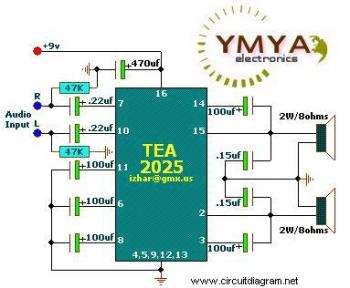
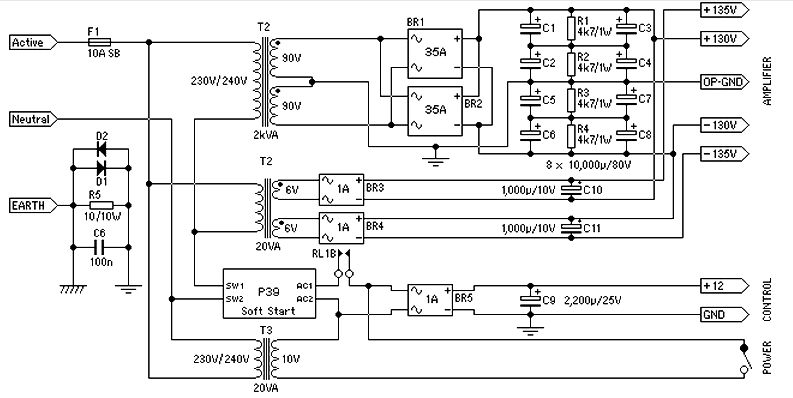
Power Audio Amplifier DMOS 2x100W using two TDA2794
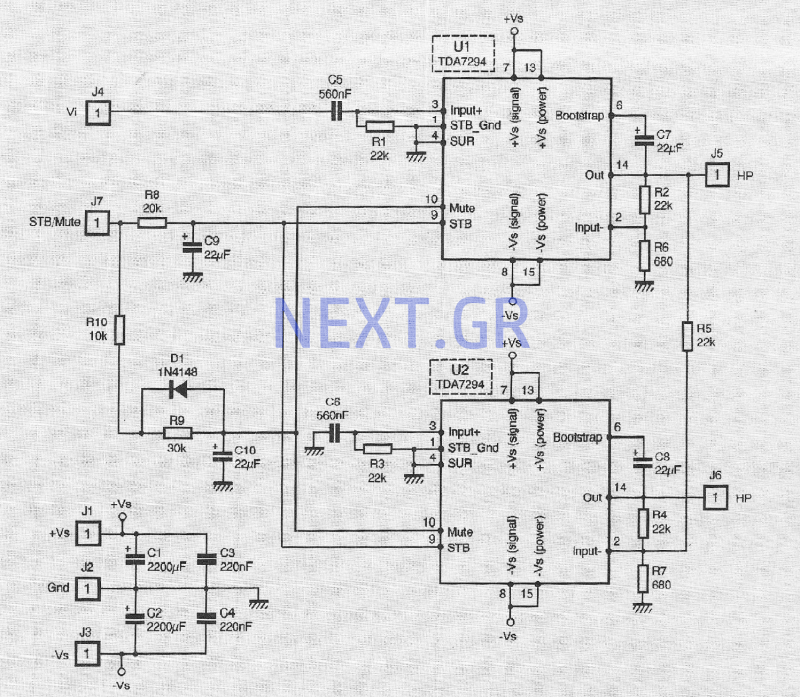


The operational area of the TDA 7294 is designed to prevent circuit destruction, which would otherwise require larger circuit sizes and increased complexity in the printed circuit board, necessitating sophisticated protection circuits. To address these challenges, the use of MOS technology is recommended, as it mitigates the second breakdown phenomenon. The TDA 7294 is constructed using a mixed technology of bipolar and high-voltage MOS, known as BCD100. It also features an internal delay activation function to restore normal operation, simplifying remote control and reducing parasitic noise.
In the design of an integrated circuit that functions as a power amplifier, the construction of the output stage is critical. The basic design includes a DMOS output buffer in the TDA 7294, which is capable of handling high currents and voltages while maintaining low harmonic distortion and good frequency response. Accurate control of the quiescent current is essential, achieved through a local loop of linear positive feedback from a differential amplifier, which allows for effective current regulation.
