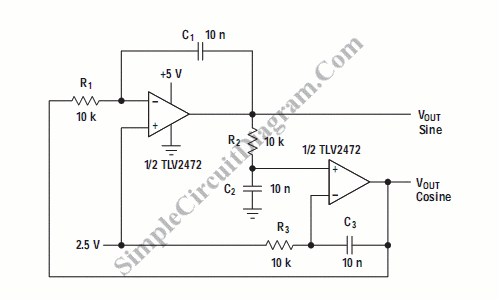
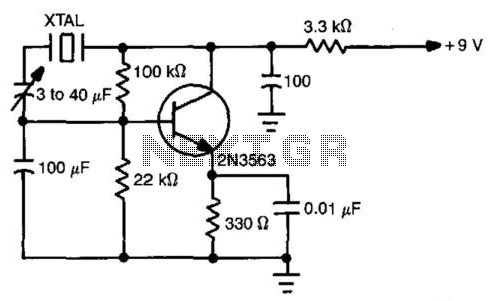
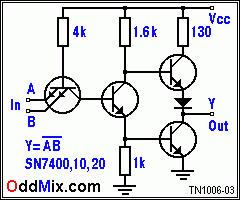
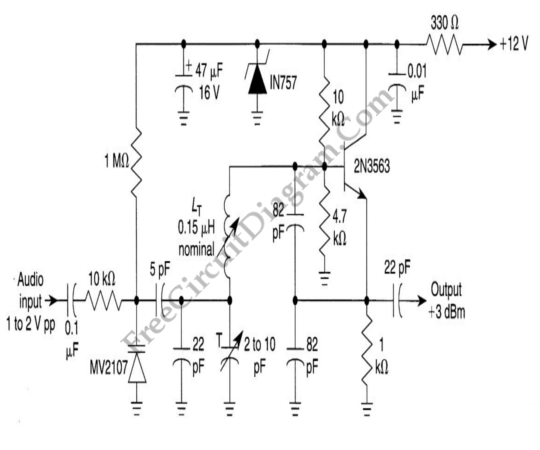
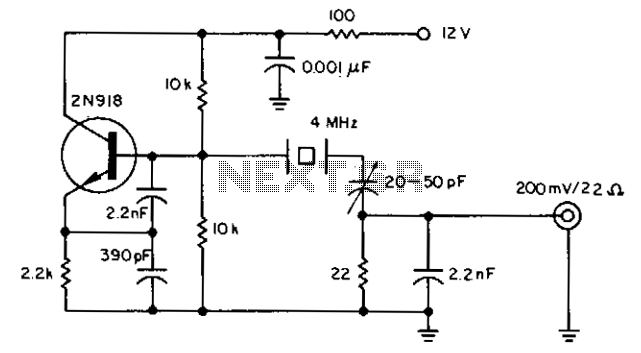
Phase-shift oscillator
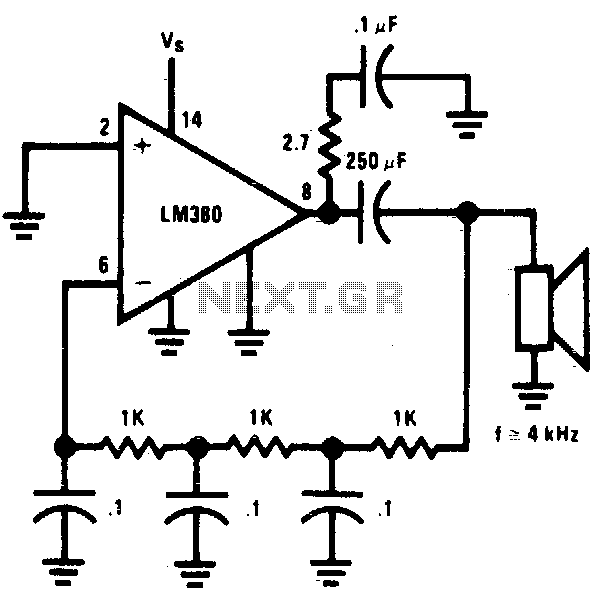
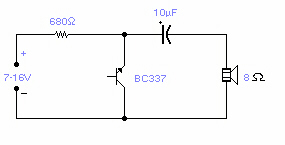
The circuit utilizes a simple RC network to generate a very high-pitched tone from a miniature speaker. With the specified component values, the circuit oscillates at a frequency of 3 kHz and drives a miniature 2W speaker at an ear-piercing volume. The output waveform is a square wave with a width of 150 µs, exhibiting sloping rise and fall times, and a peak-to-peak amplitude of 4 volts when powered by a 9-volt supply. The current drain of the oscillator is 90 mA at 9 volts, resulting in a total power dissipation of 0.1 watt, which is significantly lower than the 15 watts that the 14-pin version can handle (at room temperature) before entering a shutdown state.
