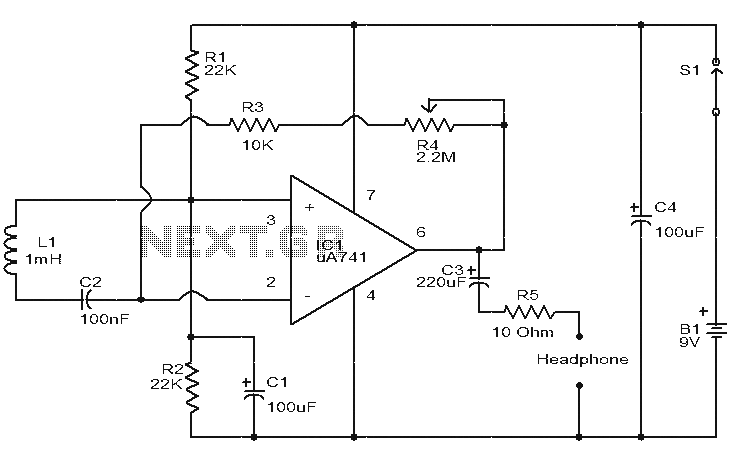
PIC16F819 Dymoclock Sensor
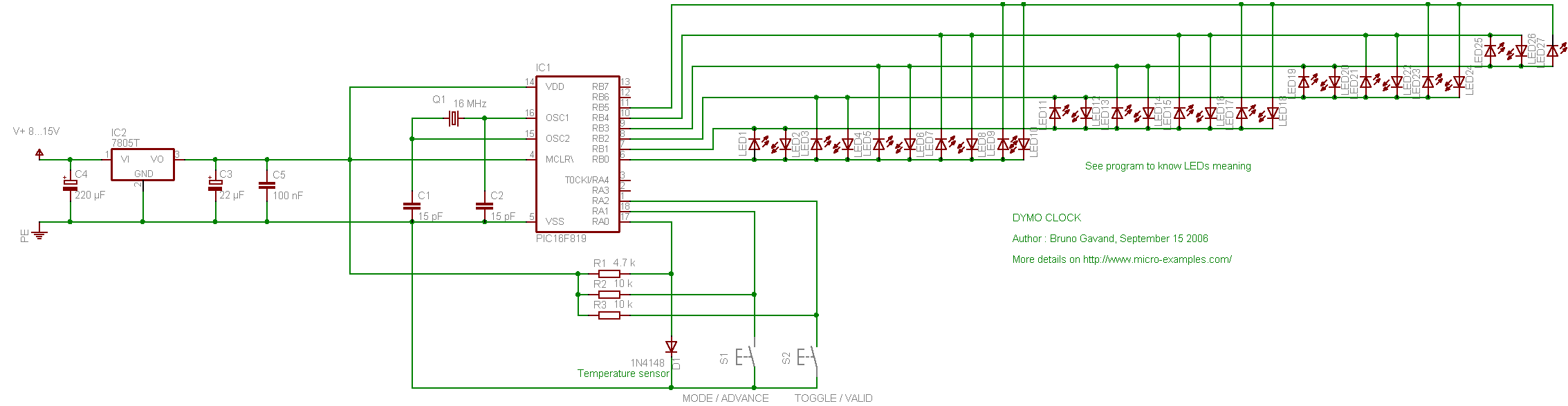
The following circuit illustrates the PIC16F819 Dymoclock Sensor Circuit Diagram. Features include an economical temperature sensor, the use of only LEDs, and the absence of a decoder.
The PIC16F819 Dymoclock Sensor Circuit utilizes a PIC16F819 microcontroller, which is a versatile 8-bit device with built-in analog-to-digital conversion capabilities. This circuit is designed to monitor temperature variations and display the readings through LED indicators, making it a cost-effective solution for temperature sensing applications.
The circuit incorporates a low-cost temperature sensor, such as the LM35 or a similar device, which outputs a voltage proportional to the temperature. The microcontroller reads the analog voltage from the temperature sensor using its integrated ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter). The ADC converts the analog signal into a digital value that can be processed by the microcontroller.
The LED indicators are used to visually represent the temperature readings. Each LED may correspond to a specific temperature range, allowing for a quick visual reference of the current temperature status. The absence of a decoder simplifies the design, reducing component count and potential points of failure, while also minimizing the overall cost of the circuit.
The operation of the circuit can be programmed using the PIC16F819's built-in features, allowing for flexibility in adjusting the temperature thresholds and LED indications. This makes the Dymoclock Sensor Circuit an ideal choice for applications where simple temperature monitoring is required, such as in weather stations, HVAC systems, or educational projects.
Overall, the PIC16F819 Dymoclock Sensor Circuit is a practical and efficient design that leverages the capabilities of the PIC microcontroller to create an effective temperature sensing solution with minimal components.The following circuit shows about PIC16F819 Dymoclock Sensor Circuit Diagram. Features: a cheap temperature sensor, only LEDs, no decoder, built .. 🔗 External reference
The PIC16F819 Dymoclock Sensor Circuit utilizes a PIC16F819 microcontroller, which is a versatile 8-bit device with built-in analog-to-digital conversion capabilities. This circuit is designed to monitor temperature variations and display the readings through LED indicators, making it a cost-effective solution for temperature sensing applications.
The circuit incorporates a low-cost temperature sensor, such as the LM35 or a similar device, which outputs a voltage proportional to the temperature. The microcontroller reads the analog voltage from the temperature sensor using its integrated ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter). The ADC converts the analog signal into a digital value that can be processed by the microcontroller.
The LED indicators are used to visually represent the temperature readings. Each LED may correspond to a specific temperature range, allowing for a quick visual reference of the current temperature status. The absence of a decoder simplifies the design, reducing component count and potential points of failure, while also minimizing the overall cost of the circuit.
The operation of the circuit can be programmed using the PIC16F819's built-in features, allowing for flexibility in adjusting the temperature thresholds and LED indications. This makes the Dymoclock Sensor Circuit an ideal choice for applications where simple temperature monitoring is required, such as in weather stations, HVAC systems, or educational projects.
Overall, the PIC16F819 Dymoclock Sensor Circuit is a practical and efficient design that leverages the capabilities of the PIC microcontroller to create an effective temperature sensing solution with minimal components.The following circuit shows about PIC16F819 Dymoclock Sensor Circuit Diagram. Features: a cheap temperature sensor, only LEDs, no decoder, built .. 🔗 External reference