Photovoltaic Light Sensors In Solar Tracker
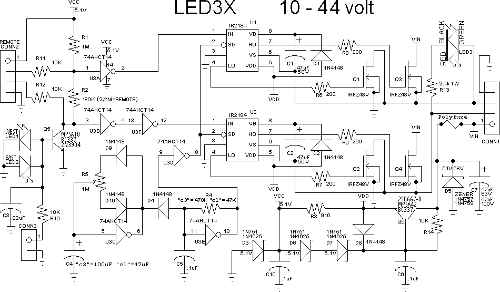
The following circuit illustrates photovoltaic light sensors in a solar tracker. Features include accuracy, low cost, simplicity, and a single-axis electronic design.
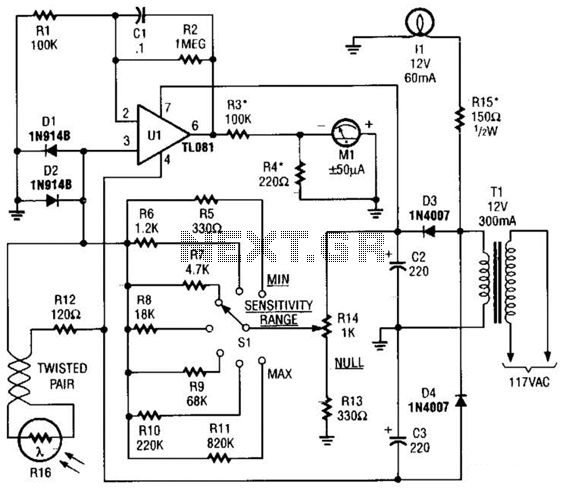
The photovoltaic light sensor circuit is designed to optimize the alignment of solar panels with respect to the sun's position, thereby enhancing energy capture efficiency. The core of the system consists of multiple photovoltaic cells that detect light intensity from different angles. These cells generate a voltage output proportional to the light they receive.
In a typical single-axis solar tracker, two or more light sensors are strategically placed on the surface of the solar panel. The output from these sensors is processed by a microcontroller or comparator circuit, which compares the voltage levels produced by each sensor. When one sensor detects more light than the other, the microcontroller sends a signal to a motor driver circuit, which adjusts the angle of the solar panel to face the light source directly.
The circuit design emphasizes cost-effectiveness by utilizing readily available components such as operational amplifiers for signal comparison and low-cost DC motors for adjustment. The simplicity of the design allows for easy implementation and maintenance, making it suitable for both residential and commercial solar applications.
To ensure accurate tracking, the circuit may include additional features such as hysteresis to prevent rapid oscillations in panel position due to fluctuating light levels. Furthermore, it may incorporate a feedback mechanism to monitor the panel's position and adjust it accordingly, ensuring optimal performance throughout the day.
Overall, this photovoltaic light sensor circuit exemplifies a practical solution for maximizing solar energy harvesting through efficient tracking mechanisms.The following circuit shows about Photovoltaic Light Sensors In Solar Tracker. Features: accurate, low cost, simple, single axis electronic solar .. 🔗 External reference
The photovoltaic light sensor circuit is designed to optimize the alignment of solar panels with respect to the sun's position, thereby enhancing energy capture efficiency. The core of the system consists of multiple photovoltaic cells that detect light intensity from different angles. These cells generate a voltage output proportional to the light they receive.
In a typical single-axis solar tracker, two or more light sensors are strategically placed on the surface of the solar panel. The output from these sensors is processed by a microcontroller or comparator circuit, which compares the voltage levels produced by each sensor. When one sensor detects more light than the other, the microcontroller sends a signal to a motor driver circuit, which adjusts the angle of the solar panel to face the light source directly.
The circuit design emphasizes cost-effectiveness by utilizing readily available components such as operational amplifiers for signal comparison and low-cost DC motors for adjustment. The simplicity of the design allows for easy implementation and maintenance, making it suitable for both residential and commercial solar applications.
To ensure accurate tracking, the circuit may include additional features such as hysteresis to prevent rapid oscillations in panel position due to fluctuating light levels. Furthermore, it may incorporate a feedback mechanism to monitor the panel's position and adjust it accordingly, ensuring optimal performance throughout the day.
Overall, this photovoltaic light sensor circuit exemplifies a practical solution for maximizing solar energy harvesting through efficient tracking mechanisms.The following circuit shows about Photovoltaic Light Sensors In Solar Tracker. Features: accurate, low cost, simple, single axis electronic solar .. 🔗 External reference