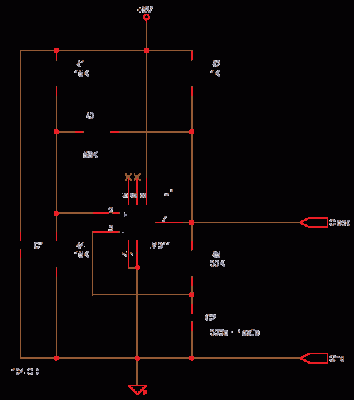
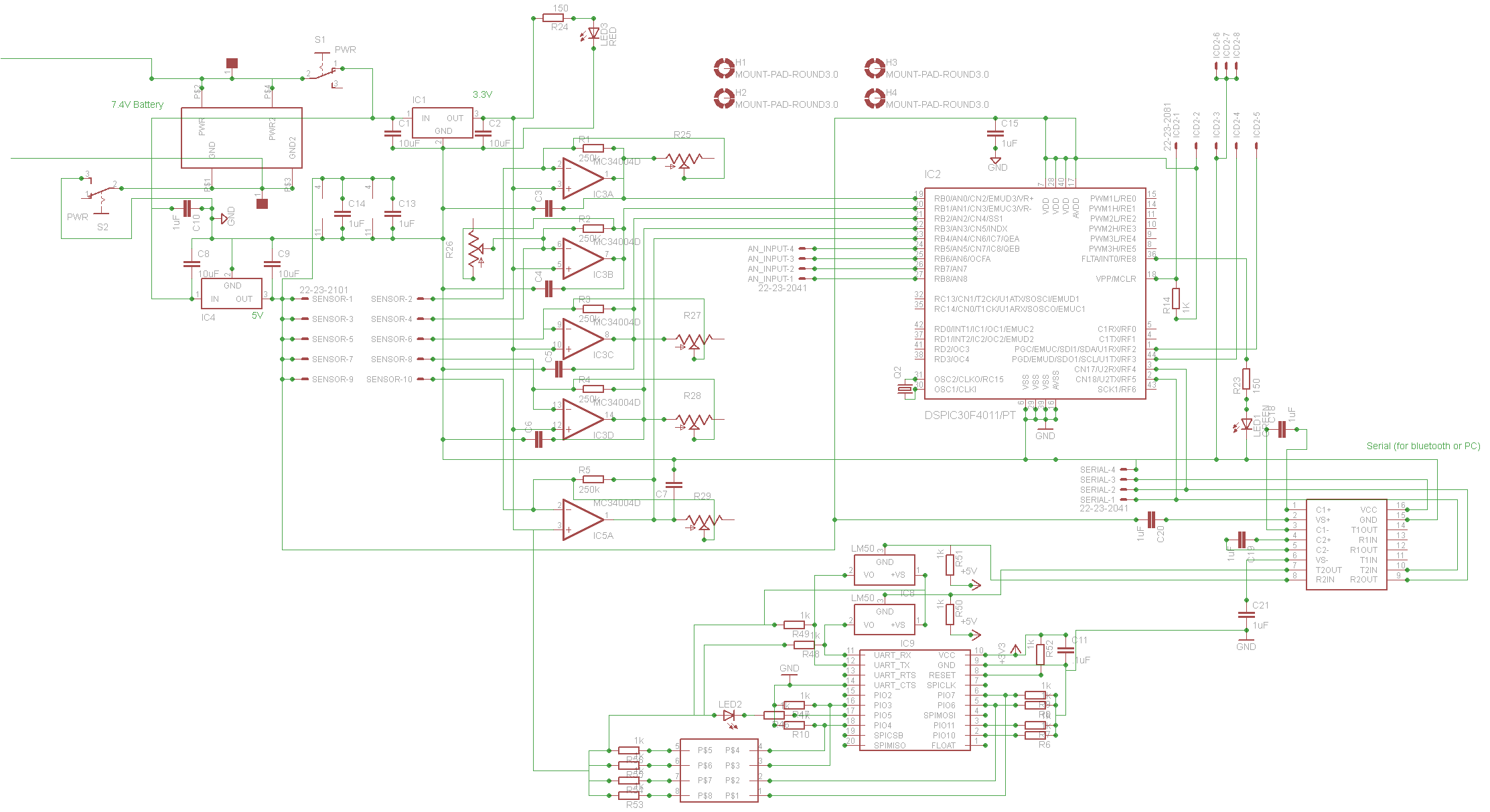
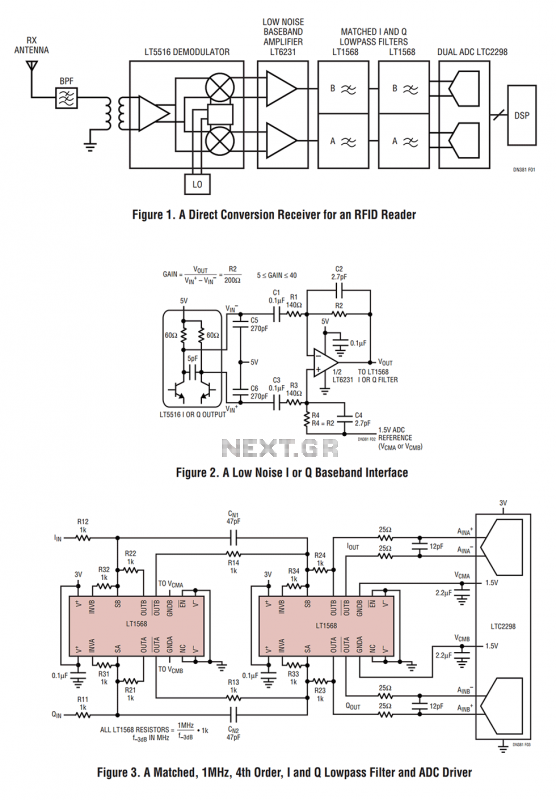
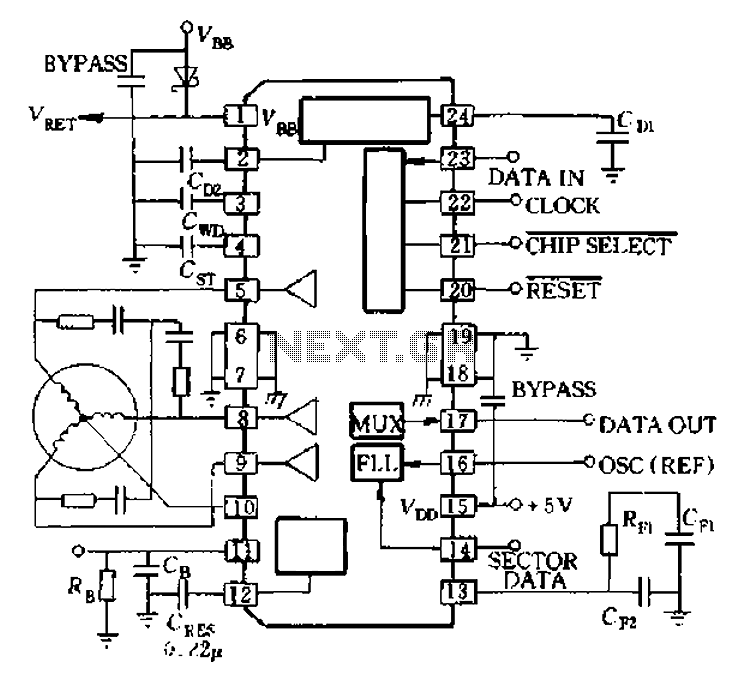
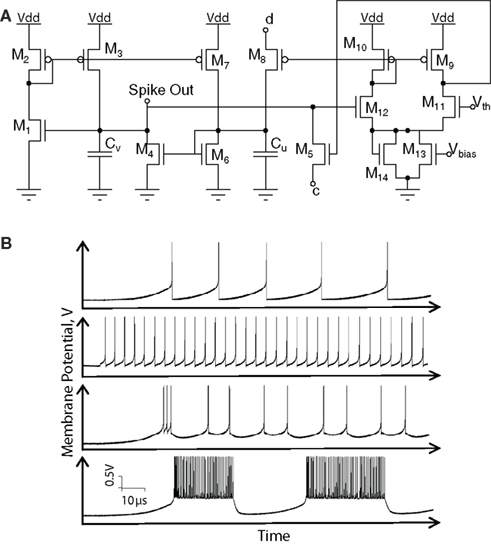
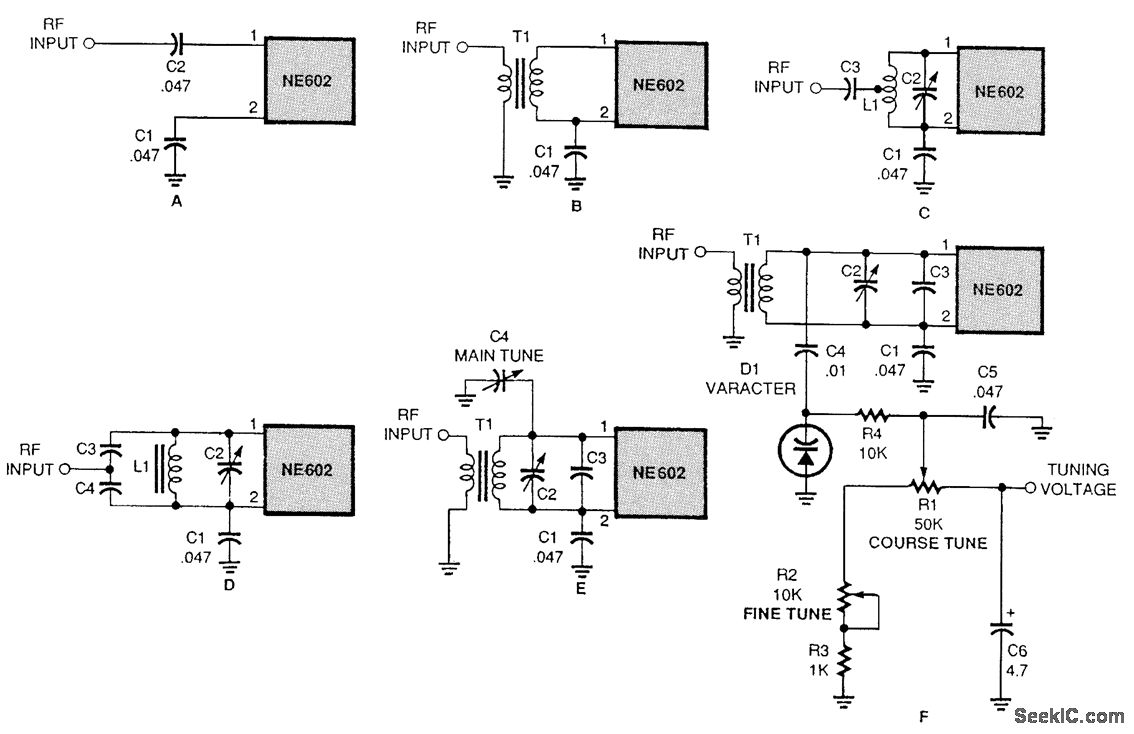
Pic Circuits
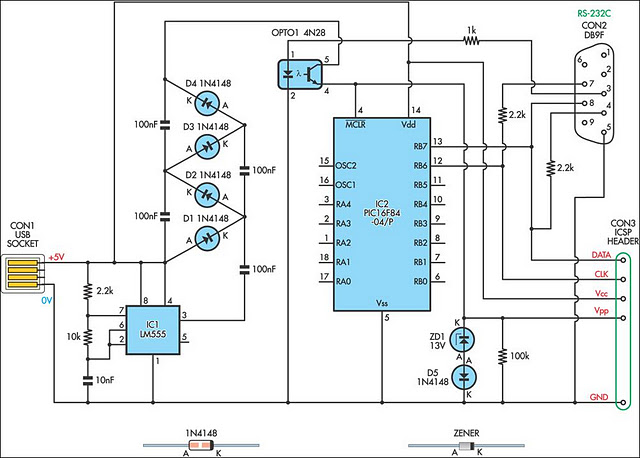
A small biped walker constructed from 2mm plywood, powered by two RC servos. It utilizes the widely available and programmable flash microcontroller PIC16F84. This simple circuit is designed to program the PIC16F84 and similar flash memory components. The project includes a bar graph, which is a series of LEDs arranged in a line, commonly seen in audio displays. Additionally, this project aims to educate users about the functionalities of this chipset and the process of displaying text on an LCD. It employs a Microchip PIC microcontroller, a serial EEPROM, and a thermistor to develop a temperature recording system.
