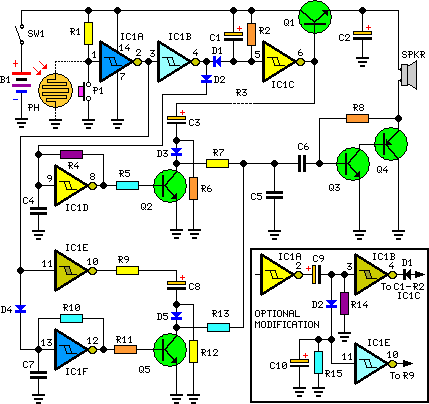
Photo relay circuit
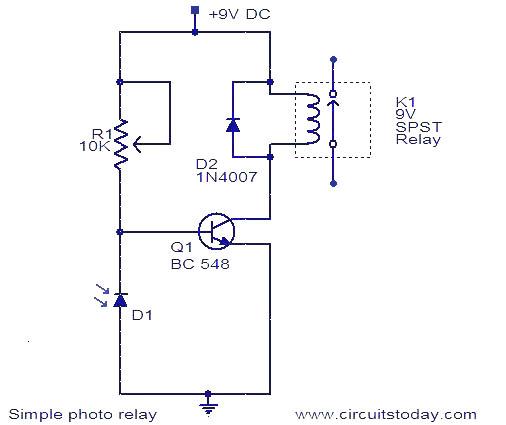
A photo relay, or light-activated relay, is a circuit that opens and closes relay contacts based on the presence of light. It utilizes a photodiode to detect light levels. The photodiode exhibits high resistance in the absence of light and is connected in reverse bias. The only current flowing through it is due to minority carriers. When light strikes the photodiode, the current from the minority carriers increases, resulting in lower resistance. Consequently, the voltage across the photodiode is insufficient to forward bias transistor Q1, keeping the relay in the OFF state. In darkness, the photodiode's resistance increases, and the voltage across it becomes adequate to forward bias transistor Q1, turning the relay ON. Diode D2 acts as a freewheeling diode, protecting the transistor from transients generated during relay switching. This configuration allows the load connected through the relay contacts to be switched ON and OFF based on the light incident on the photodiode.
The photo relay circuit operates through a straightforward mechanism that hinges on the properties of the photodiode and transistor. In the absence of light, the photodiode maintains a high resistance, which prevents significant current flow. This condition keeps the voltage across it at a level that does not suffice to forward bias the transistor Q1, thereby ensuring that the relay remains in the OFF state and the load remains disconnected.
Upon exposure to light, the photodiode's resistance drops as the minority carrier current increases. This change results in a lower voltage across the photodiode. If the voltage surpasses the threshold required to forward bias Q1, the transistor conducts, allowing current to flow through the relay coil. As a result, the relay contacts close, connecting the load to the power supply.
Moreover, the inclusion of diode D2 is crucial for protecting the transistor from voltage spikes that can occur when the relay coil is de-energized. These transients, generated by the collapsing magnetic field of the relay, can induce back electromotive force (EMF) that may damage the transistor. The freewheeling diode provides a path for this induced current, effectively clamping the voltage and safeguarding the transistor.
Overall, this circuit configuration exemplifies an effective method for controlling a load based on light intensity, leveraging the unique characteristics of photodiodes and transistors, while ensuring reliability through protective components.A photo relay or light activated relay is a circuit which opens and closes the relay contacts according to the light. Here a photo diode is used to sense the light. The photo diode offers a high resistance when there is no light falling on it. Here the photo diode is connected in reverse biased condition. The only current flowing through it will be du e to the minority carriers. When light falls on it, the current due to the minority carriers increase and the diode offers a low resistance. As a result the voltage across the diode will not be sufficient to make the transistor Q1 forward biased and the relay will OFF.
When there is darkness the photo diode resistance increases and the voltage across it will become enough to forward bias the transistor Q1 making the relay ON. The diode D2 is used as a freewheeling diode to protect the transistor from transients produced to the switching of relay.
By this way the load connected through the relay contacts can be switched ON and OFF according to the light falling on the photo diode. 🔗 External reference
The photo relay circuit operates through a straightforward mechanism that hinges on the properties of the photodiode and transistor. In the absence of light, the photodiode maintains a high resistance, which prevents significant current flow. This condition keeps the voltage across it at a level that does not suffice to forward bias the transistor Q1, thereby ensuring that the relay remains in the OFF state and the load remains disconnected.
Upon exposure to light, the photodiode's resistance drops as the minority carrier current increases. This change results in a lower voltage across the photodiode. If the voltage surpasses the threshold required to forward bias Q1, the transistor conducts, allowing current to flow through the relay coil. As a result, the relay contacts close, connecting the load to the power supply.
Moreover, the inclusion of diode D2 is crucial for protecting the transistor from voltage spikes that can occur when the relay coil is de-energized. These transients, generated by the collapsing magnetic field of the relay, can induce back electromotive force (EMF) that may damage the transistor. The freewheeling diode provides a path for this induced current, effectively clamping the voltage and safeguarding the transistor.
Overall, this circuit configuration exemplifies an effective method for controlling a load based on light intensity, leveraging the unique characteristics of photodiodes and transistors, while ensuring reliability through protective components.A photo relay or light activated relay is a circuit which opens and closes the relay contacts according to the light. Here a photo diode is used to sense the light. The photo diode offers a high resistance when there is no light falling on it. Here the photo diode is connected in reverse biased condition. The only current flowing through it will be du e to the minority carriers. When light falls on it, the current due to the minority carriers increase and the diode offers a low resistance. As a result the voltage across the diode will not be sufficient to make the transistor Q1 forward biased and the relay will OFF.
When there is darkness the photo diode resistance increases and the voltage across it will become enough to forward bias the transistor Q1 making the relay ON. The diode D2 is used as a freewheeling diode to protect the transistor from transients produced to the switching of relay.
By this way the load connected through the relay contacts can be switched ON and OFF according to the light falling on the photo diode. 🔗 External reference