Merely achieving proper biasing of the output transistors is insufficient to eliminate distortion. Even with linear transfer characteristics, the dynamic behavior of the system must be considered. A compensation system helps minimize distortion in the final stage by controlling the direct connection of the Miller capacitance at the amplifier output, introducing a local positive feedback path that includes the output stage.
When designing an integrated power circuit, special attention must be given to protection circuits against short circuits and overload conditions. The absence of the second breakdown phenomenon allows for full utilization of the operating zone for DMOS power transistors, which is limited only by the maximum consumption curve, dependent on the duration of applied disturbances.
To fully exploit the capabilities of the power transistors, the integrated system incorporates protection features, including conventional protection circuits that ensure no risk of destruction, along with a new local sensitive temperature stabilization technique that dynamically controls maximum consumption. This includes overload protection features as part of the component's specifications.The TDA 7294 of T-MICROELECTRONICS is a monolithic integrated circuit in a "Multiwatt 15" shell designed in principle to be used in amplifiers or class AB in high-fidelity applications such as stereo, active speakers, television receivers, and more. Thanks to the large feed area and the capability to offer a very high current at the outlet, it is thus possible to provide a lot high power at loads of 4Ω or 8Ω, even with a power supply that is not correct stabilized due to a very high discharge of this supply voltage.
At the consumer electronics world there is an increasing need for sound amplifiers of very high power and completed in a monolithic shell capable of include, at a low cost, performance, taken from better discrete amplifier constructions data. Work to be built this linear integrated circuit with conventional bipolar technology became extremely difficult due to the phenomenon of the second disruption.
The conventional bipolar technology limits its operating range, without the risk of destruction of the circuit and therefore, limits the maximum output power which can initially accept loads with high ohmic resistance.
TDA2794 full exploitation operating area, which is not at risk to destroy the circuit, it translates by a similar increase in size of the circuit and a more important complexity of the printed circuit which will be built, due in need of disposal of sophisticated protection circuits. To overcome these difficulties is recommended the use of MOS, which avoids the phenomenon of second decomposition.
TDA7294 has however designed with mixed bipolar technology and high voltage MOS, technology, called BCD100. This circuit also has, internally, a function activation with a delay to restore to normal function, fact that simplifies its remote control operation avoiding in this way Parasitic noises.
The basic work in designing an integrated circuit, which implements the work of the operator power amplifier, regardless of technology used, is that of the construction of the exit stage.
The solution, which appears as a basic one in figure 2 shows the buffer of the DMOS output of tDA7294. This isolator high power high signal, is capable of receiving currents and levels extremely high voltage maintaining always in an acceptable way a low harmonic distortion and good behavior across the frequency response area.
It is also required an accurate control of the resting current. A local loop of linear positive feedback produced by differential amplifier A is used to meet the requirements, previously mentioned, allowing in this way and in a simple and efficient way to define a point for the current.
A correct polarization of the output voltage of the transistors is not sufficient to guarantee the absence of distortion. Although one would have been achieved linearity of the characteristic transfer of the stage, the dynamic behavior of the system will must be taken into account.
An important help to maintain the distortion presented by the final stage, as low as possible, is provided by the compensation system, which controls the direct connection of the capacity miller at the amplifier output to introduce an alternating positive path local feedback, including the very stage of the exit.
When designing an integrated power circuit, it must be given special attention attention to the circuits involved with the protection of the accessory against short circuits or the overload conditions of the latter.
Due to the absence of the phenomenon the second split, the full exploitation of the operating zone, which is without risk of destruction for the DMOS power transistors are limited only from the maximum consumption curve, which depends on the duration of the irritations applied.
To take full advantage of the possibilities of power transistors, built-in in these system components protection, includes a conventional circuit protection, without risk of destruction, with a new local sensitive technique temperature stabilization, which dynamically controls the maximum consumption. Plus protection against the overloads described before, in his features component.