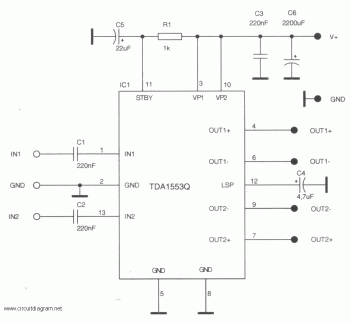
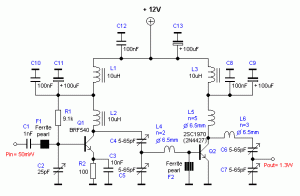
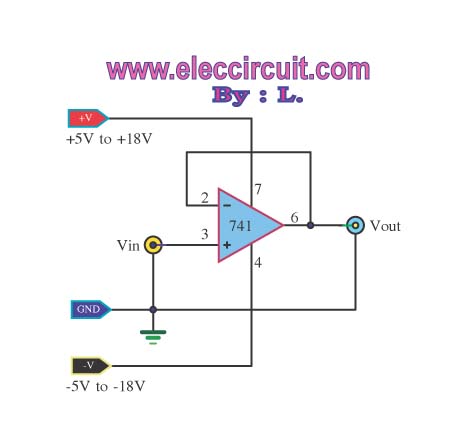
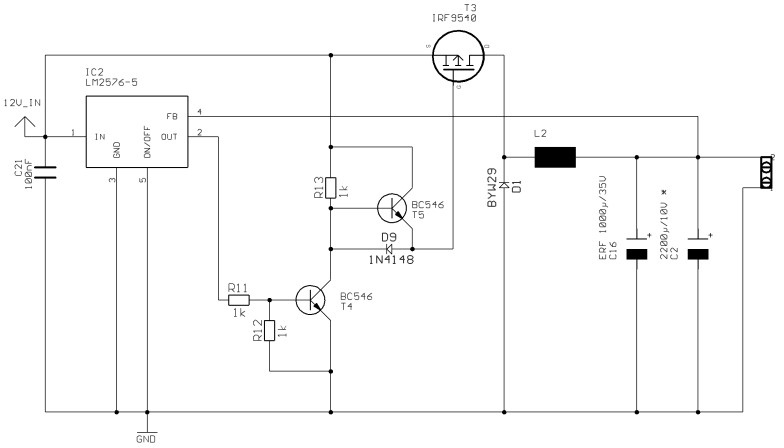
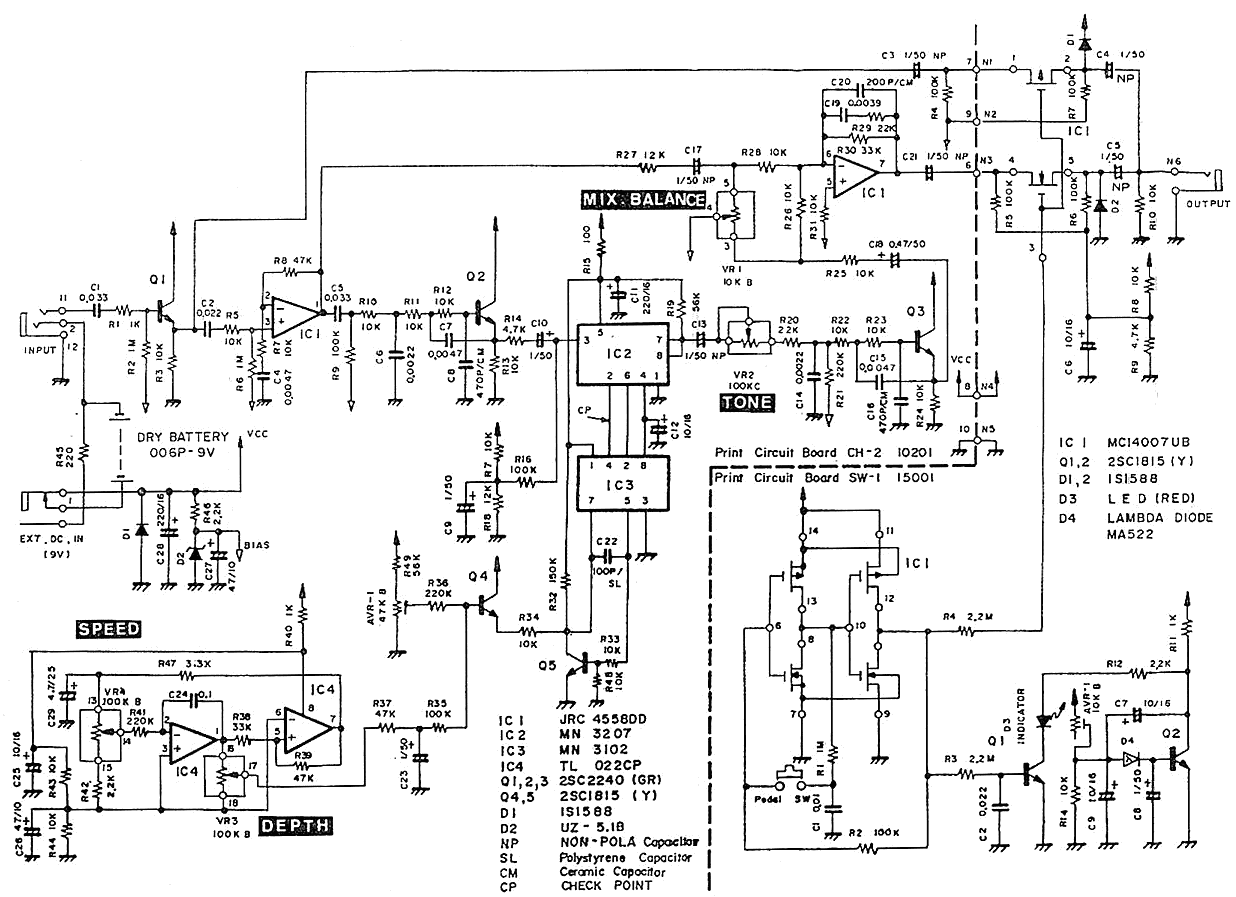
Power module unit diagram of IGBT and fly-wheel diode
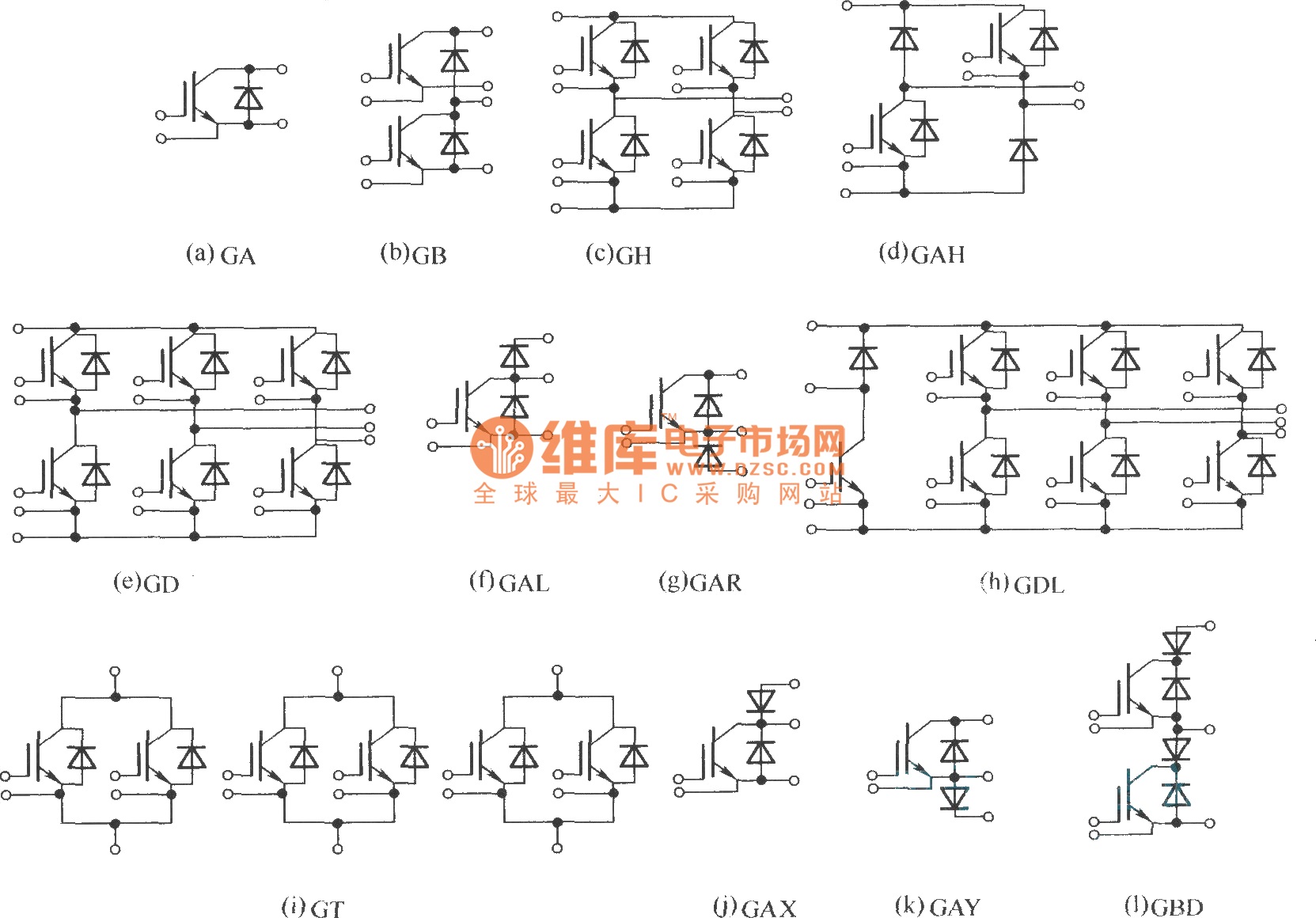
This document describes various electronic modules, including: (a) a single switch module; (b) a two-unit half bridge module; (c) an H bridge (single-phase bridge) module; (d) an asymmetrical H bridge module; (e) a three-phase bridge (six-unit or inverter bridge) module; (f) a chopping module; (g) a second chopping module; (h) a three-phase bridge GD with an added chopping GAL (braking chopper circuit) module; (i) a three-unit module consisting of three group switches; (j) a single switch with a collector end series diode (negative direction disconnecting switch) module; (k) a single switch with an emitter end series diode (negative direction disconnecting switch) module; (l) a two-unit module with a series diode (negative direction disconnecting switch).