The biped walker project serves as an excellent introduction to robotics and microcontroller programming. The structure, made from 2mm plywood, allows for lightweight construction, which is crucial for the walker’s mobility. The two RC servos provide the necessary actuation for movement, enabling the walker to mimic bipedal locomotion.
The core of the system is the PIC16F84 microcontroller, which is notable for its ease of programming and versatility in various applications. It features flash memory, allowing for easy updates and modifications to the code without needing to replace the microcontroller. The programming interface for the PIC16F84 can be established using simple circuits that connect to a computer or a dedicated programmer.
The project also incorporates a bar graph display, which consists of multiple LEDs that can visually represent data, such as the status of the walker or other parameters. This feature enhances user interaction and provides immediate feedback on the system's performance.
In addition to the walker, the project encompasses a temperature recording system that integrates a thermistor for temperature sensing. The thermistor’s resistance changes with temperature, allowing the microcontroller to read and process temperature data. A serial EEPROM is included to store this data, enabling long-term monitoring and retrieval of temperature readings.
Overall, this project not only demonstrates the principles of robotics and microcontroller programming but also provides practical experience with sensor integration and data display techniques. The combination of hardware and software components offers a comprehensive learning platform for individuals interested in electronics and embedded systems.A small biped walker made of 2mm plywood. Powered by two RC servos. it is a popular microcontroller, easily available and programmable now as flash microcontroller 16F84. This simple circuit can be used to program the PIC16F84 and similar "flash memory" type parts. The bar graph - a series of LEDs in a line, such as you see on an audio display. In this project we are going to learn various things about this chip set and displaying text on this LCD This project uses a Microchip PIC microcontroller, a serial EEPROM and a thermistor to create a temperature recorder. 🔗 External reference
The biped walker project serves as an excellent introduction to robotics and microcontroller programming. The structure, made from 2mm plywood, allows for lightweight construction, which is crucial for the walker’s mobility. The two RC servos provide the necessary actuation for movement, enabling the walker to mimic bipedal locomotion.
The core of the system is the PIC16F84 microcontroller, which is notable for its ease of programming and versatility in various applications. It features flash memory, allowing for easy updates and modifications to the code without needing to replace the microcontroller. The programming interface for the PIC16F84 can be established using simple circuits that connect to a computer or a dedicated programmer.
The project also incorporates a bar graph display, which consists of multiple LEDs that can visually represent data, such as the status of the walker or other parameters. This feature enhances user interaction and provides immediate feedback on the system's performance.
In addition to the walker, the project encompasses a temperature recording system that integrates a thermistor for temperature sensing. The thermistor’s resistance changes with temperature, allowing the microcontroller to read and process temperature data. A serial EEPROM is included to store this data, enabling long-term monitoring and retrieval of temperature readings.
Overall, this project not only demonstrates the principles of robotics and microcontroller programming but also provides practical experience with sensor integration and data display techniques. The combination of hardware and software components offers a comprehensive learning platform for individuals interested in electronics and embedded systems.A small biped walker made of 2mm plywood. Powered by two RC servos. it is a popular microcontroller, easily available and programmable now as flash microcontroller 16F84. This simple circuit can be used to program the PIC16F84 and similar "flash memory" type parts. The bar graph - a series of LEDs in a line, such as you see on an audio display. In this project we are going to learn various things about this chip set and displaying text on this LCD This project uses a Microchip PIC microcontroller, a serial EEPROM and a thermistor to create a temperature recorder. 🔗 External reference