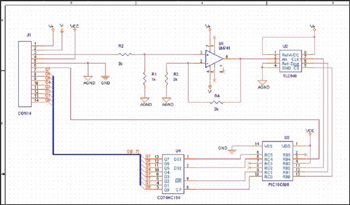
PLL FM Transmitter using LMX1601 ATtiny2313 AT90S2313

This document describes a PLL FM transmitter utilizing the LMX1601 and either the ATtiny2313 or AT90S2313 microcontrollers. A common feature of previous low-power FM transmitters developed over the years is that their operating frequency is determined by an LC resonant circuit. While some designs exhibited excellent frequency stability, others did not meet this criterion, prompting the desire to create a more reliable version.
The PLL FM transmitter circuit employs a phase-locked loop (PLL) architecture to achieve frequency modulation. The LMX1601 serves as the frequency synthesizer, providing a stable output frequency that is crucial for effective FM transmission. The ATtiny2313 or AT90S2313 microcontroller is used for controlling the PLL and managing the modulation process.
The operating frequency is primarily defined by the LC circuit, which consists of an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C) arranged to create a resonant frequency. This resonant frequency can be adjusted by varying the values of L and C or by using variable components such as a variable capacitor or inductor. The stability of the output frequency is enhanced by the PLL, which continuously adjusts the frequency of the LMX1601 to match the desired reference frequency, thus minimizing drift and ensuring consistent performance.
In this design, the microcontroller is programmed to handle the modulation scheme, allowing for flexibility in the transmission characteristics. The microcontroller interfaces with the LMX1601 to set the desired output frequency and can also implement additional features such as audio input processing, allowing for the modulation of audio signals onto the carrier frequency.
The circuit layout should be carefully designed to minimize noise and interference, which can affect the performance of the transmitter. Proper grounding techniques and the use of decoupling capacitors are essential to maintain signal integrity. Furthermore, the choice of components should consider the frequency range of operation, power consumption, and overall efficiency of the transmitter.
Overall, this PLL FM transmitter design represents a significant advancement over previous low-power FM transmitters, combining the stability of PLL technology with the flexibility of microcontroller programming to achieve a reliable and high-quality FM transmission.Here`s a PLL FM Transmitter using LMX1601, ATtiny2313 or AT90S2313 microcontrollers. The common characteristic of all of the previous low power FM transmitters I`ve built over the decades, is that their operating frequency is determined by an LC resonant circuit. Some of them had excellent stability, some of them didn`t, but I had always wanted to make one.. 🔗 External reference
The PLL FM transmitter circuit employs a phase-locked loop (PLL) architecture to achieve frequency modulation. The LMX1601 serves as the frequency synthesizer, providing a stable output frequency that is crucial for effective FM transmission. The ATtiny2313 or AT90S2313 microcontroller is used for controlling the PLL and managing the modulation process.
The operating frequency is primarily defined by the LC circuit, which consists of an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C) arranged to create a resonant frequency. This resonant frequency can be adjusted by varying the values of L and C or by using variable components such as a variable capacitor or inductor. The stability of the output frequency is enhanced by the PLL, which continuously adjusts the frequency of the LMX1601 to match the desired reference frequency, thus minimizing drift and ensuring consistent performance.
In this design, the microcontroller is programmed to handle the modulation scheme, allowing for flexibility in the transmission characteristics. The microcontroller interfaces with the LMX1601 to set the desired output frequency and can also implement additional features such as audio input processing, allowing for the modulation of audio signals onto the carrier frequency.
The circuit layout should be carefully designed to minimize noise and interference, which can affect the performance of the transmitter. Proper grounding techniques and the use of decoupling capacitors are essential to maintain signal integrity. Furthermore, the choice of components should consider the frequency range of operation, power consumption, and overall efficiency of the transmitter.
Overall, this PLL FM transmitter design represents a significant advancement over previous low-power FM transmitters, combining the stability of PLL technology with the flexibility of microcontroller programming to achieve a reliable and high-quality FM transmission.Here`s a PLL FM Transmitter using LMX1601, ATtiny2313 or AT90S2313 microcontrollers. The common characteristic of all of the previous low power FM transmitters I`ve built over the decades, is that their operating frequency is determined by an LC resonant circuit. Some of them had excellent stability, some of them didn`t, but I had always wanted to make one.. 🔗 External reference