The electronic modules described serve various functions within power electronics and control systems.
The single switch module (a) is a basic building block for controlling power flow, typically used in applications requiring simple on/off functionality. The two-unit half bridge module (b) allows for the control of voltage across a load by switching two devices, effectively enabling bidirectional current flow.
The H bridge module (c) is essential for driving motors, as it allows for control of motor direction and speed by switching the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor. The asymmetrical H bridge module (d) provides similar functionality but is optimized for specific applications where one direction of current flow is more prevalent.
The three-phase bridge module (e) consists of six switching devices and is commonly used in three-phase motor drives and inverters, providing efficient power conversion and motor control. The chopping modules (f and g) are used for pulse-width modulation (PWM) techniques, which are crucial for controlling the output voltage and current in various applications, including DC-DC converters.
The three-phase bridge GD with chopping GAL (h) incorporates a braking chopper circuit, which is vital for regenerative braking applications, allowing energy to be fed back into the power supply during deceleration. The three-unit module (i) enhances flexibility and control by allowing multiple switches to be coordinated for complex power management tasks.
The single switch modules with series diodes (j, k, and l) are designed to prevent reverse current flow, thus ensuring protection of the circuit components. The collector end series diode (j) and emitter end series diode (k) configurations provide distinct advantages depending on the specific circuit design requirements. The two-unit module with a series diode (l) offers additional redundancy and reliability in applications where disconnecting switches are necessary for safe operation.
Overall, these modules are integral to modern electronic systems, facilitating efficient power management, control, and protection in a wide array of applications.Is single switch module; (b) is two unit (half bridge) module; (c) is H bridge (single phase bridge) module; (d) is asymmetrical H bridge module; (e) is three phase bridge (six unit or inverter bridge) module; (f) is chopping module (g) is chopping module (h) is three phase bridge GD add chopping GAL (braking chopper circuit) module; (i) is three unit module, consists of three group switch; (j) is single switch add collector end series diode ( negative direction disconnecting switch) module; (k) is single switch add emitter end series diode (negative direction disconnecting switch) module; (l) is two unit module, with series diode (negative direction disconnecting switch). 🔗 External reference
The electronic modules described serve various functions within power electronics and control systems.
The single switch module (a) is a basic building block for controlling power flow, typically used in applications requiring simple on/off functionality. The two-unit half bridge module (b) allows for the control of voltage across a load by switching two devices, effectively enabling bidirectional current flow.
The H bridge module (c) is essential for driving motors, as it allows for control of motor direction and speed by switching the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor. The asymmetrical H bridge module (d) provides similar functionality but is optimized for specific applications where one direction of current flow is more prevalent.
The three-phase bridge module (e) consists of six switching devices and is commonly used in three-phase motor drives and inverters, providing efficient power conversion and motor control. The chopping modules (f and g) are used for pulse-width modulation (PWM) techniques, which are crucial for controlling the output voltage and current in various applications, including DC-DC converters.
The three-phase bridge GD with chopping GAL (h) incorporates a braking chopper circuit, which is vital for regenerative braking applications, allowing energy to be fed back into the power supply during deceleration. The three-unit module (i) enhances flexibility and control by allowing multiple switches to be coordinated for complex power management tasks.
The single switch modules with series diodes (j, k, and l) are designed to prevent reverse current flow, thus ensuring protection of the circuit components. The collector end series diode (j) and emitter end series diode (k) configurations provide distinct advantages depending on the specific circuit design requirements. The two-unit module with a series diode (l) offers additional redundancy and reliability in applications where disconnecting switches are necessary for safe operation.
Overall, these modules are integral to modern electronic systems, facilitating efficient power management, control, and protection in a wide array of applications.Is single switch module; (b) is two unit (half bridge) module; (c) is H bridge (single phase bridge) module; (d) is asymmetrical H bridge module; (e) is three phase bridge (six unit or inverter bridge) module; (f) is chopping module (g) is chopping module (h) is three phase bridge GD add chopping GAL (braking chopper circuit) module; (i) is three unit module, consists of three group switch; (j) is single switch add collector end series diode ( negative direction disconnecting switch) module; (k) is single switch add emitter end series diode (negative direction disconnecting switch) module; (l) is two unit module, with series diode (negative direction disconnecting switch). 🔗 External reference