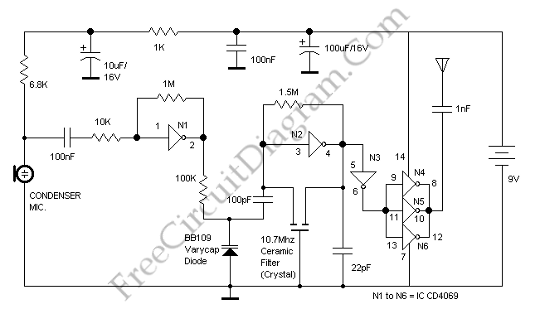
Overvoltage protection for logic

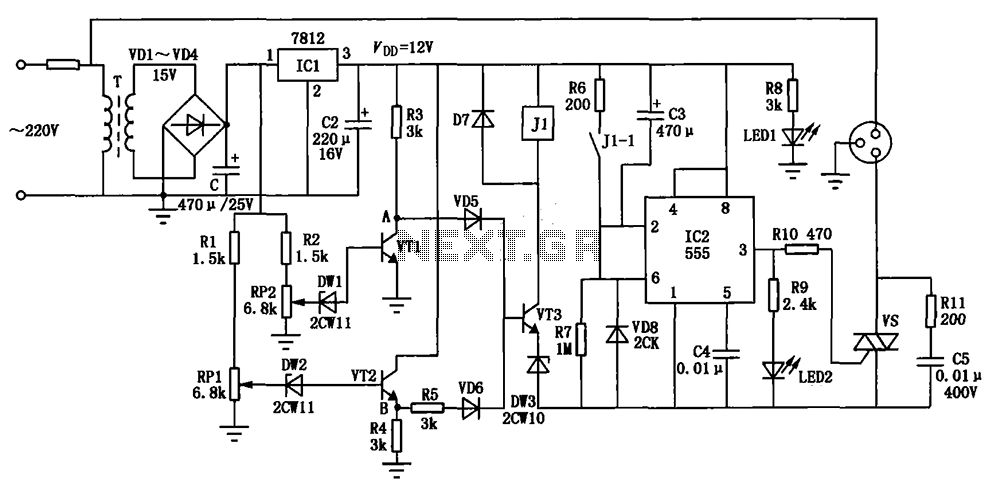
The Zener diode ZD1 monitors the supply voltage, and if the supply exceeds 6 V, transistor Q1 will activate. This activation causes transistor Q2 to conduct, thereby clamping the voltage rail. The subsequent behavior of the circuit is contingent upon the source supply, which may either shut down, enter a current limiting mode, or blow the supply fuse. Importantly, none of these scenarios will damage the TTL chips. Additionally, the rating of transistor Q2 is determined by the characteristics of the source supply and whether continuous operation is necessary during a failure. Its current rating must exceed that of the source supply.
The circuit employs a Zener diode, ZD1, which is configured to maintain a stable reference voltage. When the supply voltage rises above the designated threshold of 6 V, ZD1 becomes reverse-biased, triggering the conduction of transistor Q1. This action initiates a cascade effect, leading to the activation of transistor Q2. The role of Q2 is crucial as it clamps the output voltage rail to prevent over-voltage conditions that could potentially harm sensitive components, such as TTL chips.
The clamping action of Q2 is essential for circuit protection. If the supply voltage continues to rise beyond acceptable levels, the circuit can respond in several ways: it may completely shut down to protect the components, enter a current limiting state to prevent excessive current draw, or blow a fuse in the power supply line to interrupt the flow of electricity. Each of these protective measures is designed to ensure that the TTL chips remain unharmed during fault conditions.
The specifications for transistor Q2 are critical to the overall reliability of the circuit. The current rating of Q2 must be sufficiently high to handle the maximum output current of the source supply, particularly in scenarios where continuous operation is required during a fault condition. This ensures that Q2 can effectively clamp the voltage without entering a failure mode itself. The careful selection of components based on their ratings and the expected operating conditions is vital for optimal circuit performance and longevity.Zener diode ZD1 senses the supply, and should the supply rise above 6 V, Ql will turn on. In turn, Q2 conducts clamping the rail. Subsequent events depend on the source supply. It will either shut down, go into current limit or blow its supply fuse. None of these will damage the TTL chips The rating of Q2 depends on the source supply, and whether it will be required to operate continuously in the event of failure. Its current rating has to be in excess of the source supply.
The circuit employs a Zener diode, ZD1, which is configured to maintain a stable reference voltage. When the supply voltage rises above the designated threshold of 6 V, ZD1 becomes reverse-biased, triggering the conduction of transistor Q1. This action initiates a cascade effect, leading to the activation of transistor Q2. The role of Q2 is crucial as it clamps the output voltage rail to prevent over-voltage conditions that could potentially harm sensitive components, such as TTL chips.
The clamping action of Q2 is essential for circuit protection. If the supply voltage continues to rise beyond acceptable levels, the circuit can respond in several ways: it may completely shut down to protect the components, enter a current limiting state to prevent excessive current draw, or blow a fuse in the power supply line to interrupt the flow of electricity. Each of these protective measures is designed to ensure that the TTL chips remain unharmed during fault conditions.
The specifications for transistor Q2 are critical to the overall reliability of the circuit. The current rating of Q2 must be sufficiently high to handle the maximum output current of the source supply, particularly in scenarios where continuous operation is required during a fault condition. This ensures that Q2 can effectively clamp the voltage without entering a failure mode itself. The careful selection of components based on their ratings and the expected operating conditions is vital for optimal circuit performance and longevity.Zener diode ZD1 senses the supply, and should the supply rise above 6 V, Ql will turn on. In turn, Q2 conducts clamping the rail. Subsequent events depend on the source supply. It will either shut down, go into current limit or blow its supply fuse. None of these will damage the TTL chips The rating of Q2 depends on the source supply, and whether it will be required to operate continuously in the event of failure. Its current rating has to be in excess of the source supply.