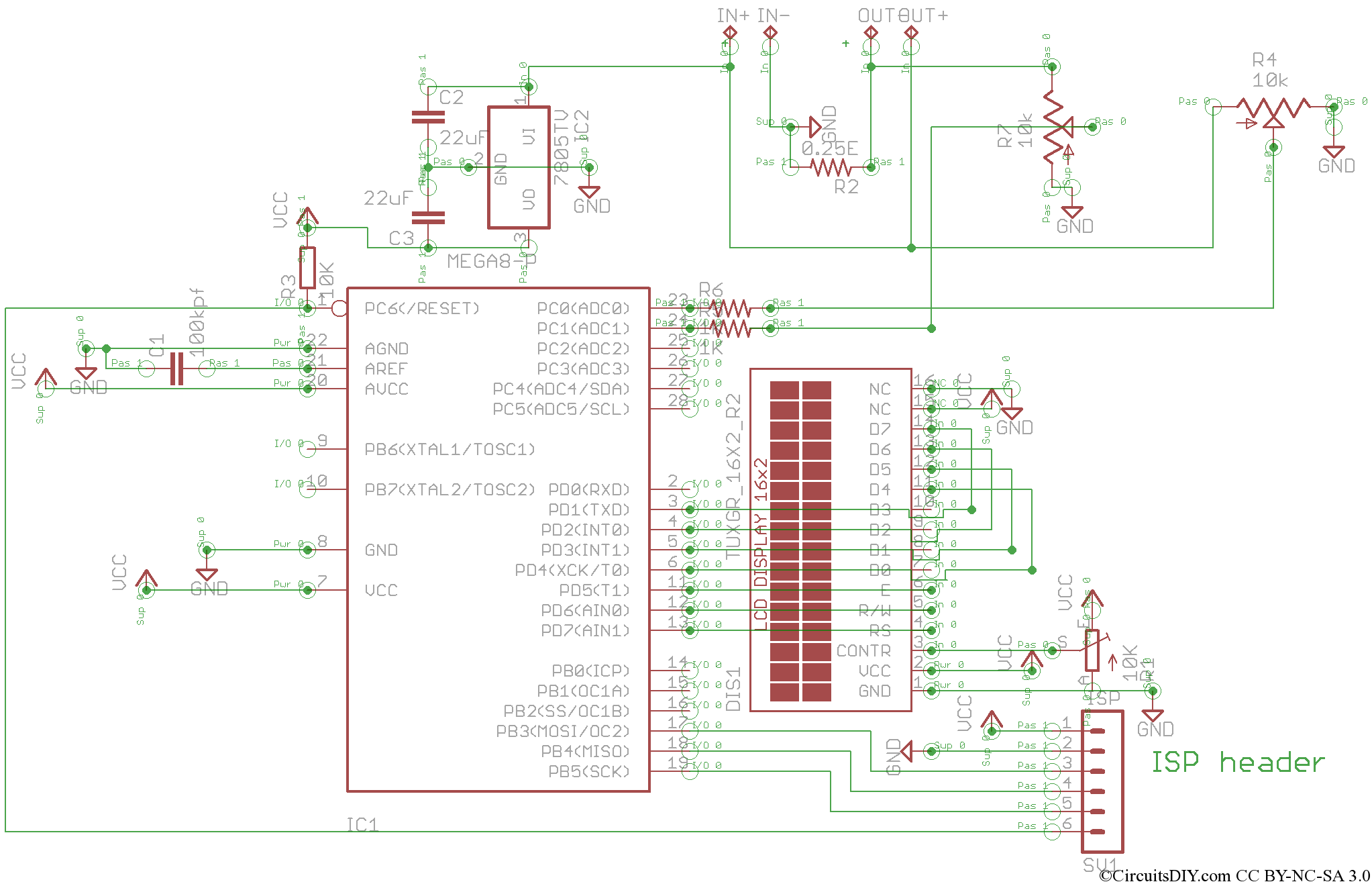
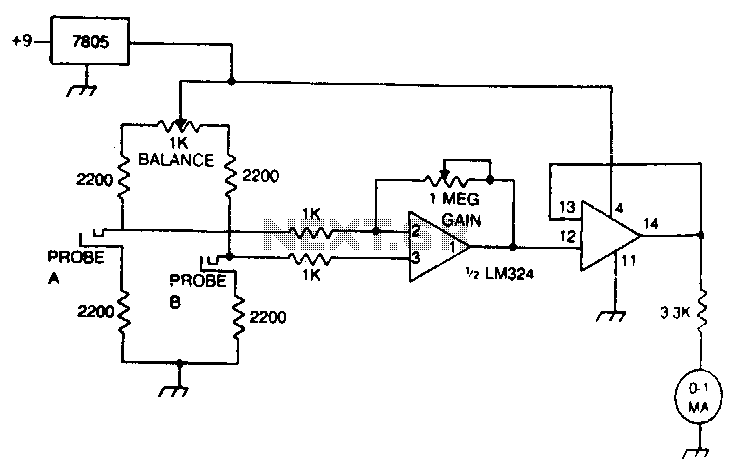
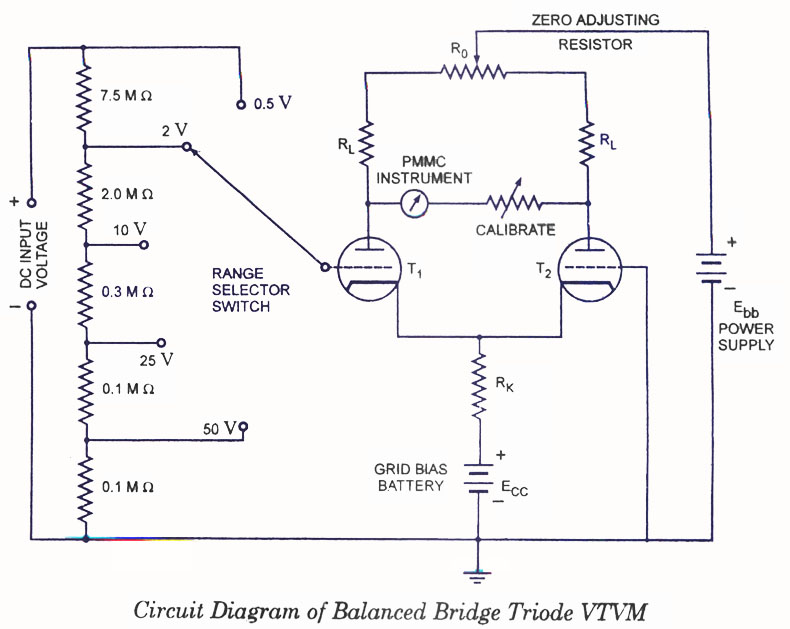
PIC16F88 SWR Meter

SWR, or standing wave ratio, is the ratio of the amplitude of a partial standing wave at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at an adjacent node (minimum).
SWR is a critical parameter in RF (radio frequency) engineering, particularly in the design and analysis of transmission lines and antennas. It quantifies the efficiency of power transfer from a source to a load, indicating how much of the signal is reflected back toward the source due to impedance mismatches. A perfect SWR of 1:1 signifies that all power is transmitted to the load without any reflections, while higher values indicate increasing levels of reflected power, which can lead to signal degradation and potential damage to RF components.
To measure SWR, an SWR meter is typically employed. This device analyzes the voltage standing wave pattern along the transmission line, calculating the ratio based on the maximum and minimum voltage levels. Understanding and minimizing SWR is essential in ensuring optimal performance in RF systems, as excessive reflections can result in overheating of transmitters, reduced efficiency, and distortion of the transmitted signal.
In practical applications, various techniques are utilized to achieve a low SWR, including properly matching the impedance of antennas to the transmission line, using matching networks, and employing baluns or transformers where necessary. Additionally, regular monitoring of SWR can help identify issues in the system that may arise over time, ensuring reliable operation in communication systems, broadcasting, and other RF applications.SWR or standing wave ratio is the ratio of the amplitude of a partial standing wave at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at an adjacent node (minimum).. 🔗 External reference
SWR is a critical parameter in RF (radio frequency) engineering, particularly in the design and analysis of transmission lines and antennas. It quantifies the efficiency of power transfer from a source to a load, indicating how much of the signal is reflected back toward the source due to impedance mismatches. A perfect SWR of 1:1 signifies that all power is transmitted to the load without any reflections, while higher values indicate increasing levels of reflected power, which can lead to signal degradation and potential damage to RF components.
To measure SWR, an SWR meter is typically employed. This device analyzes the voltage standing wave pattern along the transmission line, calculating the ratio based on the maximum and minimum voltage levels. Understanding and minimizing SWR is essential in ensuring optimal performance in RF systems, as excessive reflections can result in overheating of transmitters, reduced efficiency, and distortion of the transmitted signal.
In practical applications, various techniques are utilized to achieve a low SWR, including properly matching the impedance of antennas to the transmission line, using matching networks, and employing baluns or transformers where necessary. Additionally, regular monitoring of SWR can help identify issues in the system that may arise over time, ensuring reliable operation in communication systems, broadcasting, and other RF applications.SWR or standing wave ratio is the ratio of the amplitude of a partial standing wave at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at an adjacent node (minimum).. 🔗 External reference