The circuit is designed around a simple resistor-capacitor (RC) network that forms the basis of an oscillator. The RC values are carefully selected to achieve the desired frequency of oscillation, which is critical for producing the high-pitched tone. The oscillator output is a square wave, characterized by its rapid transitions between high and low states, which is suitable for driving a miniature speaker.
The miniature speaker, rated at 2 watts, is capable of producing loud sounds, making it ideal for applications requiring attention-grabbing audio signals. The peak-to-peak voltage of 4 volts is sufficient to drive the speaker to high volumes, ensuring that the sound produced is piercing and easily audible.
Power considerations are also important in the design of this circuit. The oscillator operates at a current drain of 90 mA when supplied with 9 volts. This results in a total power dissipation of 0.1 watt, which is well within safe operating limits. The 14-pin version of the oscillator can tolerate up to 15 watts before it risks overheating and shutting down, thus providing a robust safety margin for extended use.
In summary, this circuit is an effective solution for generating a loud, shrill tone using a minimal component count, making it suitable for various applications, including alarms and notification systems. The design ensures efficient power usage while maintaining the ability to produce high sound levels, demonstrating the effectiveness of RC oscillators in audio applications.Circuit uses a simple RC network to produce an exceptionally shrill tone from a miniature speaker. With the parts values shown, the circuit oscillates at a frequency of 3 kHz and drives a miniature 2W speaker with ear-piercing volume. The output waveform is a square wave with a width of 150 µ$, sloping rise and fall times, and a peak-to-peak amplitude of 4 volts (when powered by 9 volts)
Current drain of the oscillator is 90 mA at 9 volts, and total power dissipation at this voltage is 01 watt, which is well below the 15 watts the 14-pin version will absorb (at room temperature) before shutting down.
The circuit is designed around a simple resistor-capacitor (RC) network that forms the basis of an oscillator. The RC values are carefully selected to achieve the desired frequency of oscillation, which is critical for producing the high-pitched tone. The oscillator output is a square wave, characterized by its rapid transitions between high and low states, which is suitable for driving a miniature speaker.
The miniature speaker, rated at 2 watts, is capable of producing loud sounds, making it ideal for applications requiring attention-grabbing audio signals. The peak-to-peak voltage of 4 volts is sufficient to drive the speaker to high volumes, ensuring that the sound produced is piercing and easily audible.
Power considerations are also important in the design of this circuit. The oscillator operates at a current drain of 90 mA when supplied with 9 volts. This results in a total power dissipation of 0.1 watt, which is well within safe operating limits. The 14-pin version of the oscillator can tolerate up to 15 watts before it risks overheating and shutting down, thus providing a robust safety margin for extended use.
In summary, this circuit is an effective solution for generating a loud, shrill tone using a minimal component count, making it suitable for various applications, including alarms and notification systems. The design ensures efficient power usage while maintaining the ability to produce high sound levels, demonstrating the effectiveness of RC oscillators in audio applications.Circuit uses a simple RC network to produce an exceptionally shrill tone from a miniature speaker. With the parts values shown, the circuit oscillates at a frequency of 3 kHz and drives a miniature 2W speaker with ear-piercing volume. The output waveform is a square wave with a width of 150 µ$, sloping rise and fall times, and a peak-to-peak amplitude of 4 volts (when powered by 9 volts)
Current drain of the oscillator is 90 mA at 9 volts, and total power dissipation at this voltage is 01 watt, which is well below the 15 watts the 14-pin version will absorb (at room temperature) before shutting down.