, are essential to enhance performance and reliability.
Overall, the MOC5010-based linear opto-coupler circuit is a versatile solution for achieving electrical isolation in a wide range of electronic applications, ensuring both safety and signal integrity.Here s a design circuit for linear opto coupler circuit that is based on MOC5010 and can be used to isolate a circuit from main grid, audio interface, in medical electronics and many other applications. Here s th .. 🔗 External reference