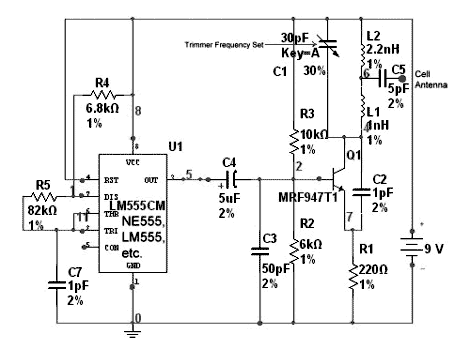
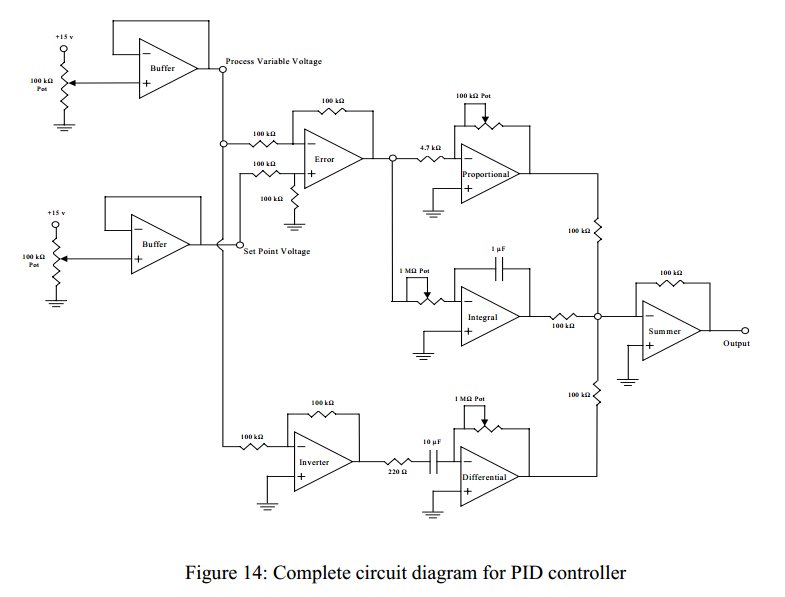
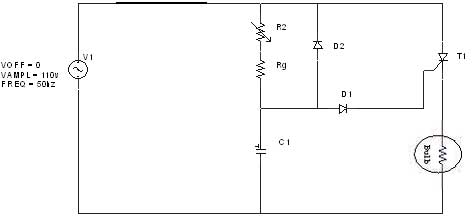
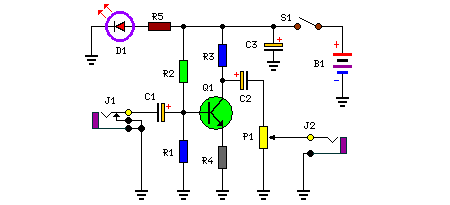
phone hold circuit
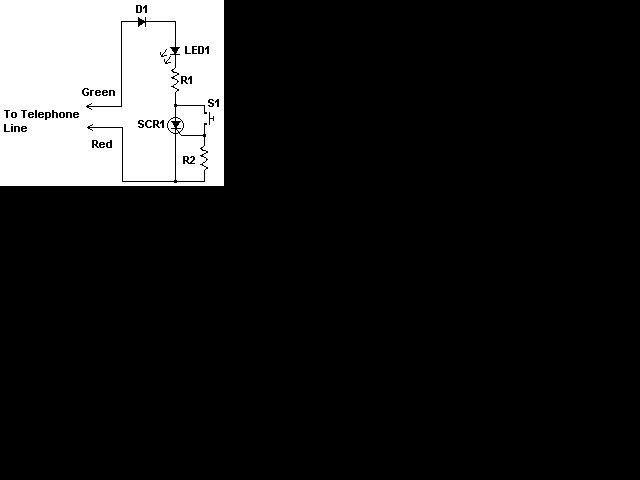
Although a hold feature is standard on most new phones, many users still utilize the original bell phones. For those who require a hold feature, this circuit is particularly useful. It is easy to construct and compact enough to be installed inside the phone without significant issues. Additionally, it is powered by the phone line itself, removing the need for batteries.
The hold feature circuit designed for use with traditional bell phones is an essential addition for users who wish to enhance their calling experience. The circuit typically involves a relay or a transistor switch that engages when the hold button is pressed. This mechanism interrupts the call while maintaining the line connection, allowing the user to attend to other matters without disconnecting.
The circuit can be constructed using a few common electronic components, including resistors, capacitors, diodes, and a relay or transistor. The relay acts as a switch that opens the line to the receiver while keeping the connection active on the line. A small capacitor can be used to filter any noise and stabilize the power supply from the phone line, ensuring that the circuit operates smoothly without interruptions.
Installation of the circuit inside the phone requires careful consideration of space and accessibility. The components should be arranged neatly to avoid interference with the phone's existing wiring. The power supply, drawn from the phone line, typically requires no additional power source, making the circuit energy-efficient and convenient.
Overall, this hold feature circuit represents a practical solution for users of original bell phones, providing a modern functionality while maintaining the integrity of the traditional device. Its compact design and reliance on the phone line for power make it an ideal modification for enhancing communication capabilities.Although a hold feature is standard on most new phones, a lot of us still use the origional bell phones. Those of us that require a hold feature will find this circuit very useful. It is easy to build, and is compact enough to be installed inside the phone with no real problem. It is also powered by the phone line itself, eliminating the need for batteries. 🔗 External reference
The hold feature circuit designed for use with traditional bell phones is an essential addition for users who wish to enhance their calling experience. The circuit typically involves a relay or a transistor switch that engages when the hold button is pressed. This mechanism interrupts the call while maintaining the line connection, allowing the user to attend to other matters without disconnecting.
The circuit can be constructed using a few common electronic components, including resistors, capacitors, diodes, and a relay or transistor. The relay acts as a switch that opens the line to the receiver while keeping the connection active on the line. A small capacitor can be used to filter any noise and stabilize the power supply from the phone line, ensuring that the circuit operates smoothly without interruptions.
Installation of the circuit inside the phone requires careful consideration of space and accessibility. The components should be arranged neatly to avoid interference with the phone's existing wiring. The power supply, drawn from the phone line, typically requires no additional power source, making the circuit energy-efficient and convenient.
Overall, this hold feature circuit represents a practical solution for users of original bell phones, providing a modern functionality while maintaining the integrity of the traditional device. Its compact design and reliance on the phone line for power make it an ideal modification for enhancing communication capabilities.Although a hold feature is standard on most new phones, a lot of us still use the origional bell phones. Those of us that require a hold feature will find this circuit very useful. It is easy to build, and is compact enough to be installed inside the phone with no real problem. It is also powered by the phone line itself, eliminating the need for batteries. 🔗 External reference