8W Fluorescent Lamp Inverter circuit
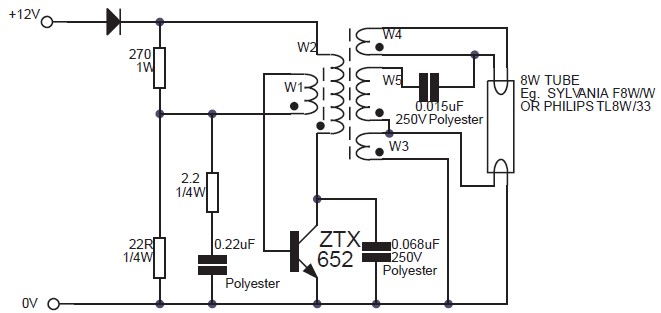
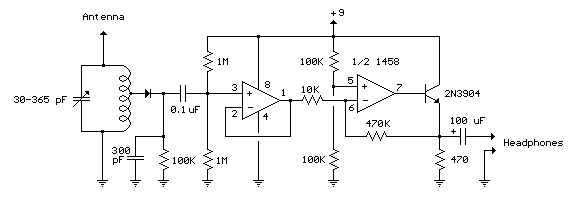
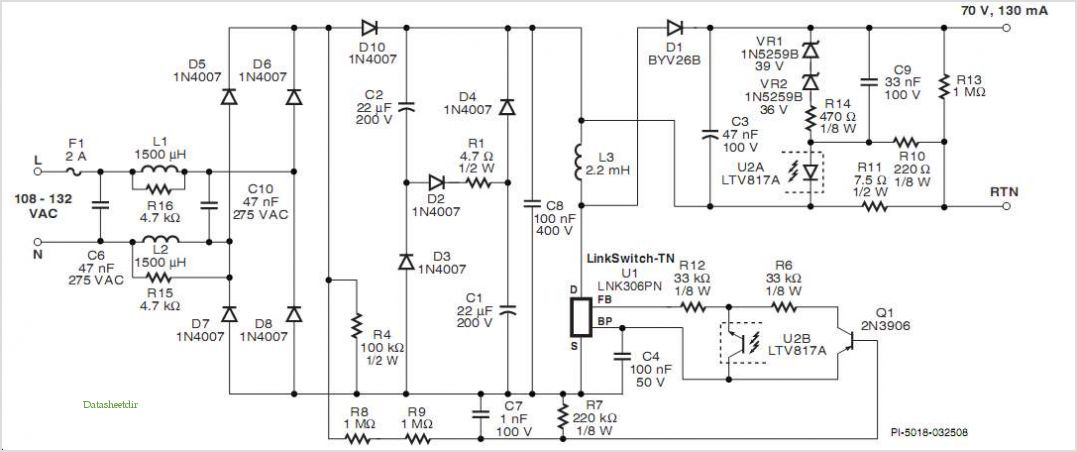
This circuit is an 8W inverter designed to drive an 8W fluorescent lamp from a 12V power supply, utilizing an inexpensive inverter based on a ZTX652 transistor. The inverter operates from power supplies ranging from 10V to 16.5V, achieving efficiencies of up to 78%. This inverter circuit can be used to power electric razors, stroboscopes, flash tubes, and small fluorescent lamps from a 12V car battery. Unlike typical feedback oscillator inverters, the oscillator in this design is separate from the output stage, allowing for easy adjustment of the oscillator frequency. Additionally, there is a simple inverter circuit that converts DC current into AC current, transforming 12V DC into 220V AC with an output power of 5W. This inverter circuit is commonly used for emergency lighting due to its limited power output of only 5W. However, it can also be utilized for other low-power applications. Furthermore, a power inverter circuit diagram is available for a 1000W inverter based on the MOSFET RFP50N06, which can handle loads up to 1000W depending on the power inverter transformer. The RFP50N06 MOSFETs are rated at 50 Amps and 60 Volts, and a heatsink is necessary for cooling the MOSFETs. Additional MOSFETs can be added in parallel. The following diagram illustrates an inverter circuit that provides 220V AC at 50Hz with a maximum power output of 100W. This inverter is constructed using transistors for both the square wave generator and the amplifier. In the inverter diagram, transistors Q1 and Q2 are used to generate the square wave, while transistors Q5 to Q8 amplify the signal and the transformer increases the AC/square wave current.
The 8W inverter circuit employs a ZTX652 transistor as the primary switching element, which is critical for converting the low-voltage DC input into a higher-voltage AC output suitable for fluorescent lamps. The design accommodates input voltages from 10V to 16.5V, making it versatile for various 12V power sources, including automotive batteries. The efficiency of up to 78% indicates a relatively low power loss, making it suitable for applications where battery life is a concern.
The separate oscillator design is a notable feature, allowing for frequency adjustments that can optimize performance based on the load characteristics. This flexibility is advantageous when powering devices with different operational requirements. The inverter's capability to drive devices such as electric razors and stroboscopes highlights its practical applications in both household and professional settings.
