Photodiode current-to-voltage converter
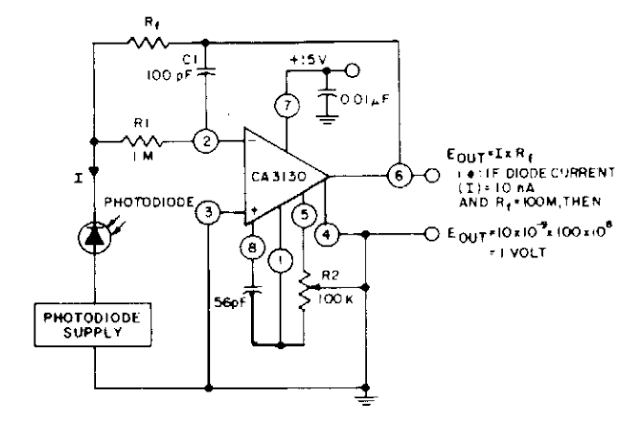
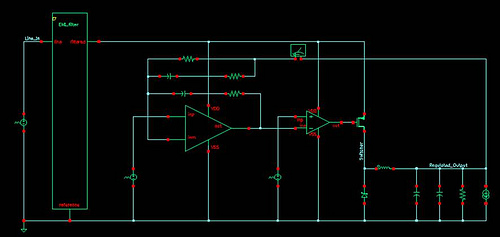
The photodiode current-to-voltage converter circuit employs three CA3130 BiMOS operational amplifiers, designed for applications that require sensitivity to sub-picoampere input currents. This circuit generates a ground-referenced output voltage that is directly proportional to the input current flowing through the photodiode.
The photodiode current-to-voltage converter is an essential component in optical detection systems, where precise measurement of light intensity is required. The CA3130 BiMOS op-amps are chosen for their low input bias current and high input impedance, making them ideal for detecting very low currents generated by photodiodes in response to light.
In this configuration, the photodiode is connected in reverse bias mode, which enhances its response speed and linearity. The output voltage from the op-amps is determined by the relationship between the photodiode current and the feedback resistor connected to the output. The gain of the circuit can be adjusted by changing the value of the feedback resistor, allowing for flexibility in the sensitivity of the system.
The circuit design incorporates additional features to minimize noise and improve stability. For example, bypass capacitors may be employed at the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out high-frequency noise. Additionally, careful layout considerations are necessary to reduce parasitic capacitance and inductance that could affect the performance of the circuit.
Overall, this photodiode current-to-voltage converter circuit is vital for applications such as optical communication, spectroscopy, and light measurement in various scientific and industrial fields, where accurate and reliable detection of low light levels is crucial.The Photodiode current-to-voltage converter circuit uses three CA3130 BiMOS op amps in an application sensitive to sub-picoampere input currents. The circuit provides a ground-referenced output voltage proportional to input current flowing through the photo-diode.
🔗 External reference
The photodiode current-to-voltage converter is an essential component in optical detection systems, where precise measurement of light intensity is required. The CA3130 BiMOS op-amps are chosen for their low input bias current and high input impedance, making them ideal for detecting very low currents generated by photodiodes in response to light.
In this configuration, the photodiode is connected in reverse bias mode, which enhances its response speed and linearity. The output voltage from the op-amps is determined by the relationship between the photodiode current and the feedback resistor connected to the output. The gain of the circuit can be adjusted by changing the value of the feedback resistor, allowing for flexibility in the sensitivity of the system.
The circuit design incorporates additional features to minimize noise and improve stability. For example, bypass capacitors may be employed at the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out high-frequency noise. Additionally, careful layout considerations are necessary to reduce parasitic capacitance and inductance that could affect the performance of the circuit.
Overall, this photodiode current-to-voltage converter circuit is vital for applications such as optical communication, spectroscopy, and light measurement in various scientific and industrial fields, where accurate and reliable detection of low light levels is crucial.The Photodiode current-to-voltage converter circuit uses three CA3130 BiMOS op amps in an application sensitive to sub-picoampere input currents. The circuit provides a ground-referenced output voltage proportional to input current flowing through the photo-diode.
🔗 External reference