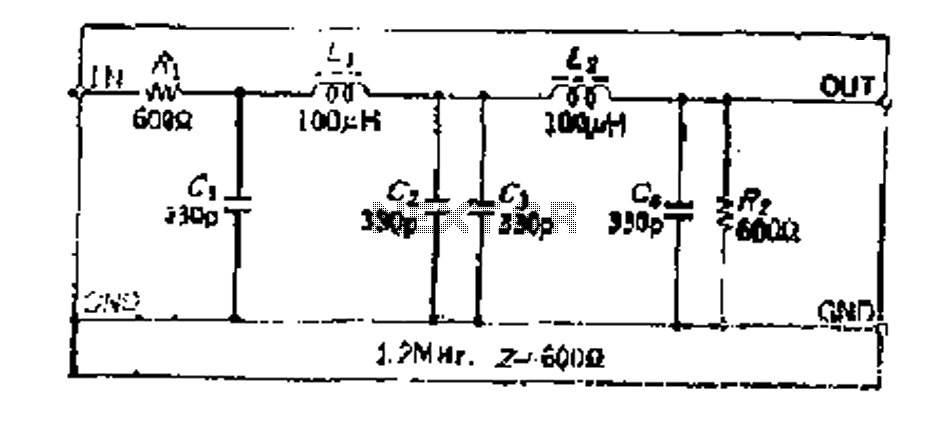
7MHz high frequency carrier oscillator
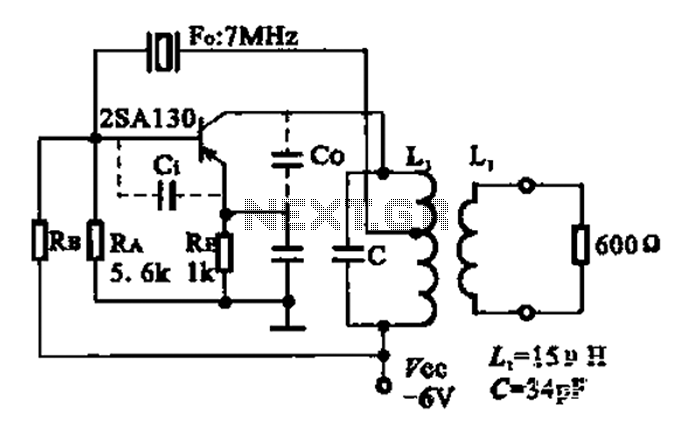
The 2SA130 transistor is used in an oscillator circuit with an oscillation frequency of 7 MHz. The power supply voltage is 6V, and the load is a frequency-selective resonant circuit with a quality factor of 600.
The circuit utilizes the 2SA130 transistor, a general-purpose NPN transistor, to create a high-frequency oscillator. In this configuration, the transistor is biased to operate in the active region, allowing it to amplify signals and sustain oscillations. The oscillation frequency of 7 MHz is determined primarily by the reactive components in the circuit, which typically include capacitors and inductors.
The power supply voltage of 6V is suitable for the 2SA130, as it can handle a maximum collector-emitter voltage of 50V, providing ample headroom for stable operation. The frequency-selective resonant circuit, characterized by a quality factor (Q) of 600, indicates a highly selective response to the oscillation frequency. A high Q factor suggests that the circuit has a narrow bandwidth, allowing it to filter out unwanted frequencies effectively while maintaining a strong response at the desired frequency of 7 MHz.
The resonant circuit can be implemented using a combination of inductors and capacitors arranged in a tank circuit configuration. The inductor and capacitor values must be chosen carefully to achieve the desired resonant frequency, which can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{LC}} \]
where \( f \) is the resonant frequency, \( L \) is the inductance in henries, and \( C \) is the capacitance in farads. The high Q factor indicates that the circuit will have minimal energy loss, making it suitable for applications requiring precise frequency generation, such as RF transmitters and receivers.
In summary, this oscillator circuit with the 2SA130 transistor is designed for efficient operation at 7 MHz, powered by a 6V supply, and utilizes a resonant circuit with a high quality factor to achieve selective frequency response. Proper component selection and circuit design are critical to ensure stable oscillation and desired performance characteristics.2SA130 transistor shown oscillator, the oscillation frequency of 7 MHz, the power supply voltage is 6V, frequency-selective resonant circuit load 600 Q.
The circuit utilizes the 2SA130 transistor, a general-purpose NPN transistor, to create a high-frequency oscillator. In this configuration, the transistor is biased to operate in the active region, allowing it to amplify signals and sustain oscillations. The oscillation frequency of 7 MHz is determined primarily by the reactive components in the circuit, which typically include capacitors and inductors.
The power supply voltage of 6V is suitable for the 2SA130, as it can handle a maximum collector-emitter voltage of 50V, providing ample headroom for stable operation. The frequency-selective resonant circuit, characterized by a quality factor (Q) of 600, indicates a highly selective response to the oscillation frequency. A high Q factor suggests that the circuit has a narrow bandwidth, allowing it to filter out unwanted frequencies effectively while maintaining a strong response at the desired frequency of 7 MHz.
The resonant circuit can be implemented using a combination of inductors and capacitors arranged in a tank circuit configuration. The inductor and capacitor values must be chosen carefully to achieve the desired resonant frequency, which can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{LC}} \]
where \( f \) is the resonant frequency, \( L \) is the inductance in henries, and \( C \) is the capacitance in farads. The high Q factor indicates that the circuit will have minimal energy loss, making it suitable for applications requiring precise frequency generation, such as RF transmitters and receivers.
In summary, this oscillator circuit with the 2SA130 transistor is designed for efficient operation at 7 MHz, powered by a 6V supply, and utilizes a resonant circuit with a high quality factor to achieve selective frequency response. Proper component selection and circuit design are critical to ensure stable oscillation and desired performance characteristics.2SA130 transistor shown oscillator, the oscillation frequency of 7 MHz, the power supply voltage is 6V, frequency-selective resonant circuit load 600 Q.