In contrast, the 1000W inverter circuit based on the RFP50N06 MOSFETs is designed for more demanding applications. The circuit can handle significant loads, making it suitable for larger devices or multiple smaller devices connected in parallel. The use of heatsinks is essential in this design to manage the thermal performance of the MOSFETs, ensuring reliability and longevity during operation.
The inclusion of a square wave generator and amplifier stage in the inverter diagram is crucial for producing the necessary AC waveform. The configuration of transistors Q1 and Q2 as the square wave generator ensures that the output waveform is suitable for driving transformers effectively, while transistors Q5 to Q8 serve to amplify the generated signal, enhancing the output current to meet the demands of the connected load. The transformer plays a vital role in stepping up the voltage from the low DC levels to the required AC levels, making this inverter circuit a practical solution for applications needing AC power from a DC source.This circuit is basically a 8W inverter circuit. The circuit continues to be intended to drive an 8W fluorescent lamp from a 12V power supply, utilizing an cheap inverter primarily based on a ZTX652 transistor. The inverter will operate from supplies in the variety of 10V to 16. 5V, obtaining efficiencies up to 78% as a. This inverter circuit can be used to power electric razors, stroboscopes and flash tubes, and small fluorescent lamps from a 12 volt car battery. In contrast to the usual feedback oscillator type of inverter, the oscillator of this inverter is separate from the output stage, which allows easy adjustment of the oscillator frequency to suit.
Here`s a very simple circuit inverter that converts DC current into AC current, from 12V DC to 220V AC with output power of 5W. Inverter circuit is typically used for emergency lighting, since the power output is small, which is about 5W only.
But you can use this inverter for other purposes that do not. 1000W Power Inverter circuit diagram: This is the power inverter circuit based MOSFET RFP50N06. The inverter capable to handle loads up to 1000W, it`s depended on your power inverter transformer. The RFP50N06 Fets are rated at 50 Amps and 60 Volts. Heatsink is required for cooling the MOSFETs. You may add some MOSFETs with parallel. The following diagram is an inverter circuit which will give you 220V AC 50Hz with maximum power of 100W. This inverter built using transistors both the square wave generator and the amplifier. Inverter Diagram: The Q1 and Q2 used generate square wave. Q5-Q8 amplify the signal and the transformer to increase the AC/square wave current. 🔗 External reference
The 8W inverter circuit employs a ZTX652 transistor as the primary switching element, which is critical for converting the low-voltage DC input into a higher-voltage AC output suitable for fluorescent lamps. The design accommodates input voltages from 10V to 16.5V, making it versatile for various 12V power sources, including automotive batteries. The efficiency of up to 78% indicates a relatively low power loss, making it suitable for applications where battery life is a concern.
The separate oscillator design is a notable feature, allowing for frequency adjustments that can optimize performance based on the load characteristics. This flexibility is advantageous when powering devices with different operational requirements. The inverter's capability to drive devices such as electric razors and stroboscopes highlights its practical applications in both household and professional settings.
In contrast, the 1000W inverter circuit based on the RFP50N06 MOSFETs is designed for more demanding applications. The circuit can handle significant loads, making it suitable for larger devices or multiple smaller devices connected in parallel. The use of heatsinks is essential in this design to manage the thermal performance of the MOSFETs, ensuring reliability and longevity during operation.
The inclusion of a square wave generator and amplifier stage in the inverter diagram is crucial for producing the necessary AC waveform. The configuration of transistors Q1 and Q2 as the square wave generator ensures that the output waveform is suitable for driving transformers effectively, while transistors Q5 to Q8 serve to amplify the generated signal, enhancing the output current to meet the demands of the connected load. The transformer plays a vital role in stepping up the voltage from the low DC levels to the required AC levels, making this inverter circuit a practical solution for applications needing AC power from a DC source.This circuit is basically a 8W inverter circuit. The circuit continues to be intended to drive an 8W fluorescent lamp from a 12V power supply, utilizing an cheap inverter primarily based on a ZTX652 transistor. The inverter will operate from supplies in the variety of 10V to 16. 5V, obtaining efficiencies up to 78% as a. This inverter circuit can be used to power electric razors, stroboscopes and flash tubes, and small fluorescent lamps from a 12 volt car battery. In contrast to the usual feedback oscillator type of inverter, the oscillator of this inverter is separate from the output stage, which allows easy adjustment of the oscillator frequency to suit.
Here`s a very simple circuit inverter that converts DC current into AC current, from 12V DC to 220V AC with output power of 5W. Inverter circuit is typically used for emergency lighting, since the power output is small, which is about 5W only.
But you can use this inverter for other purposes that do not. 1000W Power Inverter circuit diagram: This is the power inverter circuit based MOSFET RFP50N06. The inverter capable to handle loads up to 1000W, it`s depended on your power inverter transformer. The RFP50N06 Fets are rated at 50 Amps and 60 Volts. Heatsink is required for cooling the MOSFETs. You may add some MOSFETs with parallel. The following diagram is an inverter circuit which will give you 220V AC 50Hz with maximum power of 100W. This inverter built using transistors both the square wave generator and the amplifier. Inverter Diagram: The Q1 and Q2 used generate square wave. Q5-Q8 amplify the signal and the transformer to increase the AC/square wave current. 🔗 External reference